Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.13 Nervous & Hormonal Coordination- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.13 Nervous & Hormonal Coordination- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.13 Nervous & Hormonal Coordination- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.13 understand how coordination in animals is brought about through nervous and hormonal control
Coordination in Animals (Nervous Control + Hormonal Control)
🌱 Introduction
Animals use two major systems to stay coordinated and respond to changes around them. The nervous system sends rapid electrical impulses, while the hormonal system uses slower chemical messages carried in the blood. Together they keep the body balanced and functioning smoothly.
⚡ 1. Nervous Control 
Key Features
- Messages sent by electrical impulses in neurones.
- Transfer is extremely fast.
- Responses are short-lived and very specific.
- Includes the CNS (brain and spinal cord) and PNS.
How It Works
- Receptor detects a stimulus.
- Sensory neurone carries impulse to the CNS.
- CNS processes information.
- Motor neurone carries impulse to an effector.
- Effector produces a response such as a muscle contracting.
Examples
- Pulling your hand away from heat.
- Breathing rate increasing during exercise.
🌿 2. Hormonal (Endocrine) Control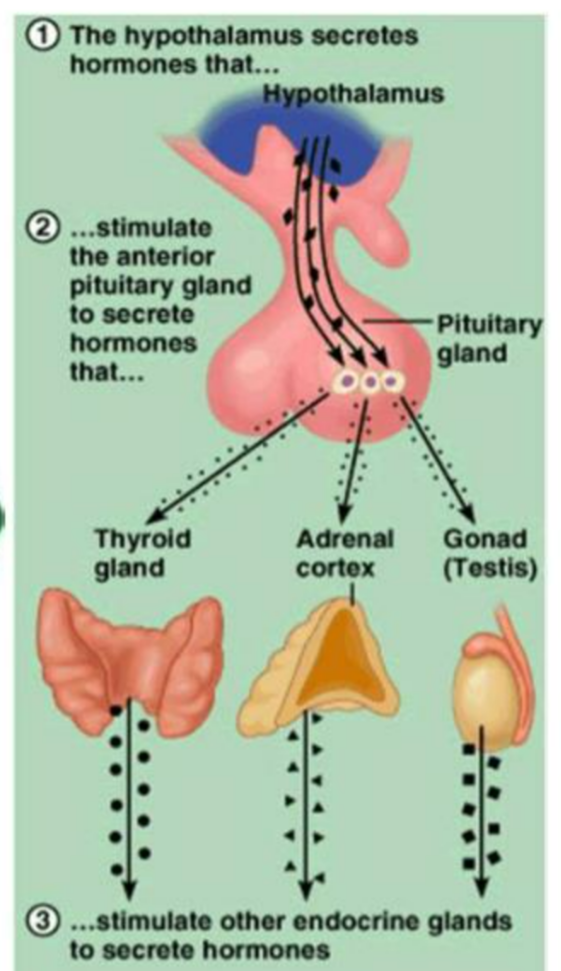
Key Features
- Uses hormones released into the bloodstream.
- Slower responses but long-lasting.
- Acts on target organs with specific receptors.
- Ideal for long-term regulation.
How It Works
- A gland produces a hormone.
- Hormone enters the blood and travels through the body.
- Hormone binds to receptors on target cells.
- Target cells change activity such as metabolism, growth, or heart rate.
Examples
- Adrenaline increasing heart rate.
- Insulin lowering blood glucose.
- Thyroxine controlling metabolism.
- Hormones guiding puberty changes.
🔗 How Both Systems Work Together
Animals often rely on both forms of control simultaneously.
- During exercise: nervous system quickly increases breathing rate, while adrenaline supports this by raising heart rate.
- During stress: brain detects danger and the adrenal glands release adrenaline to prepare the body.
Both systems help maintain homeostasis and coordinate complex behaviours.
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Nervous System | Hormonal System |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very fast | Slower |
| Type of message | Electrical impulses + neurotransmitters | Chemical hormones |
| Transport | Neurones | Blood |
| Duration | Short | Long-lasting |
| Target | Very specific cells | Many cells with receptors |
| Example | Reflex actions | Blood glucose control |
📦 Quick Recap
Nervous system: very fast, electrical impulses, short-term and precise.
Hormonal system: slower, chemical messages, long-term and widespread effects.
Both systems work together to coordinate responses and maintain balance in the body.
Nervous system: very fast, electrical impulses, short-term and precise.
Hormonal system: slower, chemical messages, long-term and widespread effects.
Both systems work together to coordinate responses and maintain balance in the body.
