Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.1 Neurones: Types and Functions- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.1 Neurones: Types and Functions- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.1 Neurones: Types and Functions- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.1 know the structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurones, including Schwann cells and myelination
Structure & Function of Neurones
🌱 Introduction
Neurones transmit electrical impulses in the nervous system.
There are three main types: sensory, relay, and motor neurones.
They work together to detect stimuli, process information, and trigger responses.
Schwann cells and myelination help impulses travel faster.
📌 1. Sensory Neurones

Structure
- Long dendron carries impulse from receptor to cell body.
- Short axon carries impulse from cell body to CNS.
- Cell body is outside CNS in a ganglion.
- Myelinated in most cases.
Function
- Transmit impulses from receptors (skin, eyes, ears) to CNS.
📌 2. Relay (Inter) Neurones
Structure
- Many short dendrites and a single short axon.
- Found entirely within CNS (brain/spinal cord).
- Usually unmyelinated for short local connections.
Function
- Connect sensory neurones to motor neurones.
- Integrate information and coordinate responses.
📌 3. Motor Neurones
Structure
- Cell body inside CNS.
- Long axon carries impulse from CNS to effector (muscle/gland).
- Short dendrites receive impulses from relay neurones.
- Myelinated for faster conduction.
Function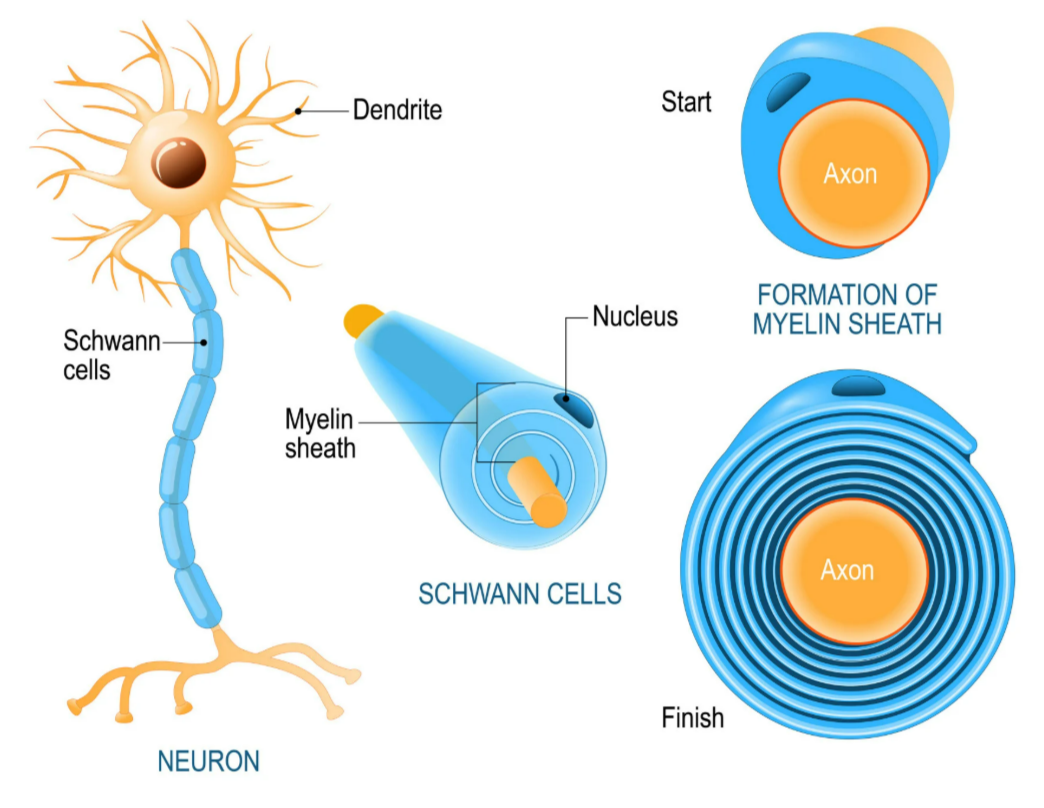
- Transmit impulses from CNS to effectors to trigger a response.
📌 4. Schwann Cells & Myelination
Schwann Cells
- Wrap around axon of neurones.
- Produce myelin sheath in PNS.
Myelin Sheath
- Fatty layer surrounding axon.
- Acts as insulator → speeds up electrical impulses.
- Impulses jump between nodes of Ranvier (gaps in myelin) — called saltatory conduction.
- Advantages: faster, more efficient, less energy loss.
📊 Summary Table
| Neurone Type | Structure | Function | Myelination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory | Dendron → cell body → axon | Receptor → CNS | Usually myelinated |
| Relay | Short dendrites + short axon | Connects sensory → motor | Usually unmyelinated |
| Motor | Dendrites + long axon | CNS → effector | Myelinated |
| Feature | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Schwann cells | Wrap axons in PNS, form myelin |
| Myelin sheath | Insulates axon, speeds conduction |
| Nodes of Ranvier | Gaps in myelin, allow saltatory conduction |
📦 Quick Recap
Sensory neurones: receptor → CNS
Relay neurones: CNS → CNS
Motor neurones: CNS → effector
Schwann cells: make myelin in PNS
Myelin: insulation → faster impulse, saltatory conduction
Sensory neurones: receptor → CNS
Relay neurones: CNS → CNS
Motor neurones: CNS → effector
Schwann cells: make myelin in PNS
Myelin: insulation → faster impulse, saltatory conduction
