Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.13 Calculation of Cardiac Output- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.13 Calculation of Cardiac Output- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.13 Calculation of Cardiac Output- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 7.13 (i) be able to calculate cardiac output
(ii) understand how variations in ventilation and cardiac output enable rapid delivery of oxygen to tissues and the removal of carbon dioxide from them, including how the heart rate and ventilation rate are controlled and the roles of the cardiovascular control centre and the ventilation centre in the medulla oblongata
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Control
🌟 Introduction
The body must deliver oxygen (O₂) to tissues and remove carbon dioxide (CO₂) efficiently. This is achieved by adjusting cardiac output and ventilation rate, which are controlled by centres in the medulla oblongata.
🧮 (i) Cardiac Output
Definition: Cardiac output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
Formula
CO = SV × HR
Where:
Stroke Volume (SV): Blood pumped per beat (mL)
Heart Rate (HR): Beats per minute (bpm)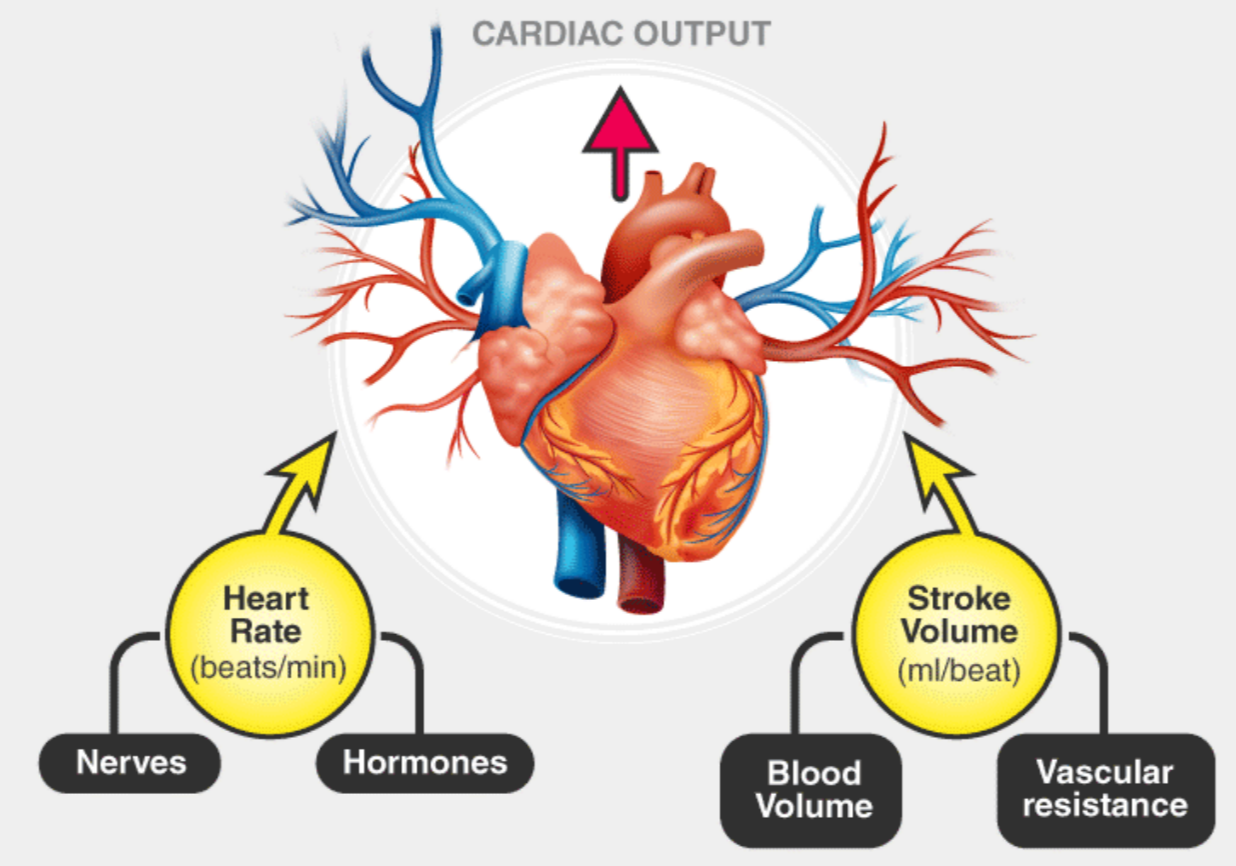
Example Calculation
SV = 70 mL
HR = 75 bpm
CO = 70 × 75 = 5250 mL/min ≈ 5.25 L/min
Key point: CO increases during exercise to meet higher oxygen demand.
⚡ (ii) Variations in Ventilation and Cardiac Output
Purpose
- Rapid O₂ delivery to tissues.
- Efficient CO₂ removal from tissues.
Mechanisms
- Increased Heart Rate (HR): Pumps more blood per minute.
- Increased Stroke Volume (SV): More blood per beat.
- Increased Ventilation Rate (Breathing Rate): Brings in more O₂ and removes CO₂ faster.
Result: Oxygen delivery rises, CO₂ is removed quickly, sustaining aerobic respiration during activity.
🧠 Control of Heart Rate and Ventilation
1. Cardiovascular Control Centre (Medulla Oblongata)
– Monitors blood pressure, blood O₂ and CO₂ levels.
– Sends autonomic signals to heart:
- Sympathetic nervous system: Increases HR
- Parasympathetic nervous system: Decreases HR
2. Ventilation Centre (Medulla Oblongata)
– Controls rate and depth of breathing.
– Responds to:
- High CO₂ → increases breathing rate
- Low O₂ → increases breathing rate (less sensitive than CO₂)
– Sends signals to respiratory muscles (diaphragm, intercostals) to adjust ventilation.
🔹 Integration During Exercise
- Muscles produce more CO₂ and use more O₂.
- Chemoreceptors detect changes in blood chemistry.
- Medulla increases HR and ventilation rate.
- Cardiac output rises, and oxygen delivery matches demand.
Memory tip: “More CO₂ → faster breath; more activity → faster heart.”
📌 Summary Table
| Parameter | Definition / Role | How it changes to meet demand |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Output (CO) | Blood/min pumped by heart | Increases with HR & SV during exercise |
| Heart Rate (HR) | Beats per minute | Controlled by cardiovascular centre |
| Stroke Volume (SV) | Blood/beat | Increases with exercise intensity |
| Ventilation Rate | Breaths/min | Controlled by ventilation centre in medulla |
| Chemoreceptors | Detect O₂ & CO₂ in blood | Stimulate medulla to adjust HR & ventilation |
CO = HR × SV
Exercise → ↑ HR, ↑ SV, ↑ ventilation → O₂ delivery ↑, CO₂ removal ↑
Cardiovascular centre: Adjusts heart rate via autonomic nerves
Ventilation centre: Adjusts breathing rate/depth via medulla
Chemoreceptors: Detect blood gases, trigger responses
Coordinated changes maintain tissue oxygenation during rest and activity.
