Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.10 Central & Peripheral Nervous System- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.10 Central & Peripheral Nervous System- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.10 Central & Peripheral Nervous System- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.10 know that the mammalian nervous system consists of the central and peripheral nervous systems
Mammalian Nervous System
🌱 Introduction
The mammalian nervous system is a complex communication network that controls body functions by transmitting electrical impulses. It enables mammals to:
- Respond quickly to the environment
- Coordinate internal body activities
- Maintain homeostasis
It consists of two main divisions: Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
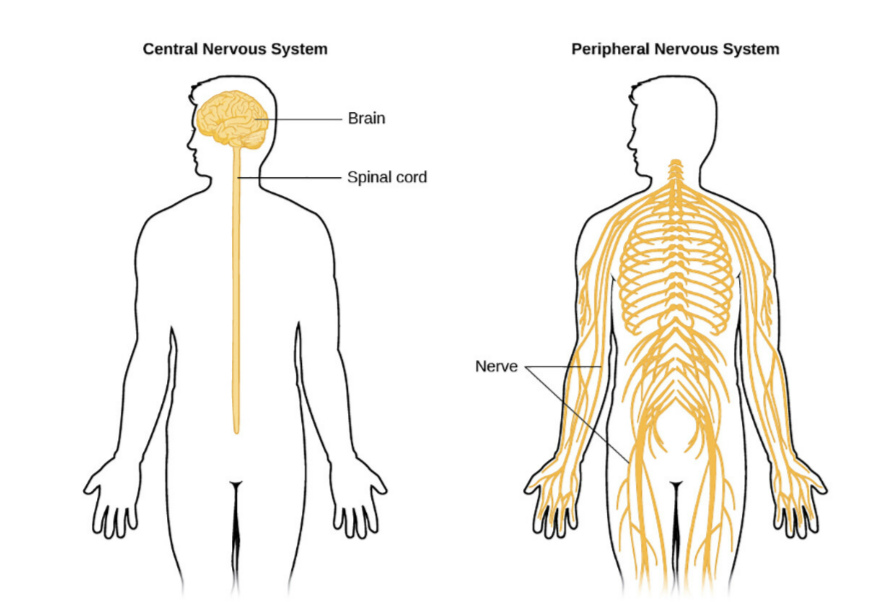
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Structure:
- Brain: Controls higher functions (thinking, memory, coordination, emotions)
- Spinal cord: Connects brain to the body; acts as a reflex centre
- Function:
- Integration: Processes incoming sensory information
- Decision making: Generates appropriate responses
 Reflex actions: Provides fast automatic responses
Reflex actions: Provides fast automatic responses
- Protection:
- Encased in skull (brain) and vertebrae (spinal cord)
- Cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Surrounded by meninges
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Structure: All neurones outside CNS, includes sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) neurones
- Function:
- Sensory (afferent) nerves: Carry impulses from receptors to CNS
- Motor (efferent) nerves: Carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)
- Divisions:
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary actions (skeletal muscles)
- Autonomic Nervous System: Controls involuntary actions (heart, glands, smooth muscles)
Key Points
- CNS: Integrates information, controls voluntary and involuntary responses
- PNS: Connects CNS with the rest of the body
- Sensory nerves = input to CNS
- Motor nerves = output from CNS
- Autonomic system ensures internal organs function automatically
📊 Summary Table
| Component | Structure | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | Brain + spinal cord | Processes info, generates response | Reflex action, thinking |
| PNS | All other neurones | Connects CNS to body | Sensory & motor nerves |
| Sensory neurones | Afferent | Receptor → CNS | Touch, pain, light |
| Motor neurones | Efferent | CNS → effector | Muscle contraction |
| Autonomic NS | Part of PNS | Involuntary control | Heart rate, digestion |
| Somatic NS | Part of PNS | Voluntary control | Walking, writing |
📦 Quick Recap
Nervous system = CNS + PNS.
CNS: Brain + spinal cord → integrates info, controls responses.
PNS: Links CNS to body → sensory (input) + motor (output).
Divisions: Somatic (voluntary), Autonomic (involuntary).
Nervous system = CNS + PNS.
CNS: Brain + spinal cord → integrates info, controls responses.
PNS: Links CNS to body → sensory (input) + motor (output).
Divisions: Somatic (voluntary), Autonomic (involuntary).
