Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.16 Brain Disease- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.16 Brain Disease- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.16 Brain Disease- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.16 understand how imbalances in certain naturally-occurring brain chemicals can contribute to ill health, including dopamine in Parkinson’s disease and serotonin in depression, and to the development of new drugs
Brain Chemicals, Ill Health and Drug Development
🌱 Introduction
The brain uses chemical messengers called neurotransmitters to pass signals between neurones. When their levels become too low or too high, brain function becomes disrupted and diseases can develop. Two key examples are dopamine and serotonin.
📍 Dopamine and Parkinson’s Disease
What Dopamine Normally Does
- Controls smooth, coordinated movement.
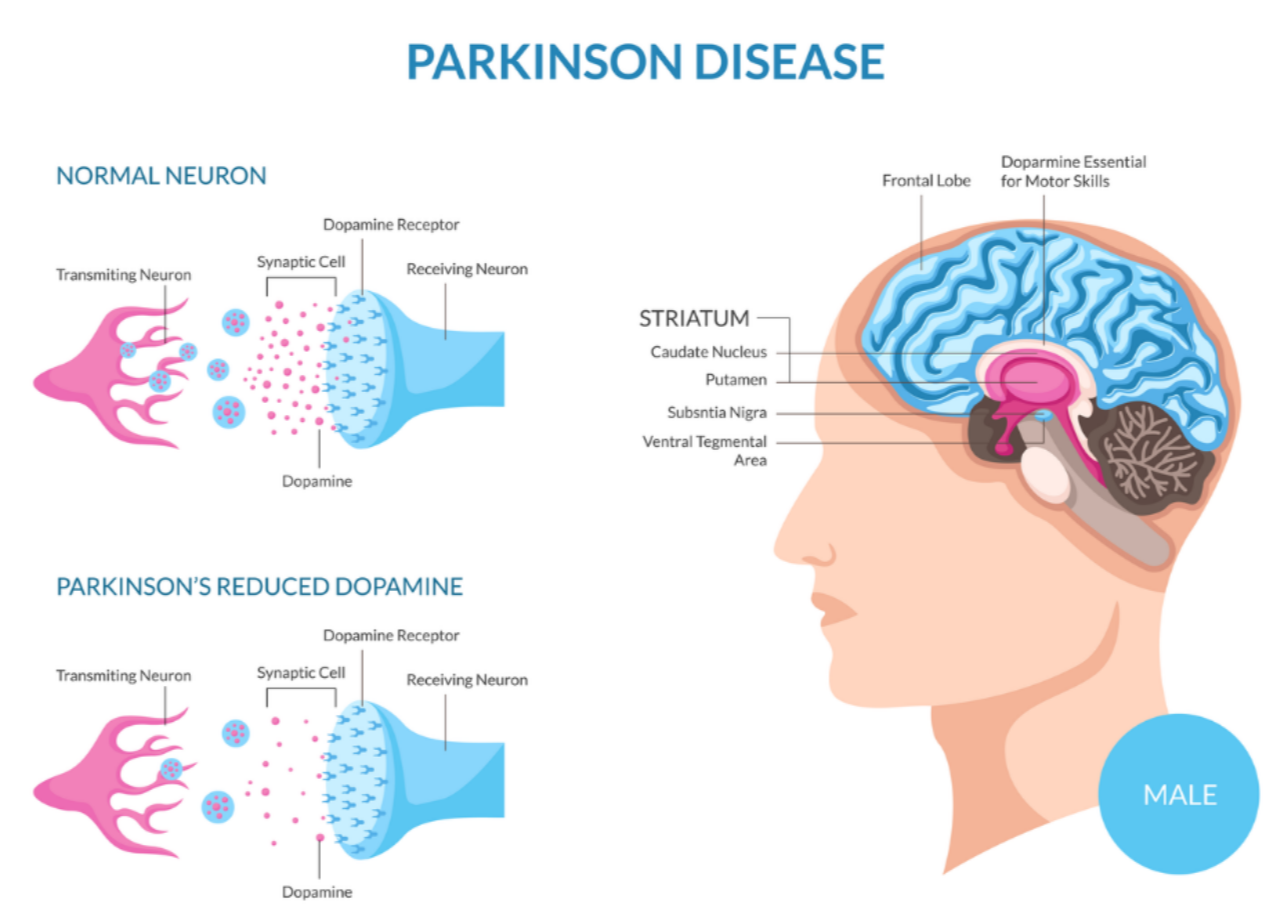 Released by neurones in the basal ganglia, especially the substantia nigra.
Released by neurones in the basal ganglia, especially the substantia nigra.
What Goes Wrong in Parkinson’s
- Dopamine-producing neurones degenerate and die.
- Leads to very low dopamine levels.
- Motor pathways cannot operate smoothly.
Symptoms
- Tremors in hands
- Muscle stiffness
- Slow movement
- Difficulty starting or stopping movement
- Poor balance
How This Led to New Drugs
- Lack of dopamine inspired drugs that increase dopamine levels.
- Main treatment: L-DOPA, converted into dopamine by the brain.
- Often combined with drugs that slow L-DOPA breakdown.
- Some drugs mimic dopamine’s action (dopamine agonists).
💊 Serotonin and Depression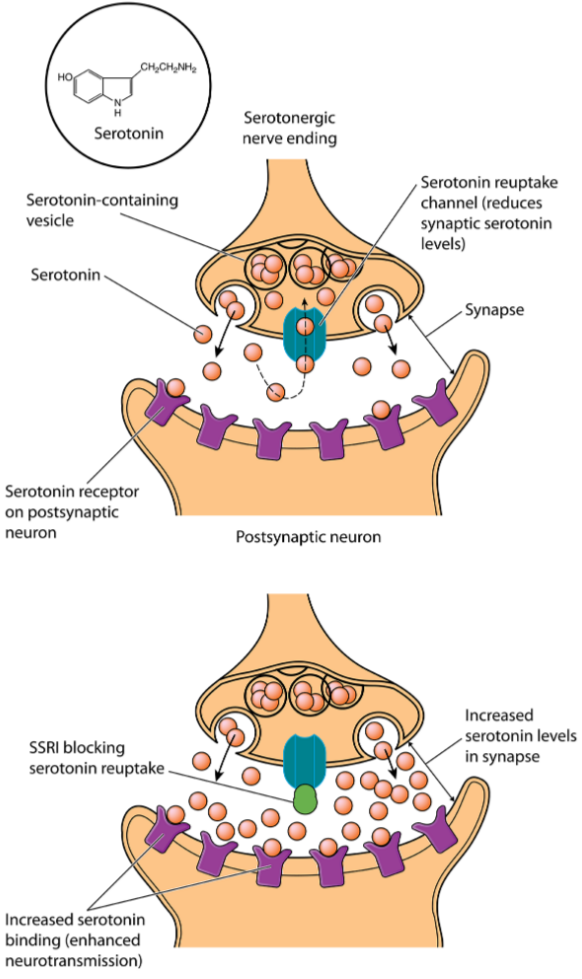
What Serotonin Normally Does
- Regulates mood, sleep, appetite and emotions.
- Low levels linked to low mood.
What Goes Wrong in Depression
- Serotonin levels in synapses drop too low.
- Weakens signalling in brain regions linked to mood, memory and reward.
Symptoms
- Persistent sadness
- Loss of motivation
- Sleep disturbances
- Low energy
- Anxiety
How This Led to New Drugs
- Goal is to increase serotonin levels in synapses.
- Most common treatment: SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors).
- SSRIs block reuptake pumps so serotonin stays longer in the synapse.
- Strengthens signalling and improves mood.
⭐ Why Understanding Brain Chemicals Helps Drug Development
- Reveals which neurotransmitters are too low or too high.
- Helps design targeted drugs that:
- Replace the missing chemical
- Prevent its breakdown
- Increase its release
- Or mimic its action
- Leads to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
📦 Quick Recap
Dopamine low → Parkinson’s disease
Movement problems
Treated with L-DOPA and dopamine-boosting drugs
Serotonin low → Depression
Low mood and sleep issues
Treated with SSRIs to keep serotonin in synapses
Dopamine low → Parkinson’s disease
Movement problems
Treated with L-DOPA and dopamine-boosting drugs
Serotonin low → Depression
Low mood and sleep issues
Treated with SSRIs to keep serotonin in synapses
