Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.23 Mutation, Natural Selection & Evolution- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.23 Mutation, Natural Selection & Evolution- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.23 Mutation, Natural Selection & Evolution- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.23 understand how evolution (a change in allele frequency) can come about through gene mutation and natural selection
Evolution Through Gene Mutation and Natural Selection
🌱 Introduction
Evolution happens when the frequency of alleles in a population changes across generations. Two main drivers of this change are:
- Gene mutation
- Natural selection
Together, they explain how species adapt and why populations look different over time.
🧪 Gene Mutation (the source of variation)
What is a mutation?
A mutation is a random change in DNA. It creates new alleles or alters existing ones.
Why mutations matter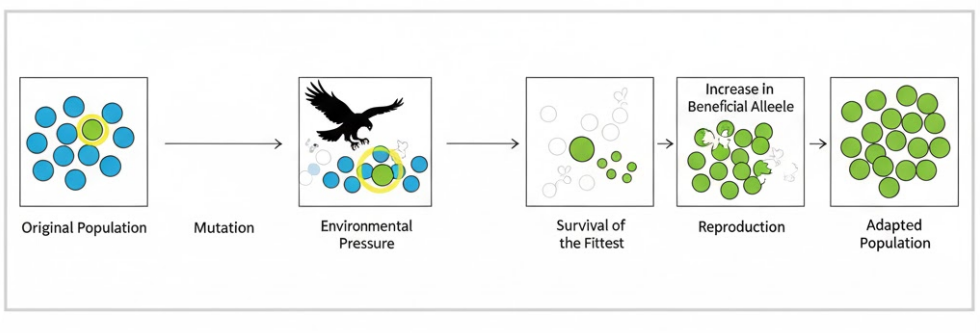
- They introduce genetic variation.
- Without mutations, all individuals would have identical alleles and evolution could not occur.
🌿 Types of mutations (simple exam-friendly list)
- Beneficial → increases survival or reproduction
- Neutral → no effect
- Harmful → decreases survival
Key idea
Mutation = new allele enters the population → gives natural selection something to act on.
🦁 Natural Selection (the sorting process)
What natural selection does
- Individuals with advantageous alleles survive better and reproduce more.
- These alleles get passed on more often.
- Over generations, the population has more of the advantageous allele.
🧠 Memory Trick
Survive → Reproduce → Pass on → Increase
(How an advantageous allele becomes common)
🔄 How Mutation + Natural Selection Change Allele Frequency
- A mutation creates a new allele.
- If this allele is advantageous, organisms carrying it survive better.
- These survivors produce more offspring.
- More offspring carry the advantageous allele.
- Over time, the frequency of this allele increases.
- Harmful alleles become less common because individuals carrying them survive less.
This steady shift in allele proportions is evolution.
📊 Summary Table
| Process | What Happens | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Mutation | New alleles appear randomly | Creates variation |
| Natural selection | Best-adapted individuals survive and reproduce | Advantageous alleles increase |
| Evolution | Allele frequency changes over time | Population becomes better adapted |
✔ Mutation creates new alleles
✔ Natural selection spreads beneficial alleles
✔ Individuals with useful traits survive and reproduce
✔ Allele frequencies shift → this is evolution
✔ Harmful alleles decrease, advantageous alleles increase
