Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.2 Glycolysis- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.2 Glycolysis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.2 Glycolysis- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.2 understand the roles of glycolysis in aerobic and anaerobic respiration, including the phosphorylation of hexoses, the production of ATP by substrate level phosphorylation, reduced coenzyme, pyruvate and lactate
Details of intermediate stages and compounds are not required.
Glycolysis in Respiration
🌱 Introduction
Glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose (6-carbon) into two molecules of pyruvate (3-carbon).
Roles of Glycolysis
Phosphorylation of Hexoses
- Glucose is phosphorylated using ATP to form hexose phosphates.
- Traps glucose in the cell and makes it more reactive for breakdown.
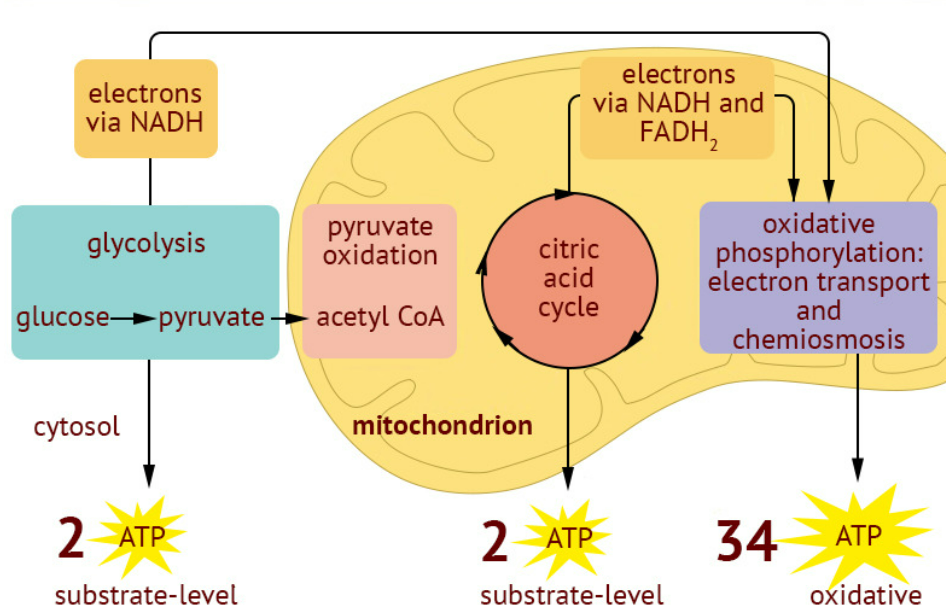
Production of ATP by Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
- Some ATP is produced directly during glycolysis.
- Provides a small, immediate supply of energy even without oxygen.
Formation of Reduced Coenzymes
- NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH, which carries electrons to mitochondria in aerobic respiration.
Production of Pyruvate
- End product is pyruvate, central to both pathways:
- Aerobic: pyruvate → mitochondria → Krebs cycle → ETC.
- Anaerobic: pyruvate → lactate (animals) or ethanol + CO₂ (yeast).
Lactate Formation (Anaerobic)
- In absence of oxygen, pyruvate is reduced to lactate using NADH.
- Regenerates NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue.
📋 Summary Table
| Feature | Role / Outcome |
|---|---|
| Phosphorylation of hexoses | Traps and activates glucose |
| ATP production | Small immediate energy via substrate-level phosphorylation |
| Reduced coenzyme | NADH formed for aerobic respiration |
| Pyruvate | End product; enters mitochondria (aerobic) or forms lactate (anaerobic) |
| Lactate | Regenerates NAD⁺ under anaerobic conditions |
Glycolysis: glucose → 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH.
Occurs in cytoplasm, first step of aerobic & anaerobic respiration.
ATP produced via substrate-level phosphorylation.
NADH → used in ETC (aerobic) or converted to NAD⁺ (anaerobic).
Pyruvate → mitochondria (aerobic) or lactate (anaerobic).
