Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.15 Techniques to Investigate the Brain- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.15 Techniques to Investigate the Brain- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.15 Techniques to Investigate the Brain- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.15 understand how magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) are used in medical diagnosis and the investigation of brain structure and function
Brain Imaging Techniques (MRI, fMRI, PET, CT)
🌱 Introduction
Doctors use several non-invasive scans to study the brain. These techniques help reveal both structure and function, making diagnosis and research safer and clearer.
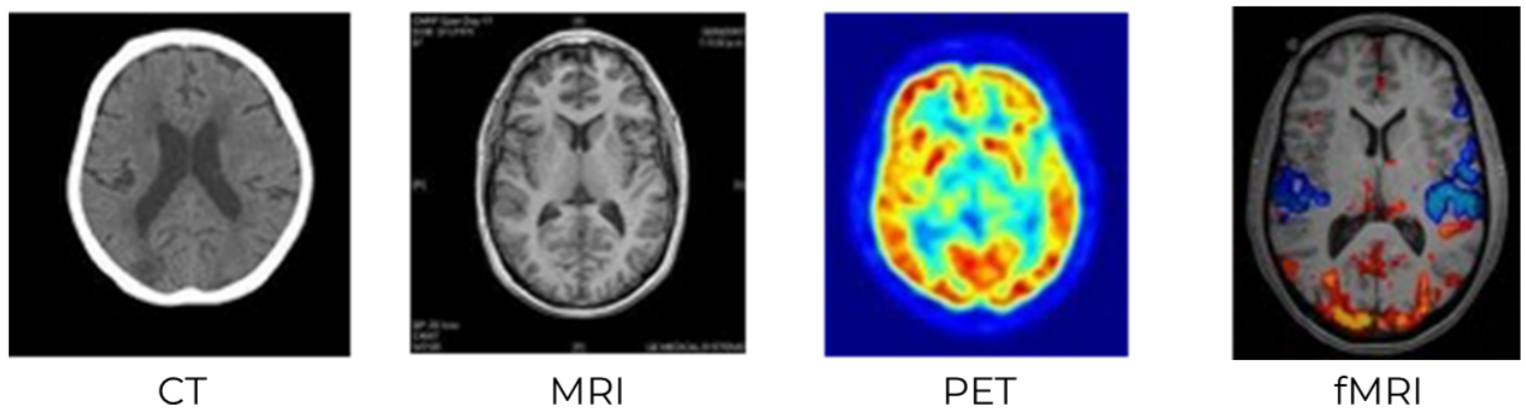
🌟 1. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
What It Is
- A scan using strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create high-resolution images of brain structure.
How It Works
- Hydrogen atoms in tissues align with the magnetic field.
- Radio waves disturb this alignment.
- As atoms return to normal, they emit signals.
- A computer converts these signals into sharp anatomical images.
What It Shows
- Tumours, inflammation, strokes and other brain damage.
- Clear contrast between grey and white matter.
Why It’s Useful
- No ionising radiation.
- Great for detailed brain anatomy.
🌟 2. fMRI (Functional MRI)
What It Is
- A type of MRI that tracks brain activity by monitoring blood oxygen levels.
How It Works
- Active brain areas need more oxygen.
- More oxygenated blood flows to those regions.
- fMRI detects these changes and creates coloured activity maps.
What It Shows
- Regions involved in vision, movement, speech and emotion.
- Activity patterns during tasks, memory or learning studies.
Why It’s Useful
- Non-invasive and real-time.
- Great for pre-surgery brain mapping.
🌟 3. PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
What It Is
- A scan that uses radioactive tracers, usually glucose labelled with a positron emitter, to show metabolic activity.
How It Works
- The tracer releases positrons.
- These collide with electrons, producing gamma rays.
- The scanner detects these rays to map metabolic hotspots.
What It Shows
- Early signs of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Cancers and abnormal brain metabolism.
Why It’s Useful
- Very sensitive to biochemical changes.
- Can detect problems even before structural damage is visible.
🌟 4. CT (Computed Tomography)
What It Is
- An imaging method using X-rays from many angles to create cross-sectional brain slices.
How It Works
- Multiple X-ray images are taken rapidly.
- A computer assembles these into 2D or 3D scans.
What It Shows
- Bleeding, swelling, fractures and tumours.
- Quick detection of strokes.
Why It’s Useful
- Very fast, ideal for emergencies.
- Useful for patients who cannot stay still for MRI.
| Technique | Shows | Key Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI | Brain structure | Magnetic fields and radio waves | Tumours, strokes, inflammation |
| fMRI | Brain function | Blood oxygen level changes | Mapping active brain areas |
| PET | Metabolic activity | Radioactive glucose tracer | Early disease detection |
| CT | Structural slices | X-rays from multiple angles | Emergency diagnosis |
📦 Quick Recap
MRI gives sharp structural images using magnetic fields.
fMRI shows active brain areas by tracking oxygenated blood.
PET uses radioactive glucose to reveal metabolic activity and early disease.
CT uses X-rays for quick, clear brain slices, ideal in emergencies.
MRI gives sharp structural images using magnetic fields.
fMRI shows active brain areas by tracking oxygenated blood.
PET uses radioactive glucose to reveal metabolic activity and early disease.
CT uses X-rays for quick, clear brain slices, ideal in emergencies.
