Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.11 Developing Immunity- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.11 Developing Immunity- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.11 Developing Immunity- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.11 understand how individuals may develop immunity (natural, artificial, active and passive)
Immunity: Natural, Artificial, Active, Passive
🌱 Introduction
Immunity is the body’s ability to resist infections. It can be developed in different ways depending on how the body receives antigens or antibodies. The four main forms are natural active, natural passive, artificial active and artificial passive immunity.
🩺 Types of Immunity
Natural Active Immunity
- Develops when a person becomes infected naturally.
- The immune system detects antigens, produces antibodies and forms memory cells.
- Provides long-term protection.
- Example: Recovering from chickenpox.
Key idea: The body’s own immune system carries out the full response.
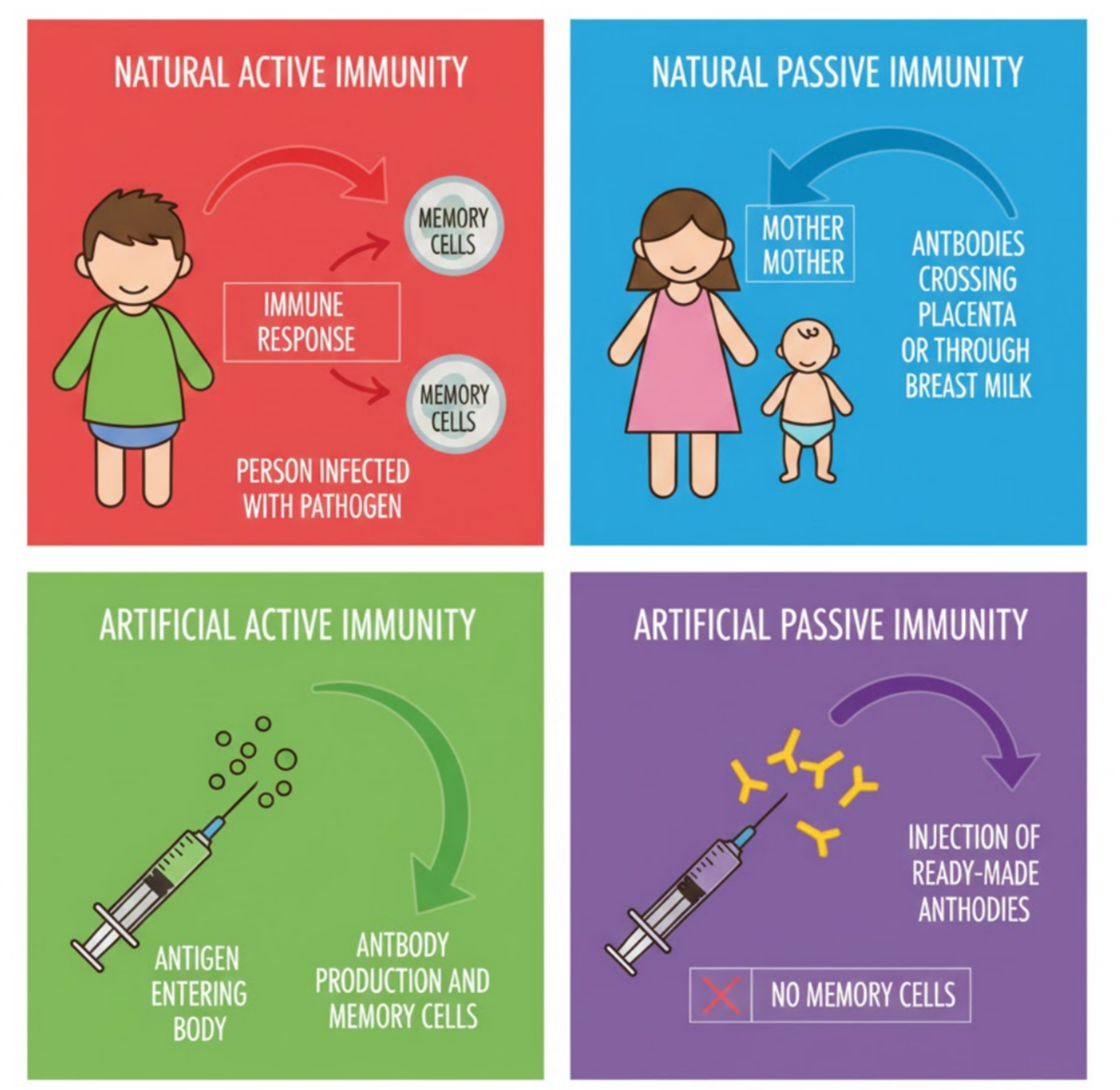
Natural Passive Immunity
- Antibodies are transferred naturally from another source.
- No antigen exposure and no memory cells formed.
- Protection is immediate but short-lived.
- Examples: Antibodies from mother to baby via placenta or through breast milk (colostrum).
Key idea: Ready-made antibodies enter the body.
Artificial Active Immunity
- Gained through vaccination.
- Vaccines contain weakened, dead or harmless forms of pathogens or antigens.
- The immune system responds by making antibodies and memory cells.
- Provides long-term protection similar to natural active immunity.
- Example: MMR vaccine.
Key idea: The body is encouraged to make its own immunity.
Artificial Passive Immunity
- Ready-made antibodies are injected directly into the body.
- Gives immediate but temporary protection.
- Used when rapid defence is needed.
- Examples: Antiserum for snake bites, monoclonal antibody treatments.
Key idea: No memory cells are formed; fast but short-lasting protection.
📋 Summary Table
| Type of Immunity | How Antibodies Enter | Memory Cells? | Speed | Duration | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Active | Produced by body after infection | Yes | Slow | Long-term | Recovering from measles |
| Natural Passive | From mother to baby | No | Immediate | Short-term | Placental antibodies |
| Artificial Active | Body produces after vaccination | Yes | Slow | Long-term | HPV vaccine |
| Artificial Passive | Injected from another source | No | Immediate | Short-term | Antivenom |
Active → body produces antibodies and memory cells.
Passive → receives ready-made antibodies.
Natural → happens naturally (infection or maternal transfer).
Artificial → medical method (vaccines or antibody injections).
