Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.18 Gel Electrophoresis in Forensics- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.18 Gel Electrophoresis in Forensics- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.18 Gel Electrophoresis in Forensics- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.18 know how gel electrophoresis can be used to separate DNA fragments of different length
Gel Electrophoresis: Separating DNA Fragments
🌱 Introduction
Gel electrophoresis is a lab technique used to separate DNA fragments by size. Smaller fragments travel further, while larger ones move shorter distances. This helps compare DNA samples, check PCR products and analyse genetic differences.
🟣 Why DNA Can Be Separated This Way
- DNA has a negative charge because of its phosphate groups.
- When electric current is applied, DNA moves toward the positive electrode.
- The gel behaves like a sieve:
- Small fragments move quickly
- Large fragments move slowly
🔵 Materials Needed
- Agarose gel
- Buffer solution
- DNA samples
- Loading dye
- DNA ladder (known fragment sizes)
- Power supply
- UV or blue-light viewer
🟢 How Gel Electrophoresis Works
1. Preparing the Gel
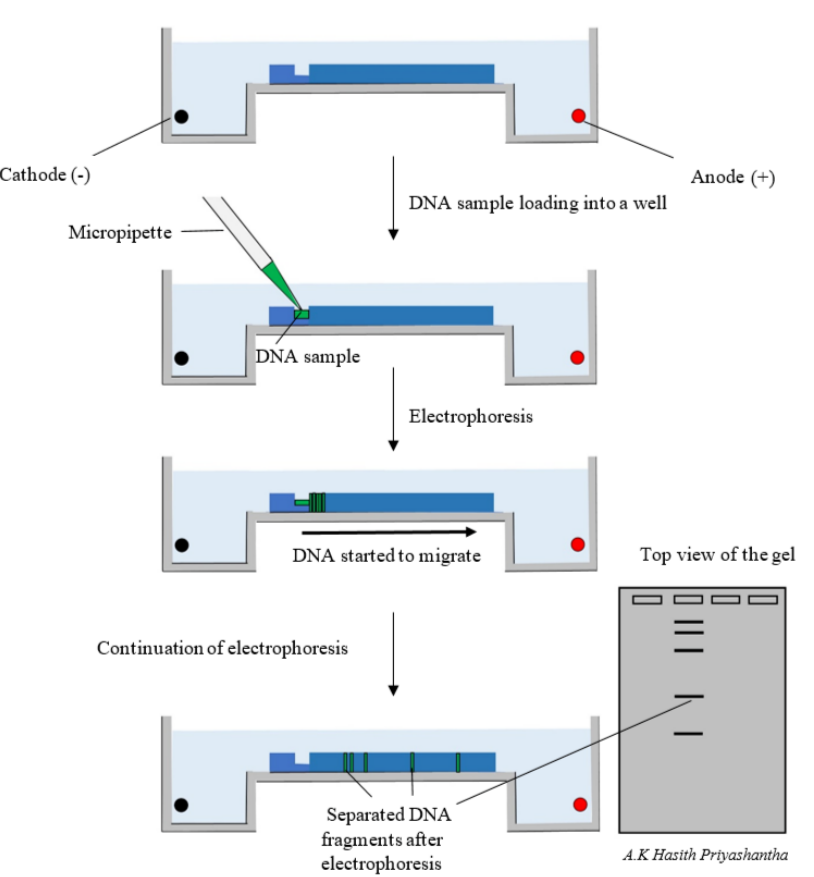
- Agarose is melted in buffer and poured into a tray with a comb.
- As it cools, it forms a gel with wells for DNA samples.
2. Loading DNA into Wells
- DNA is mixed with loading dye for visibility and weight.
- Samples and a DNA ladder are pipetted into the wells.
3. Running the Electric Current
- Gel is placed inside a tank filled with buffer.
- Electric current is applied:
- DNA moves from the negative end to the positive end.
- Small fragments move further through the gel pores.
4. Viewing the Results
- Gel is stained using a DNA dye (e.g. ethidium bromide or SYBR Safe).
- Under UV or blue light, DNA appears as bands.
- Bands are compared with the DNA ladder to estimate sizes.
🟠 What the Results Show
- Each band corresponds to DNA fragments of a specific length.
- Same band pattern suggests matching DNA sequences.
- Useful for:
- Checking PCR success
- DNA fingerprinting
- Genetic disease testing
- Restriction enzyme analysis
📋 Summary Table
| Step | What Happens | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Prepare agarose gel | Form gel with wells | Medium for DNA separation |
| Load DNA and ladder | Place samples in wells | Allow comparison of fragment sizes |
| Apply current | DNA moves through gel | Smaller fragments travel further |
| View bands | Stain and illuminate | Determine fragment lengths |
🧠 Quick Recap
DNA is negatively charged → moves to the positive electrode.
Gel separates fragments by size, not charge.
Smaller pieces travel faster and further.
DNA ladder gives reference sizes.
Used for DNA fingerprinting, PCR analysis and genetic testing.
DNA is negatively charged → moves to the positive electrode.
Gel separates fragments by size, not charge.
Smaller pieces travel faster and further.
DNA ladder gives reference sizes.
Used for DNA fingerprinting, PCR analysis and genetic testing.
