Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.10 Lymphocytes: Types & Roles- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.10 Lymphocytes: Types & Roles- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.10 Lymphocytes: Types & Roles- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.10 understand the differences between the roles of B cells (B memory and B effector cells), and T cells (T helper, T killer and T memory cells) in the host’s immune response
Roles of B Cells and T Cells in the Immune Response
🌱 Introduction
The immune system relies on two major groups of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. Each group has specialised roles in recognising antigens, making antibodies, and destroying infected cells.
🧫 B Cells
1. B Effector Cells
- These form when B cells are activated by T helper cells.
- They divide and produce plasma cells.
- Plasma cells release large amounts of specific antibodies.
- Work mainly during the primary response.
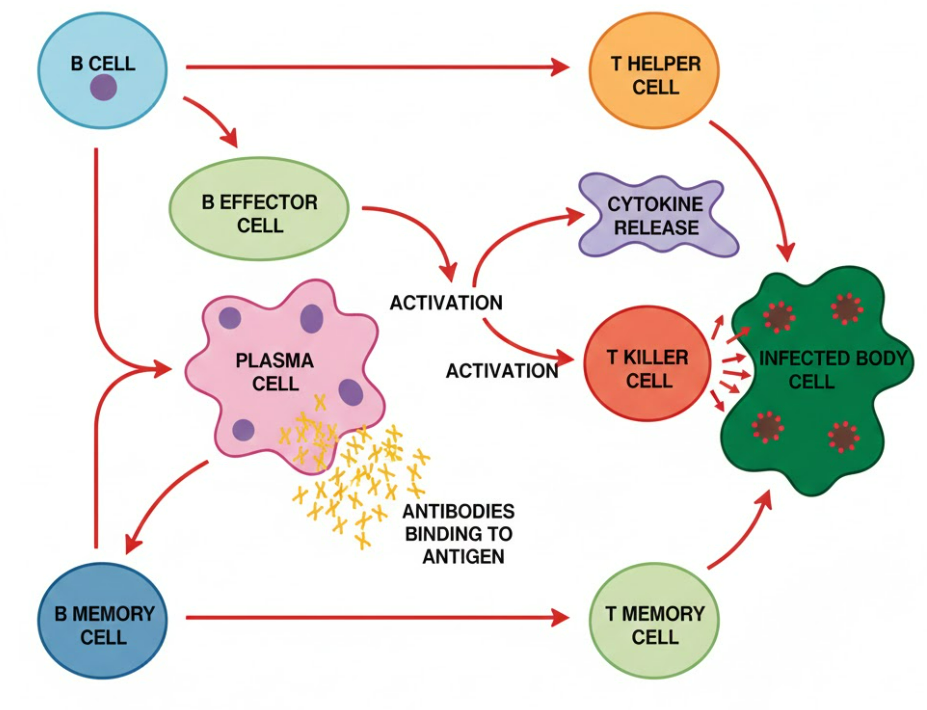
Key role: Immediate antibody production to remove the current infection.
2. B Memory Cells
- Long-lived cells formed after the first infection.
- Remain in the bloodstream for years.
- Do not make antibodies straight away.
Key role: Provide long-term immunity. When the same antigen returns, they quickly form plasma cells, making the secondary response much faster.
🧠 T Cells
1. T Helper Cells (Th Cells)
- Activated by antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
- Release cytokines for communication.
Key role: Coordinate the immune response by:
- Activating B cells to form plasma cells.
- Activating T killer cells.
- Supporting phagocytes in destroying pathogens.
2. T Killer Cells (Cytotoxic T Cells)
- Destroy virus-infected or abnormal body cells.
- Release perforin to break down infected cell membranes.
Key role: Directly kill infected host cells to stop virus spread. Important for clearing viral infections and targeting cancerous cells.
3. T Memory Cells
- Remain in the body after infection.
- Activate quickly on future exposure to the same antigen.
Key role: Provide a rapid and strong secondary response by producing new T helper and T killer cells quickly.
📋 Summary Table
| Cell Type | Main Function | Works in Primary or Secondary Response? |
|---|---|---|
| B Effector | Form plasma cells and produce antibodies | Primary |
| B Memory | Long-term cells enabling rapid antibody production | Secondary |
| T Helper | Activate B cells and T killer cells; release cytokines | Both |
| T Killer | Destroy infected or abnormal body cells | Primary and strengthened in secondary |
| T Memory | Enable fast activation of T cells in later infections | Secondary |
B effector → become plasma cells → make antibodies.
B memory → long-term immunity and rapid secondary response.
T helper → activate B cells and T killer cells.
T killer → destroy virus-infected or abnormal cells.
T memory → fast T cell response when the antigen returns.
