Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.6 Tuberculosis & HIV- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.6 Tuberculosis & HIV- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -6.6 Tuberculosis & HIV- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 6.6 understand how Mycobacterium tuberculosis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infect human cells, causing symptoms that may result in death
How Mycobacterium tuberculosis and HIV Infect Human Cells and Cause Disease
🌱 Introduction
Two major pathogens cause serious human diseases:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (bacterium) causes TB.
- HIV (virus) causes AIDS.
- Both target specific cells and weaken essential body systems, leading to symptoms that may become fatal.
🦠 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB)
How TB Infects the Body
- Enters the body mainly by inhalation of droplets from an infected person.
- Bacteria reach the alveoli in the lungs.
- Macrophages attempt to engulf them by phagocytosis.
- TB bacteria survive inside macrophages, avoiding destruction.
- They multiply slowly inside these cells.
Formation of Granulomas (Tubercules)
- The immune system builds a wall of cells around infected macrophages.
- This forms granulomas, areas of infected but contained tissue.
- TB can stay dormant for years.
🩺 Symptoms of Active TB
When the immune system weakens, bacteria break out of granulomas and spread.
- Persistent cough
- Coughing blood
- Chest pain
- Fever and night sweats
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
⚠️ How TB Causes Death
- Severe lung damage reduces gas exchange.
- Spread to other organs like kidneys, bones, brain (miliary TB).
- Respiratory failure or organ failure can occur.
- Vulnerable groups (elderly, weak immunity) are at highest risk.
🧬 HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)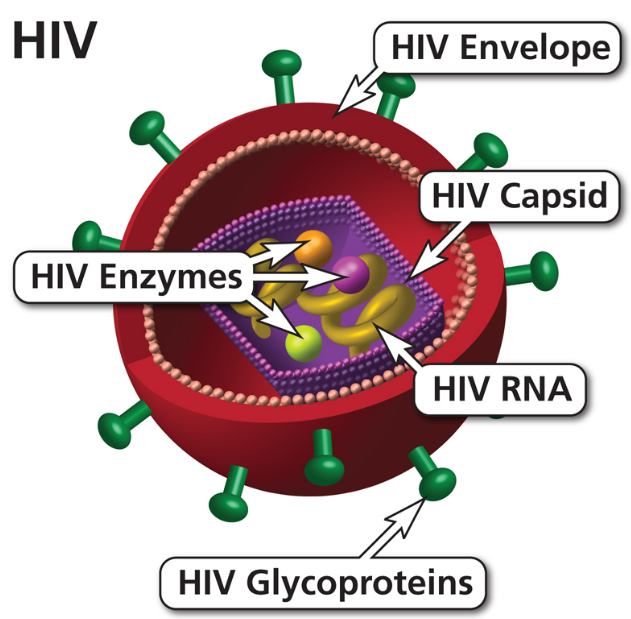
How HIV Infects the Body
- Spread through blood, semen, vaginal fluids, shared needles, or from mother to child.
- Targets CD4 helper T cells, a key part of the immune system.
Infection Steps
- Attachment
HIV glycoprotein (gp120) binds to CD4 receptors on T helper cells. - Fusion & Entry
Virus envelope fuses with the cell membrane. - Reverse Transcription
Viral RNA is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase. - Integration
Viral DNA enters host genome using integrase. - Virus may stay latent for years.
- Replication & Release
Activation leads to new virus particles being produced. CD4 cells eventually die, reducing immune function.
🩺 Symptoms of HIV/AIDS
Early infection:
- Mild flu-like symptoms
- Swollen lymph nodes
Latency:
- Often no symptoms for several years
AIDS (late stage):
- Extremely low CD4 count
- Recurrent infections (TB, pneumonia, fungal infections)
- Weight loss
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Cancers like Kaposi’s sarcoma
⚠️ How HIV Causes Death
- The immune system becomes severely weakened.
- The person cannot fight off even minor infections.
- Opportunistic infections or cancers become fatal.
- Respiratory failure, systemic infections, or organ damage can lead to death.
📋 Summary Table
| Feature | TB (M. tuberculosis) | HIV |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Bacterium | Virus |
| Entry | Inhaled droplets | Body fluids |
| Target Cells | Macrophages | CD4 T helper cells |
| Key Mechanism | Survives inside macrophages | Integrates viral DNA into host DNA |
| Dormancy | Yes | Yes (latent stage) |
| Main Damage | Lung destruction | Immune system collapse |
| Cause of Death | Respiratory failure/organ spread | Opportunistic infections |
🧠 Quick Recap
TB enters lungs, hides inside macrophages, forms granulomas, later reactivates.
Symptoms: cough, blood, fever, weight loss.
Death from lung failure or organ spread.
HIV infects CD4 T cells using gp120, reverse transcriptase and integrase.
Progressive immune failure leads to AIDS.
Death from opportunistic infections, not directly from HIV.
TB enters lungs, hides inside macrophages, forms granulomas, later reactivates.
Symptoms: cough, blood, fever, weight loss.
Death from lung failure or organ spread.
HIV infects CD4 T cells using gp120, reverse transcriptase and integrase.
Progressive immune failure leads to AIDS.
Death from opportunistic infections, not directly from HIV.
