Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.5 Chloroplasts- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.5 Chloroplasts- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.5 Chloroplasts- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.5 understand the structure of chloroplasts in relation to their role in photosynthesis
Structure of Chloroplasts & Their Role in Photosynthesis
🌱 Introduction
Chloroplasts are the photosynthetic organelles found in green plants and algae. They are the sites where light energy is converted into chemical energy (glucose) through the process of photosynthesis.
Each structure inside the chloroplast is perfectly adapted to make this process efficient.
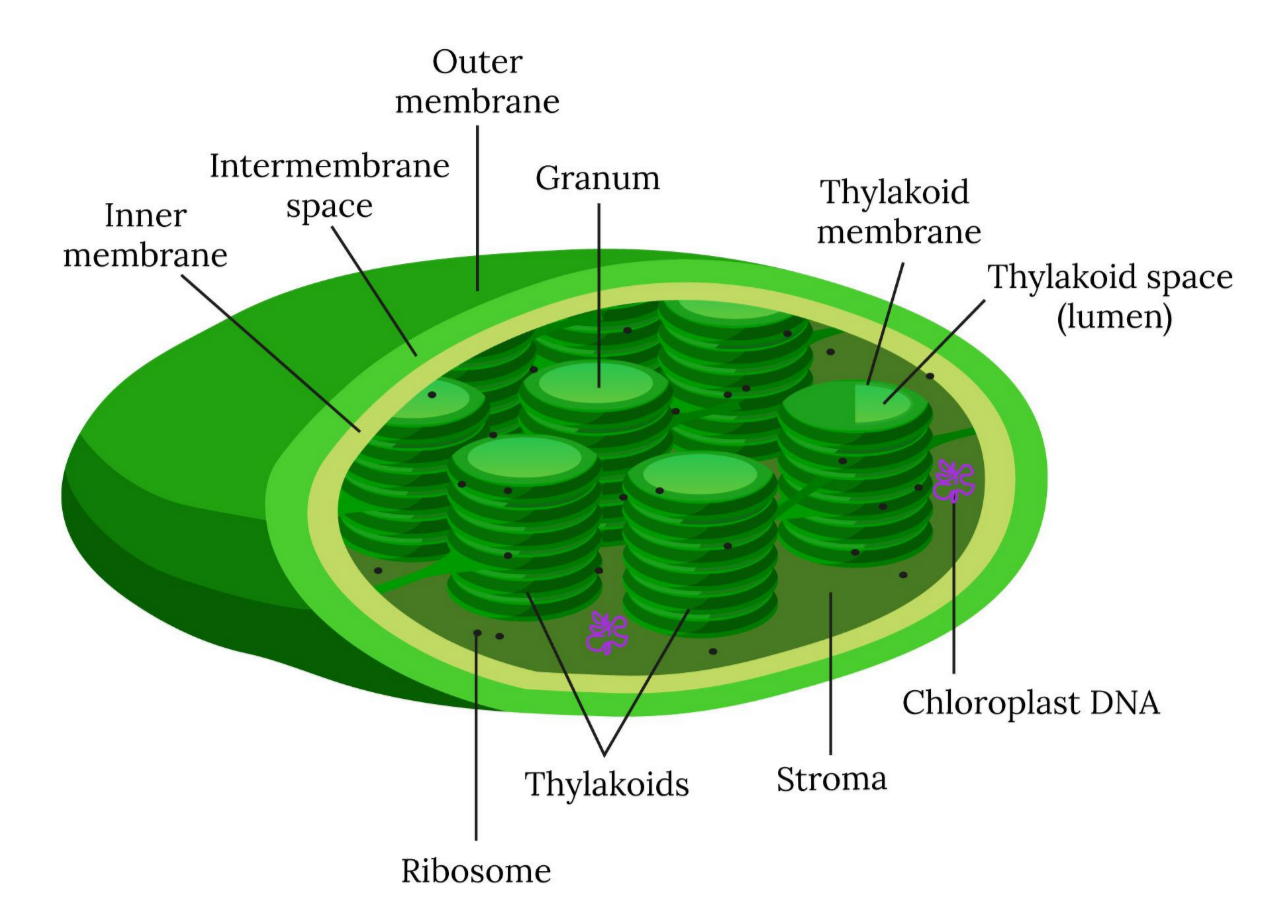
🧩 Structure of a Chloroplast
| Part | Description | Role in Photosynthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Double membrane (envelope) | Outer and inner membrane with intermembrane space | Controls movement of substances in/out of chloroplast |
| Stroma | Gel-like fluid containing enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, starch grains | Site of light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) |
| Thylakoids | Flattened membrane sacs stacked into grana | Contain chlorophyll & electron transport chain site of light-dependent reactions |
| Grana (plural of granum) | Stacks of thylakoids linked by lamellae | Increase surface area for light absorption & ATP formation |
| Intergranal lamellae | Thin membrane connections between grana | Transfer of energy and materials between grana |
| Chlorophyll pigments | Green pigment embedded in thylakoid membrane | Absorbs light energy to excite electrons |
| Starch grains | White, dense granules in stroma | Temporary storage of glucose formed from photosynthesis |
| DNA & 70S ribosomes | Similar to bacterial ones | Allow chloroplast to make its own proteins and enzymes (semi-autonomous) |
☀️ Functional Design – How Structure Supports Function
| Structural Feature | Functional Advantage |
|---|---|
| Large surface area of thylakoid membranes | Maximises light absorption and placement of chlorophyll & ETC proteins |
| Pigment molecules arranged in photosystems (PSI & PSII) | Efficient capture of light at different wavelengths |
| ATP synthase in thylakoid membrane | Produces ATP using proton gradient from light reactions |
| Stroma filled with enzymes | Ideal medium for Calvin Cycle reactions (e.g., RuBisCO enzyme) |
| Close link between grana & stroma | Allows easy transfer of ATP & NADPH between light and dark stages |
| Presence of chloroplast DNA and ribosomes | Enables synthesis of necessary photosynthetic enzymes internally |
🧬 Summary: Reactions and Locations
| Reaction | Location in Chloroplast | Main Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Light-dependent reactions | Thylakoid membranes (in grana) | ATP, reduced NADP, O₂ |
| Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) | Stroma | Glucose (from CO₂ fixation) |
⚡ Quick Recap
| Concept | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Location | Found in leaf mesophyll cells |
| Site of light reactions | Thylakoid membranes |
| Site of dark reactions | Stroma |
| Pigment | Chlorophyll traps light energy |
| ATP formation | Occurs via photophosphorylation in thylakoids |
| Sugar synthesis | Happens in stroma (Calvin Cycle) |
| DNA & ribosomes | Allow partial self-replication |
