Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.18 The Kidney: Structure- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.18 The Kidney: Structure- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.18 The Kidney: Structure- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 7.18 know the gross and microscopic structure of the mammalian kidne
Kidney Structure
🌱 Introduction
The kidney filters blood removes waste such as urea, balances water and salts, and produces urine. Its efficiency comes from a well organised gross structure and a detailed microscopic arrangement.
🔍 GROSS STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY (Outside + Visible Internal Regions)
Shape and Position
- Bean shaped, located on either side of the spine.
- Renal artery brings blood in and the renal vein carries filtered blood out.
- Ureter transports urine to the bladder.
Main Regions (Cut Open View) 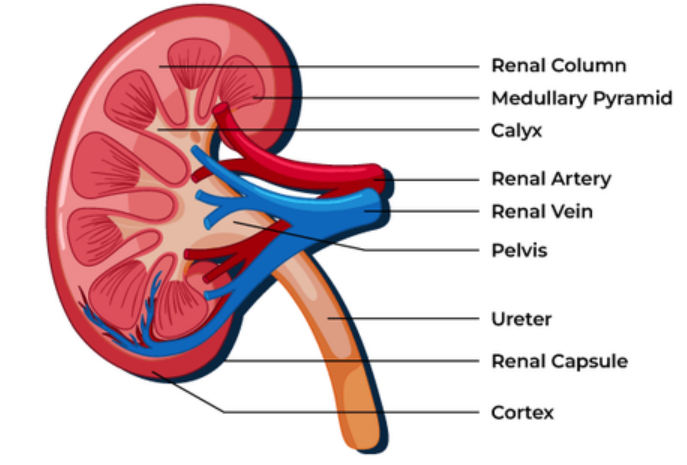
1. Cortex
- Outer, lighter region.
- Contains Bowman’s capsules and convoluted tubules.
- Site of ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption.
2. Medulla
- Inner, darker region arranged into pyramids.
- Contains loops of Henle and collecting ducts.
- Creates salt gradients for water reabsorption.
3. Renal Pelvis
- Funnel shaped cavity that collects urine from collecting ducts.
- Leads into the ureter.
Blood Supply
- Renal artery branches into arterioles leading to the glomerulus in each nephron.
- Renal vein returns filtered blood to circulation.
- High pressure helps efficient filtration.
🧬 MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY (Nephron Level)
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and each kidney contains about one million nephrons.
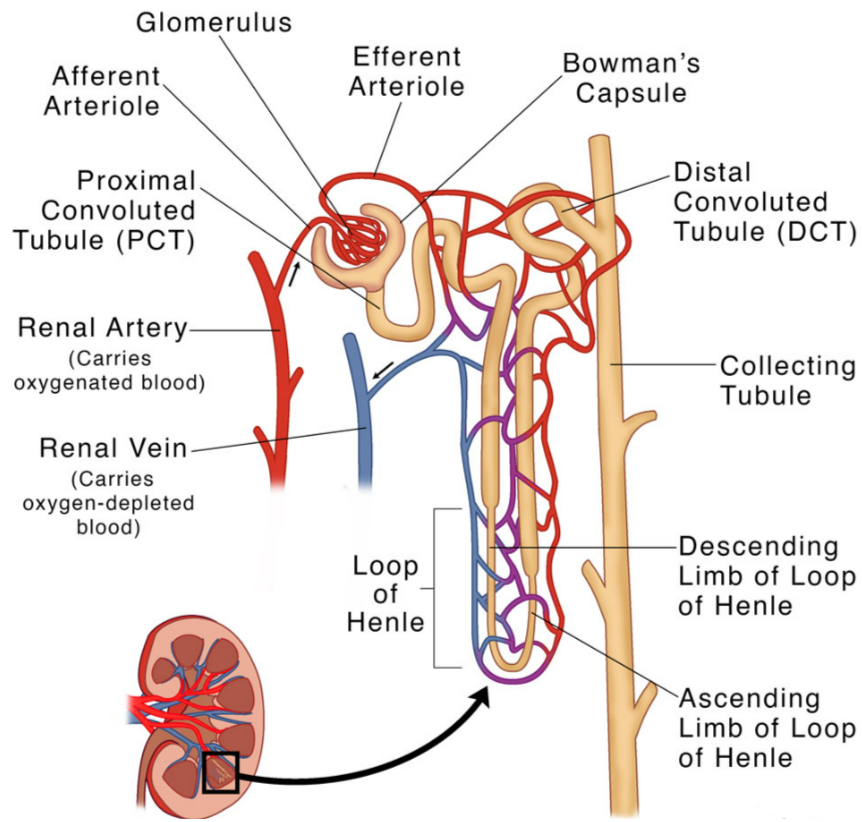
Structure of a Nephron
1. Bowman’s Capsule + Glomerulus
- Cup shaped capsule holding a capillary knot known as the glomerulus.
 Main site of ultrafiltration.
Main site of ultrafiltration.- Filtration barrier formed by basement membrane and podocytes.
2. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- Coiled tube following the capsule.
- Microvilli provide a large surface area.
- Main site of selective reabsorption including glucose, amino acids, ions and water.
3. Loop of Henle
- Descending limb: permeable to water.
- Ascending limb: pumps out Na+ and Cl- but is impermeable to water.
- Creates a salt gradient in the medulla to help water reabsorption.
4. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Adjusts ion balance including Na+, K+ and Ca2+.
- Partly controlled by hormones such as aldosterone.
5. Collecting Duct
- Collects urine from several nephrons.
- Permeability controlled by ADH.
- Final site for water reabsorption.
🧪 Key Histology Features (Microscope View)
| Structure | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Bowman’s capsule | Large circular space with glomerulus inside |
| PCT | Small lumen, thick wall, brush border (microvilli) |
| DCT | Larger lumen, no microvilli |
| Loop of Henle | Thin simple epithelium |
| Collecting ducts | Large circular tubules with clear lumen |
📊 Summary Table
| Region | Function | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| Cortex | Filtration and reabsorption | Bowman’s capsules, PCT and DCT |
| Medulla | Water conservation | Loops of Henle and collecting ducts |
| Pelvis | Urine drainage | Funnel shaped cavity |
| Nephron | Basic functional unit | Selective reabsorption and filtration |
Kidney has cortex, medulla, pelvis and major blood vessels.
Nephron is the functional unit of the kidney.
Bowman’s capsule is the site of filtration.
PCT performs major reabsorption using microvilli.
Loop of Henle creates a salt gradient for water recovery.
DCT fine tunes ion balance.
Collecting duct is controlled by ADH for water reabsorption.
Cortex holds capsules and convoluted tubules while medulla has loops and ducts.

 Main site of ultrafiltration.
Main site of ultrafiltration.