Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.8 Core Practical 10: Rate of Photosynthesis- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.8 Core Practical 10: Rate of Photosynthesis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.8 Core Practical 10: Rate of Photosynthesis- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.8 nvestigate the effects of light intensity, light wavelength, temperature and availability of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis using a suitable aquatic plant.
CORE PRACTICAL 10 – Investigating Factors Affecting Rate of Photosynthesis
🌱 Introduction
This practical measures how light intensity, light wavelength, temperature, and CO₂ availability affect the rate of photosynthesis in a suitable aquatic plant (e.g., Elodea / Cabomba / pondweed).
Common measurable proxy: rate of O₂ evolution (bubble count or gas collected) or change in dissolved O₂.
🧪 Aim
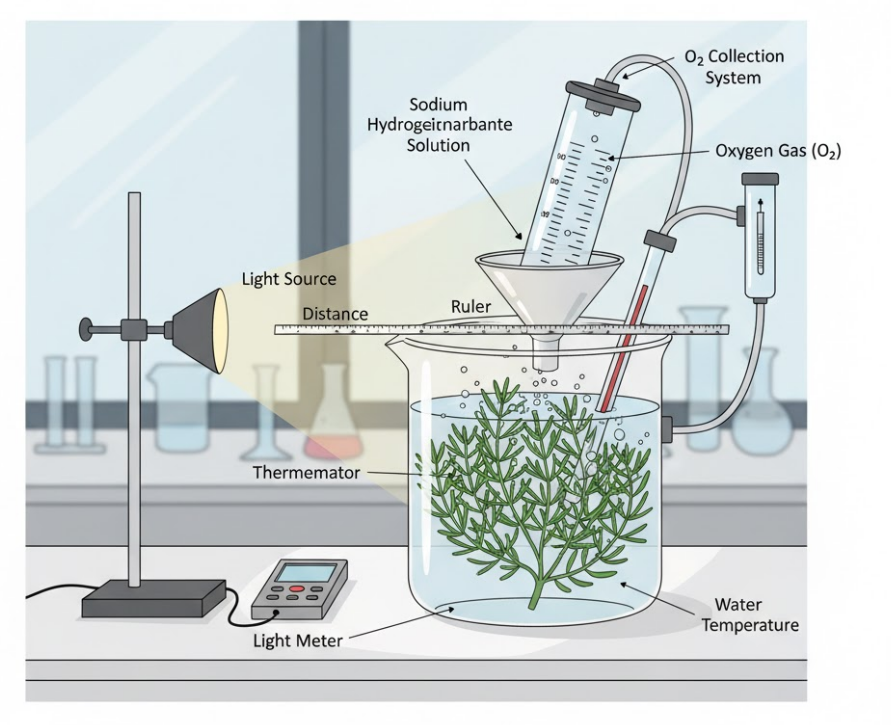
Investigate one factor at a time (light intensity / wavelength / temperature / CO₂) and measure its effect on photosynthesis rate.
✅ Apparatus & Materials
- Aquatic plant (Elodea / pondweed) — healthy cut, similar size
- Beaker or conical flask (100–250 ml)
- Gas syringe or inverted graduated tube for O₂ collection / stopwatch + bubble counting
- Light source (lamp) with adjustable distance or variable power
- Coloured filters (red, blue, green) or LED light sources
- Thermometer and water bath / ice packs (temperature control)
- Sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO₃) solution as CO₂ source
- Ruler or light meter for intensity measurement
- Clamp stand, boss head, stopwatch, paper towels, goggles
⚖️ Variables & Controls
| Type | Variable |
|---|---|
| Independent | Factor you change (e.g., light intensity) |
| Dependent | Rate of photosynthesis (ml O₂ min⁻¹ or bubbles min⁻¹) |
| Control | Plant species, size, volume of water, CO₂ conc., light wavelength, duration, temperature, time of day |
🔬 Method – General (Bubble-count / Gas syringe)
- Preparation: Cut similar lengths of pondweed and remove air bubbles by placing underwater until steady bubbling begins.
- Place a single piece of plant in a beaker containing water with NaHCO₃ (unless CO₂ is the variable). Allow 5–10 minutes to acclimatise.
- Setup: Invert a graduated cylinder over water trough or connect the setup to a gas syringe to collect O₂.
- Position the light source at a measured distance or set filters/LEDs for wavelength control.
- Run: Start the stopwatch and record O₂ volume every minute for 5–10 min, or count bubbles per minute. Repeat for each variable level three times and calculate mean values.
Example Ranges:
- Light intensity → distances: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 cm
- Wavelength → red, green, blue filters
- Temperature → 10°C to 30°C (use water bath)
- CO₂ → increasing NaHCO₃ concentrations (0.0%–0.08%)
📐 Calibration & Measurement Notes
- If bubble size varies → use gas syringe method.
- Light intensity ∝ 1 / distance² (inverse square law).
- Keep light intensity consistent during wavelength tests.
🔢 Calculations & Data Treatment
Rate = Volume of O₂ collected (ml) ÷ Time (min)
If using bubble count: 1 bubble = x ml (calibrated).
Example: 5 ml O₂ in 5 min → rate = 1.0 ml min⁻¹
20 bubbles in 2 min (1 bubble = 0.05 ml) → 1.0 ml total → rate = 0.5 ml min⁻¹
Use means and standard deviation for repeats, plot mean ± error bars.
📈 Graphs & Expected Patterns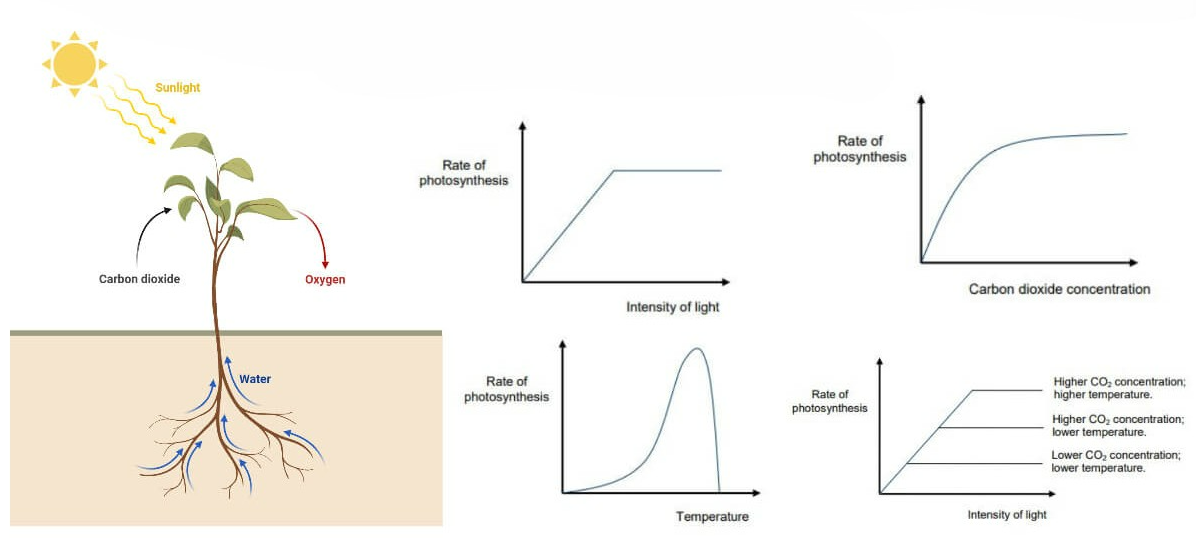
- Light intensity: Rises linearly then plateaus (light saturation).
- Wavelength: Peaks in blue & red; low in green.
- Temperature: Bell-shaped curve with optimum (~20–30°C).
- CO₂ concentration: Increases then plateaus (no longer limiting).
Plot: Independent variable on x-axis, rate (ml min⁻¹) on y-axis.
🔍 Sources of Error & Reductions
- Variable bubble size → gas syringe preferred.
- Plant variation → uniform samples.
- Unequal filter intensity → measure light intensity.
- Temperature drift → use thermostatic bath.
- Human error in counting → use video/automated methods.
♻️ Evaluation & Improvements
- Use more replicates and calibrate bubble volume.
- Use oxygen probe for continuous data.
- Control CO₂ precisely using buffered solutions.
- Use thermostatic water bath; avoid lamp heat with angled setup.
⚠️ Safety
- Wear goggles when handling glass and hot water.
- Keep electrical items away from water.
- Use heatproof mats for hot setups.
🧾 Example Data Table
| Condition | Repeat 1 (ml O₂/min) | Repeat 2 | Repeat 3 | Mean rate | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light 50 cm | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.02 |
| Light 40 cm | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.02 |
| Light 30 cm | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 0.03 |
| Light 20 cm | 1.20 | 1.18 | 1.25 | 1.21 | 0.04 |
🧠 Mnemonics
- S.P.A.C.E. → Setup, Process, All variables fixed, Collect data, Evaluate
- I-SWOT → Intensity, Spectrum, Water/CO₂, Optimum temp, Time
