Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.8 Core Practical 16: Respirometer to Calculate RQ- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.8 Core Practical 16: Respirometer to Calculate RQ- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -7.8 Core Practical 16: Respirometer to Calculate RQ- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 7.8 Use a simple respirometer to determine the rate of respiration and RQ of a suitable material (such as germinating seeds or small invertebrates).
CORE PRACTICAL 16
Using a Respirometer to Measure Respiration and RQ
🌱 Introduction
A respirometer measures the rate of respiration by detecting the uptake of oxygen and/or release of carbon dioxide.
The respiratory quotient (RQ) can be calculated using:
RQ = \(\dfrac{CO_2 \ produced}{O_2 \ consumed}\)
This helps identify which substrate (carbohydrate, fat, protein) the organism is respiring.
Principle
- Germinating seeds or small invertebrates consume oxygen during respiration.
- Oxygen uptake causes a drop in volume or movement of liquid in a manometer/respirometer.
- CO₂ can be absorbed by KOH to measure O₂ uptake only.
- Rate of oxygen uptake = respiration rate.
- Measuring both O₂ consumed and CO₂ produced allows calculation of RQ.
Materials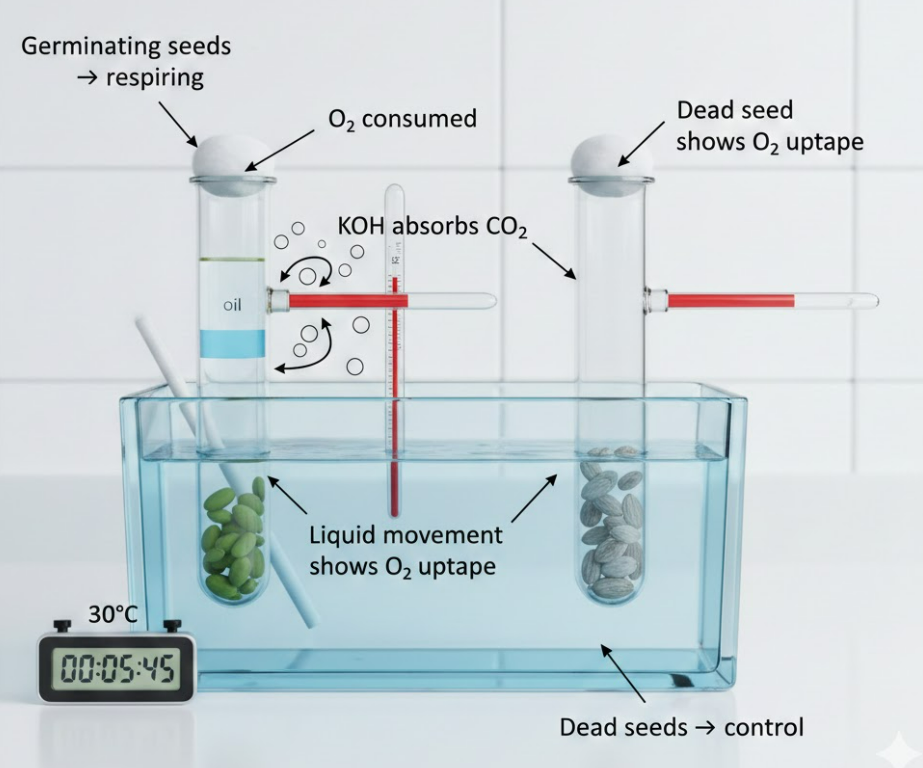
- Germinating seeds (e.g., beans, peas) or small invertebrates
- Respirometer setup: test tube / respiratory chamber, capillary tubing with scale, syringe/manometer
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) to absorb CO₂
- Oil to reduce evaporation
- Cotton wool plug
- Timer / stopwatch
- Water bath (optional)
Method
- Place respiring material in a test tube or respirometer chamber.
- Add KOH if measuring only oxygen uptake.
- Seal with cotton plug and connect to capillary tube with scale/liquid indicator.
- Set up a control tube with dead material or no respiring organism.
- Place in constant temperature environment.
- Measure liquid movement over time and record readings.
- Calculate rate of oxygen consumption and RQ using measurements.
🟡 Variables
Independent variable: Type of substrate, temperature, or organism used
Dependent variable: Rate of oxygen consumption (respiration rate) and RQ value
Controlled variables: Temperature, volume of respiring material, type of respirometer/chemical, measurement intervals
📋 Example Data Table
| Time (min) | Volume of liquid moved (mm) | Rate of O₂ uptake (mm³/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | – |
| 5 | 2 | 0.4 |
| 10 | 4 | 0.4 |
| 15 | 6 | 0.4 |
🟠 Calculations
- Rate of respiration: \( \text{Rate} = \dfrac{\text{Change in O₂ volume}}{\text{Time}} \)
- Respiratory Quotient (RQ): \( \text{RQ} = \dfrac{CO_2 \ produced}{O_2 \ consumed} \)
- RQ values indicate substrate:
- Carbohydrate ≈ 1.0
- Fat ≈ 0.7
- Protein ≈ 0.8–0.9
🦺 Safety & Ethical Considerations
- Use small, non-harmful organisms.
- Avoid overheating or stressing animals.
- Handle chemicals like KOH carefully.
- Wash hands after handling seeds, animals, or chemicals.
Respirometer measures oxygen uptake → respiration rate.
KOH absorbs CO₂ if only measuring O₂.
RQ = CO₂ produced ÷ O₂ consumed → shows which substrate is respired.
Use controls and maintain constant conditions.
Example materials: germinating seeds, small invertebrates.
