Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.22 Control of Gene Expression- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.22 Control of Gene Expression- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.22 Control of Gene Expression- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 7.22 understand how genes can be switched on and off by DNA transcription factors, including the role of peptide hormones acting extracellularly and steroid hormones acting intracellularly
Gene Switching by Transcription Factors
🌱 Introduction
Cells control which proteins they make by switching genes on or off. This mainly happens during transcription, using transcription factors. Hormones also guide gene activity.
📘 What Are Transcription Factors
- Proteins that bind to DNA near a gene.
- They either start (activate) or stop (repress) transcription.
- Control which genes are expressed in a cell.
🧩 How Genes Are Switched ON
- Transcription factor binds to promoter region.
- Helps RNA polymerase attach.
- Gene is transcribed into mRNA.
- Protein gets made.
🧩 How Genes Are Switched OFF
- Transcription factor blocks the promoter.
- RNA polymerase cannot bind.
- Gene is silent, no protein made.
🌟 Role of Hormones
Hormones tell cells which transcription factors to activate.
🧪 Peptide Hormones (extracellular action)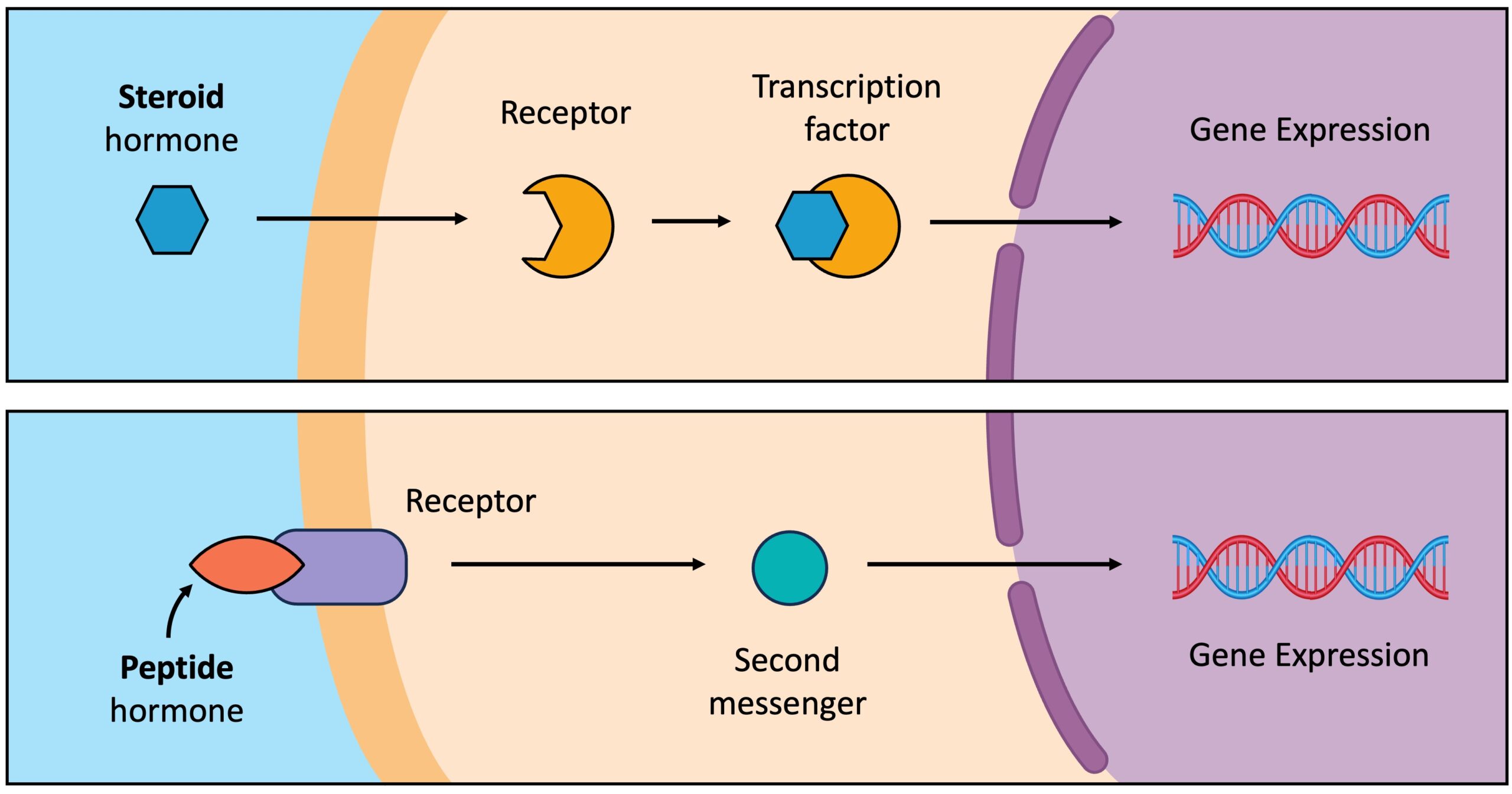
Examples: insulin, adrenaline
- Cannot enter cell.
- Bind to receptors on the cell surface.
- Trigger a signal cascade inside the cell.
- This cascade activates or inactivates transcription factors.
- Result: gene expression increases or decreases.
Shortcut: Peptide hormones = stay outside, send messages inside.
🧪 Steroid Hormones (intracellular action)
Examples: oestrogen, testosterone, cortisol
- Lipid soluble, so they enter the cell.
- Bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus.
- Hormone receptor complex binds directly to DNA as a transcription factor.
- Switches specific genes on or off.
Shortcut: Steroid hormones = go inside and act directly on DNA.
📌 Summary Table
| Feature | Peptide Hormones | Steroid Hormones |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Water soluble | Lipid soluble |
| Can enter cell | No | Yes |
| Receptor location | Cell membrane | Cytoplasm or nucleus |
| How they affect genes | Use second messengers to activate transcription factors | Complex binds directly to DNA |
| Speed of action | Fast | Slower but long lasting |
Transcription factors decide whether genes are ON or OFF.
Peptide hormones act outside cell and use second messengers.
Steroid hormones act inside cell and directly control DNA.
Remember: Peptide = Periphery, Steroid = Straight to DNA.
