Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.14 Core Practical 14: The Effects of Different Antibiotics- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.14 Core Practical 14: The Effects of Different Antibiotics- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.14 Core Practical 14: The Effects of Different Antibiotics- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.14 Investigate the effect of different antibiotics on bacteria.
Investigate the Effect of Different Antibiotics on Bacteria
🧪 Aim
To compare the effectiveness of different antibiotics on bacterial growth using the agar disk diffusion method.
🌱 Introduction
Antibiotics are chemicals that inhibit or kill bacteria. The agar disk diffusion method measures bacterial sensitivity by observing the zone of inhibition around an antibiotic disk. A larger zone indicates greater bacterial inhibition under the conditions used.
⚙️ Variables
- Independent variable: Type of antibiotic (or concentration).
- Dependent variable: Diameter of zone of inhibition (mm).
- Control variables: Agar type, inoculum density, incubation temperature & time, disk size, volume of antibiotic, plate thickness.
🧾 Materials
- Non-pathogenic bacterial culture (e.g., E. coli K-12)
- Sterile nutrient agar plates (90 mm)
- Antibiotic disks or filter paper disks soaked in antibiotic solutions
- Sterile saline for inoculum
- Sterile cotton swabs
- Sterile forceps / tweezers
- Ruler or calipers
- Incubator (~25°C for school-safe use)
- Marker and labels
- Disinfectant (10% bleach) and autoclave access
- Gloves, lab coat, eye protection
🔬 Method
Prepare bacterial lawn:
- Mix bacterial colonies in sterile saline and adjust turbidity.
- Dip sterile swab, remove excess, streak agar evenly in three directions.
- Let surface dry ~2 min.
Place antibiotic disks: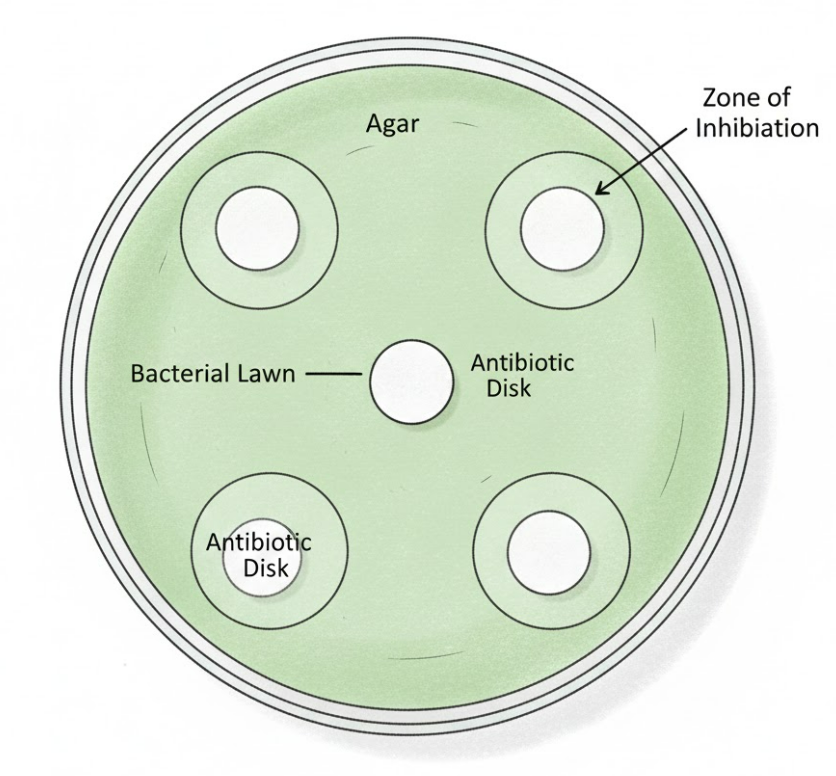
- Use sterile forceps to place disks evenly (3–4 per plate).
- Label underside of plate with antibiotic name/concentration.
Include controls:
- Negative control: sterile disk with no antibiotic.
- Optional positive control: antibiotic with known effect.
Incubate plates:
- Invert and incubate at 25°C for 24–48 h.
- Avoid 37°C unless approved and with proper containment.
Measure zones:
- Measure diameter of clear inhibition zones in two perpendicular directions; calculate mean.
- Repeat at least three replicates per antibiotic.
Dispose safely:
- Do not open plates after incubation.
- Autoclave or soak in 10% bleach before disposal.
📊 Example Data Table
| Plate ID | Antibiotic | Concentration | Replicate | Zone diameter 1 (mm) | Zone diameter 2 (mm) | Mean (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Ampicillin | 10 µg | 1 | 14 | 15 | 14.5 |
| P1 | Ampicillin | 10 µg | 2 | 13 | 14 | 13.5 |
| P1 | Ampicillin | 10 µg | 3 | 15 | 14 | 14.5 |
🧮 Analysis & Calculations
Mean:
\[ \bar{x} = \frac{\sum x}{n} \]
Standard deviation to show variation. Rank antibiotics: larger mean → more effective. Consider diffusion rates, molecule size, or bacterial resistance.
🔎 Evaluation / Sources of Error
- Uneven inoculum → standardise turbidity and streak technique.
- Variable agar depth → pour plates to ~4 mm thickness.
- Disk placement or size errors → uniform disks and sterile forceps.
- Environmental factors → same temperature & incubation time.
- Measurement error → measure twice, use calipers.
🟢 Conclusion
- Compare zones of inhibition to determine relative effectiveness.
- Larger zones indicate stronger inhibition, but in vitro results may not reflect clinical effectiveness.
- Mention bacteriostatic vs bactericidal action if relevant.
Use agar disk diffusion to compare antibiotics.
Measure zone of inhibition (mm) as indicator of effectiveness.
Control variables: agar type, inoculum density, incubation conditions, disk size.
Perform replicates and calculate mean ± SD.
Follow strict biosafety rules: non-pathogenic strains, aseptic technique, proper disposal.
