Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.19 DNA Profiling- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.19 DNA Profiling- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.19 DNA Profiling- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.19 understand how DNA profiling is used for identification and determining genetic relationships between organisms (plants and animals)
DNA Profiling: Identification & Genetic Relationships
🌱 Introduction
DNA profiling (or DNA fingerprinting) identifies individuals or determines genetic relationships based on unique DNA sequences. No two individuals (except identical twins) have exactly the same DNA.
🟣 How DNA Profiling Works
Sample Collection
- Obtain DNA from blood, hair, skin, saliva, plant tissue, or other cells.
DNA Extraction
- Cells are lysed and DNA is purified from other cellular material.
Amplification (PCR)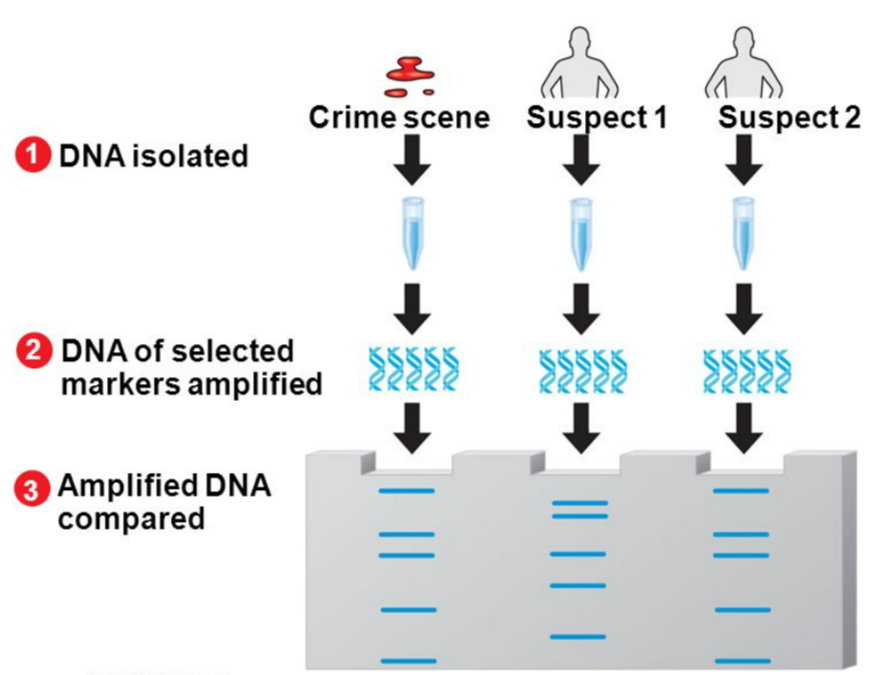
- Specific DNA regions are copied multiple times to ensure sufficient material.
Fragment Separation (Gel Electrophoresis)
- DNA fragments are separated by size using gel electrophoresis.
- DNA ladder allows estimation of fragment lengths.
Visualization & Comparison
- DNA bands are visualized with staining or fluorescent dyes.
- Band patterns are compared between individuals or species.
🔵 Applications
- Identification of Individuals
- Forensics: match crime scene DNA with suspects.
- Paternity testing: compare child and parent DNA bands.
- Conservation biology: identify individuals in a population.
- Determining Genetic Relationships
- Compare DNA band patterns between species or populations.
- Close relatives share more similar DNA patterns.
- Used in parentage confirmation, evolutionary studies, and breeding programs.
🟢 Key Features
- Highly specific – focuses on variable regions like short tandem repeats (STRs) or microsatellites.
- Non-coding regions often used because they vary more between individuals.
- Requires only small DNA samples.
- Can be matched against DNA databases for identification or population studies.
📋 Summary Table
| Purpose | Method | How DNA is Used |
|---|---|---|
| Identification | Forensics, paternity | Compare band patterns to match individuals |
| Genetic relationships | Parentage testing, breeding, conservation | Compare similarity of DNA bands between individuals/species |
| Population studies | Biodiversity or evolutionary studies | Assess genetic similarity and variation |
🧠 Quick Recap
DNA profiling uses unique DNA sequences for identification or genetic relationship analysis.
Steps: DNA extraction → PCR → Gel electrophoresis → Band comparison.
Close relatives have more similar patterns.
Applications: forensics, paternity testing, breeding programs, conservation, evolutionary studies.
DNA profiling uses unique DNA sequences for identification or genetic relationship analysis.
Steps: DNA extraction → PCR → Gel electrophoresis → Band comparison.
Close relatives have more similar patterns.
Applications: forensics, paternity testing, breeding programs, conservation, evolutionary studies.
