Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.14 Human Brain Structures & Functions- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.14 Human Brain Structures & Functions- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.14 Human Brain Structures & Functions- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.14 know the location and main functions of the cerebral hemispheres, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, cerebellum and medulla oblongata of the human brain
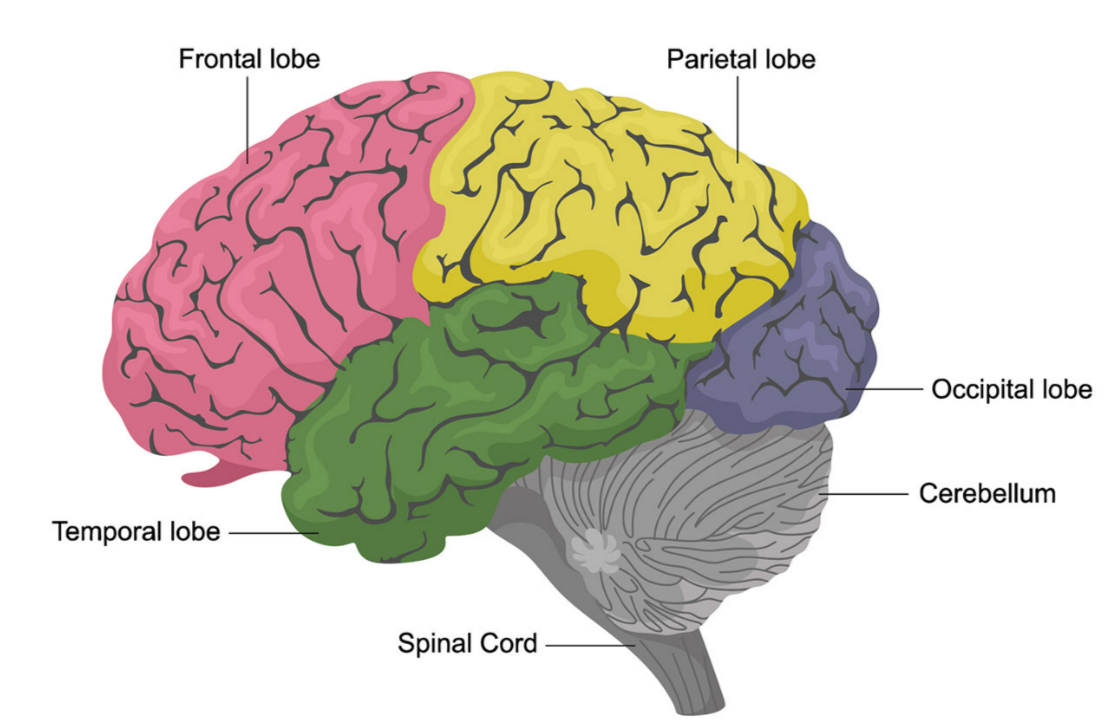
Parts of the Human Brain
🌱 Introduction
The human brain is divided into several specialised regions. Each part carries out specific functions that support movement, memory, behaviour, coordination and overall homeostasis.
1. Cerebral Hemispheres
📍 Location
- Largest and uppermost region of the brain.
- Split into left and right hemispheres.
- Outer surface is the cerebral cortex.
🎯 Main Functions
- Higher thinking such as reasoning and problem solving.
- Voluntary movement through the motor cortex.
- Sensory perception including touch, vision, smell, taste and hearing.
- Memory formation, learning and shaping personality.
- Speech and language areas such as Broca’s and Wernicke’s regions.
2. Hypothalamus
📍 Location
- Tiny region beneath the thalamus.
- Located just above the pituitary gland.
🎯 Main Functions
- Acts as the main homeostasis control centre.
- Monitors temperature, water content, ion concentration and blood glucose.
- Contains osmoreceptors for maintaining water balance.
- Controls the autonomic nervous system.
- Produces releasing hormones that guide pituitary activity.
3. Pituitary Gland
📍 Location
- Small, pea-shaped gland located below the hypothalamus.
- Connected by the infundibulum.
🎯 Main Functions
- Known as the master gland.
- Releases hormones that regulate other endocrine glands.
- Anterior pituitary secretes FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, GH and prolactin.
- Posterior pituitary releases ADH and oxytocin (made in the hypothalamus).
- Controls growth, metabolism, reproduction and water balance.
4. Cerebellum
📍 Location
- Situated at the back of the brain.
- Lies beneath the cerebral hemispheres.
- Characterised by a highly folded surface.
🎯 Main Functions
- Maintains posture and balance.
- Coordinates fine motor movements.
- Ensures smooth and accurate movement patterns.
- Stores motor memory such as cycling or playing instruments.
5. Medulla Oblongata
📍 Location
- Located at the base of the brainstem.
- Connects directly to the spinal cord.
🎯 Main Functions
- Controls essential involuntary reflexes.
- Regulates breathing, heart rate and blood pressure.
- Coordinates reflex actions such as swallowing and coughing.
- Critical for survival as it manages autonomic processes.
| Brain Part | Location | Main Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebral Hemispheres | Upper part of brain | Thinking, memory, voluntary movement, senses |
| Hypothalamus | Below thalamus | Homeostasis, temperature, water balance, hormone control |
| Pituitary Gland | Beneath hypothalamus | Master gland regulating hormones and ADH release |
| Cerebellum | Back of brain | Balance, coordination, precision |
| Medulla Oblongata | Brainstem | Breathing, heart rate, blood pressure |
📦 Quick Recap
Cerebral hemispheres: upper brain, control thinking, senses and voluntary actions.
Hypothalamus: homeostasis centre and autonomic control.
Pituitary: master endocrine gland regulating hormones including ADH.
Cerebellum: balance and movement coordination.
Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing and heart rate.
Cerebral hemispheres: upper brain, control thinking, senses and voluntary actions.
Hypothalamus: homeostasis centre and autonomic control.
Pituitary: master endocrine gland regulating hormones including ADH.
Cerebellum: balance and movement coordination.
Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing and heart rate.
