Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.11 Effects of Plant Hormones- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.11 Effects of Plant Hormones- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.11 Effects of Plant Hormones- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.11 understand how phytochrome, auxin (IAA) and gibberellins bring about responses in plants, including their effects on transcription
Plant Hormones and Light Responses
🌿 Introduction
Plants sense and respond to light and other environmental signals through hormones and special pigments. These signals adjust gene transcription so the plant grows in the best possible way. The main players are phytochrome, auxin, and gibberellins.
🔴 1. Phytochrome
What it is
- Light-sensitive pigment found in plant tissues.
- Exists in two reversible forms:
- Pr absorbs red light (600 nm)
- Pfr absorbs far-red light (700 nm)
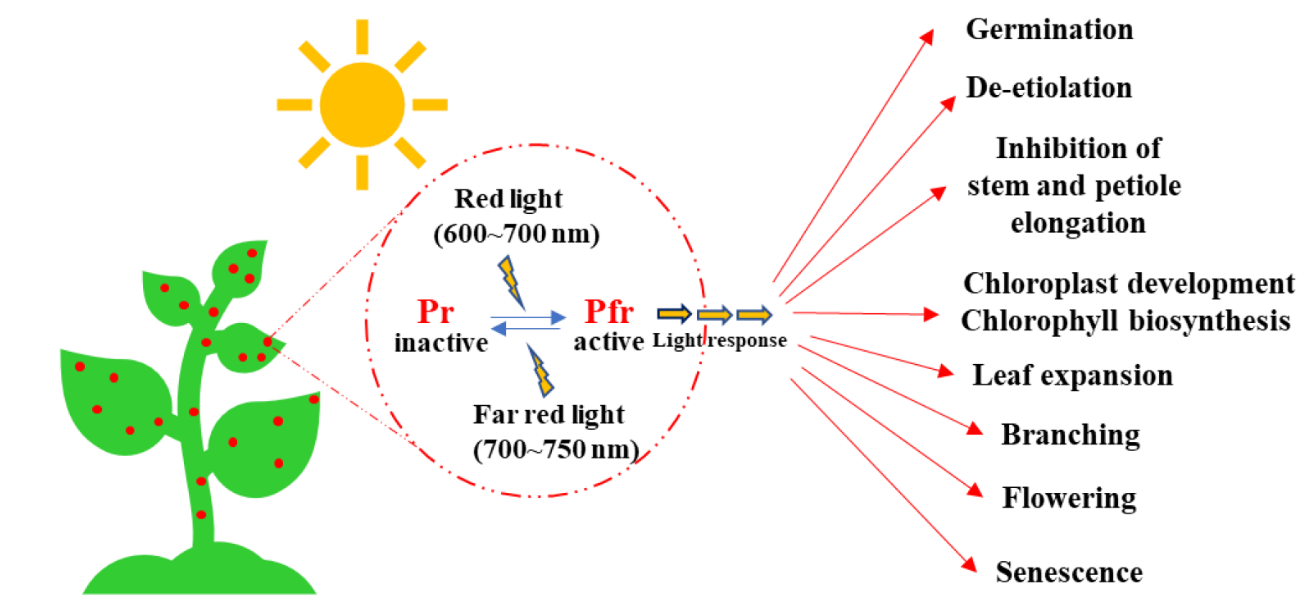
How it works
- Daylight converts Pr to Pfr.
- Darkness slowly converts Pfr back to Pr.
- Pfr is the active form that triggers plant responses.
Roles
- Controls germination, flowering, stem elongation and leaf expansion.
- Detects day length for photoperiodism.
Link to Transcription
- Pfr interacts with transcription factors.
- This increases or decreases transcription of genes controlling:
- Chlorophyll synthesis
- Flowering signals
- Germination enzymes such as amylase
Example
Seeds exposed to red light convert Pr to Pfr which switches on amylase-producing genes. Amylase breaks down starch to fuel germination.
🌿 2. Auxin (IAA)
What it is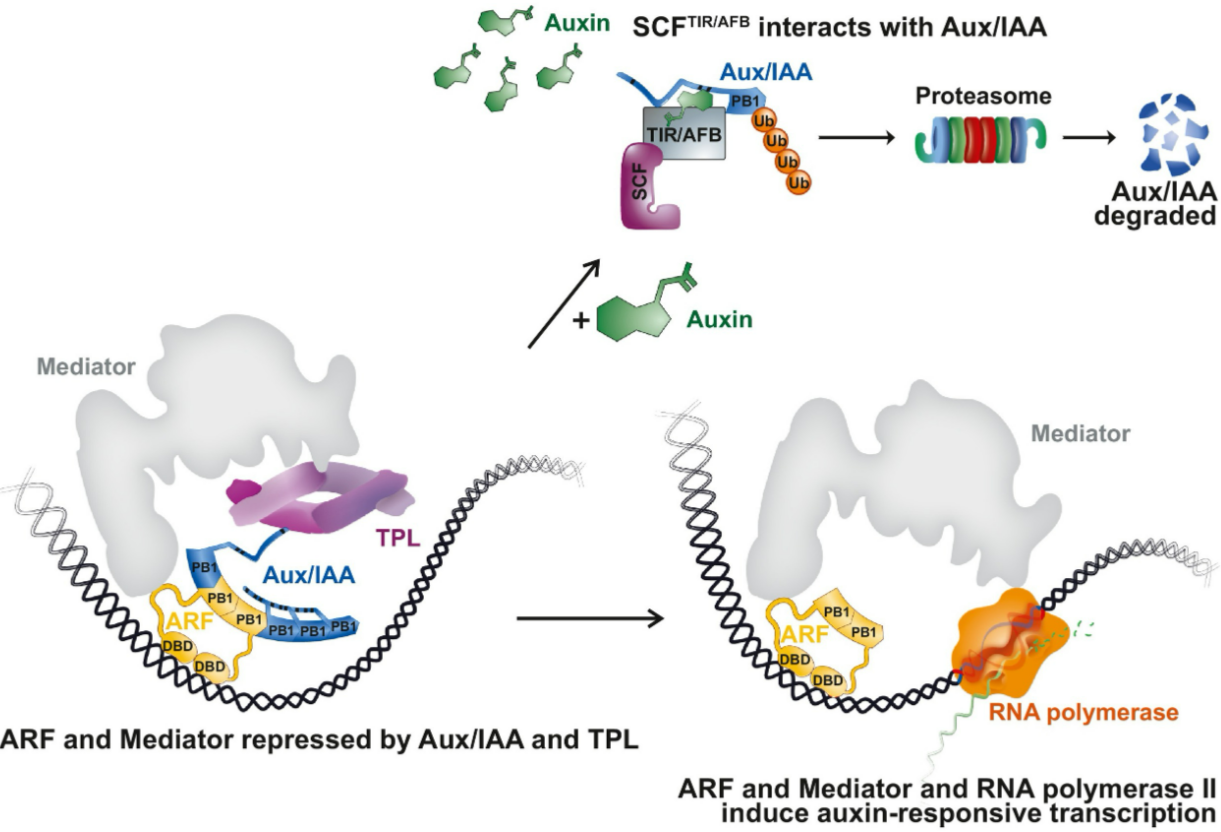
- Growth hormone produced mainly in shoot tips.
Main Functions
- Stimulates cell elongation.
- Controls phototropism and gravitropism.
- Maintains apical dominance.
How it works in Phototropism
- Auxin collects on the shaded side of the shoot.
- Cells on that side elongate more.
- Shoot bends towards the light.
Link to Transcription
- Auxin binds to receptors that activate transcription factors.
- Genes for expansin proteins turn on.
- Expansins loosen the cell wall so the cell can stretch and elongate.
Extra Key Idea
- High auxin in shoots promotes growth.
- High auxin in roots inhibits growth.
🌾 3. Gibberellins
What they are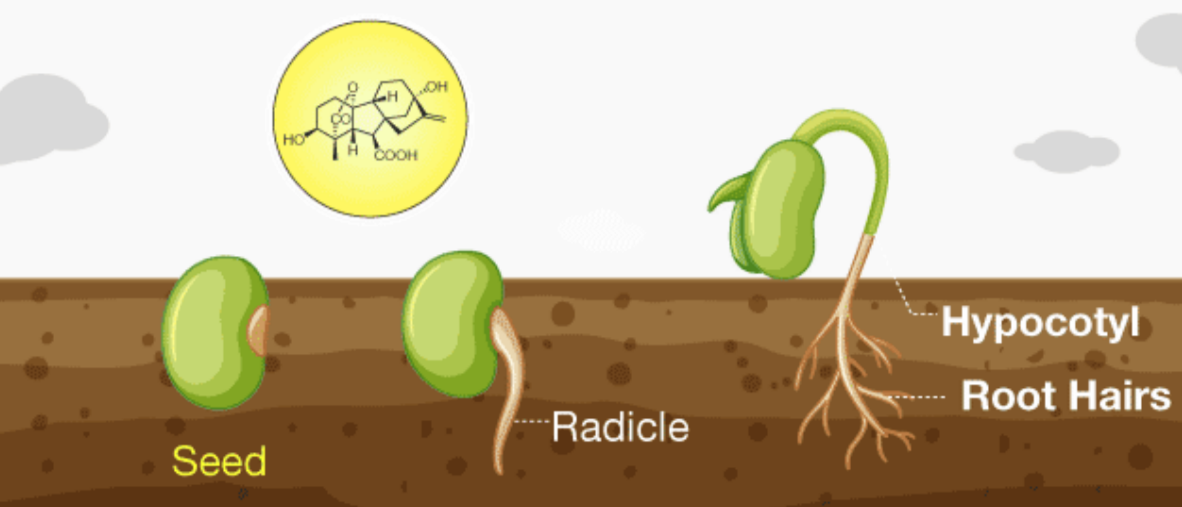
- Hormones involved in stem elongation and seed germination.
Functions
- Stimulate cell elongation and division.
- Break seed dormancy.
- Promote production of enzymes such as amylase.
Link to Transcription
- Gibberellin binds to receptors which remove DELLA proteins (growth repressors).
- With DELLA removed, transcription factors switch on genes for growth and enzyme production.
Example
In barley seeds, gibberellin from the embryo reaches the aleurone layer and activates amylase genes. Amylase breaks starch to maltose which powers early growth.
📊 Summary Table
| Hormone / Pigment | Main Role | How Response Happens | Effect on Transcription |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phytochrome (Pr/Pfr) | Detects light, controls flowering and germination | Light converts Pr to Pfr | Pfr regulates transcription factors |
| Auxin (IAA) | Phototropism and elongation | Moves to shaded side and causes elongation | Turns on expansin-coding genes |
| Gibberellins | Stem growth and germination | Remove DELLA repressors | Activate genes for enzymes and growth |
Phytochrome: Pfr is the active light form that regulates gene expression.
Auxin: Moves to shaded side and activates expansin genes for elongation.
Gibberellins: Trigger germination and growth by removing DELLA inhibitors.
