Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.18 Recombinant DNA- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.18 Recombinant DNA- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.18 Recombinant DNA- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.18 understand how recombinant DNA can be produced, including the roles of restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase
Recombinant DNA Production
🌱 Introduction
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) is DNA formed by combining genetic material from different sources. It allows scientists to produce specific proteins or modify organisms.
🔍 Key Terms
- Vector: DNA molecule used to carry foreign gene into a host (e.g., plasmid).
- Insert: The gene of interest that we want to clone or express.
- Host: Organism (bacteria, yeast) that receives the recombinant DNA.
🌟 Steps to Produce Recombinant DNA
1. Isolate the Gene of Interest
- DNA containing the target gene is extracted.
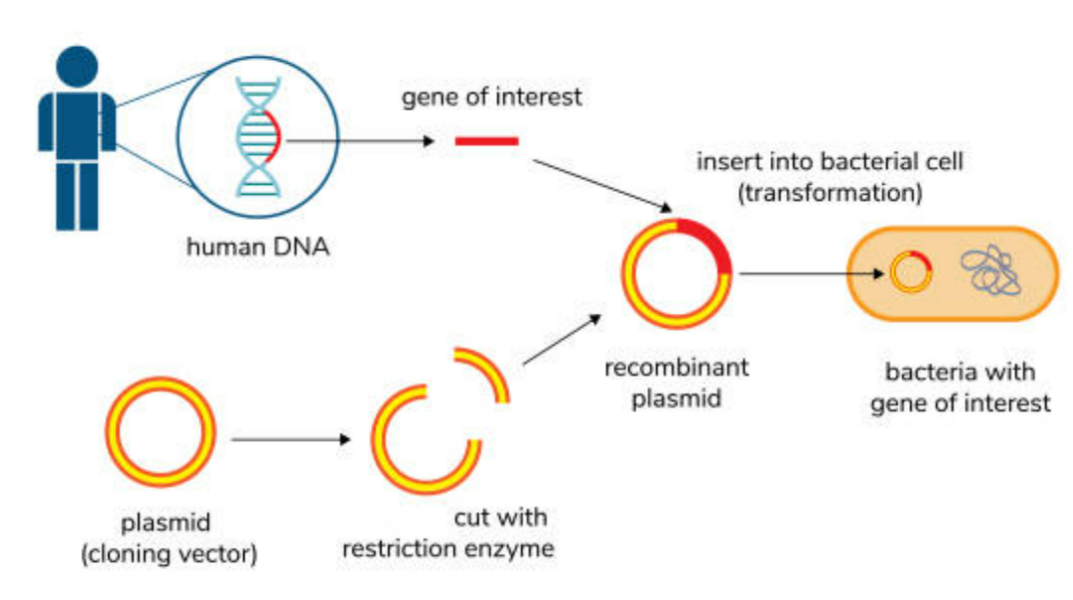
- The gene is cut out using restriction endonucleases.
2. Cut the Vector DNA
- A plasmid (vector) is cut using the same restriction endonuclease.
- This ensures matching sticky ends for the insert.
3. Join Gene and Vector
- The gene is inserted into the plasmid.
- DNA ligase seals the sugar-phosphate backbone, forming stable recombinant DNA.
4. Introduce rDNA into Host
- Recombinant plasmid is inserted into a host organism (e.g., E. coli) using transformation techniques.
- Host replicates and expresses the foreign gene.
Roles of Key Enzymes
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Restriction Endonuclease | Cuts DNA at specific sequences → creates sticky or blunt ends |
| DNA Ligase | Seals the DNA backbone → joins gene and vector to form rDNA |
Example
- Human insulin production:
- Insulin gene cut from human DNA.
- Plasmid vector cut with same enzyme.
- Gene joined to plasmid using DNA ligase → recombinant plasmid.
- Plasmid inserted into E. coli, which produces insulin.
📦 Quick Recap
Recombinant DNA: DNA from two different sources.
Restriction enzymes: cut DNA at specific sites.
DNA ligase: joins DNA fragments to make stable rDNA.
Vector: carries foreign gene into host.
Host: expresses the foreign gene to produce desired protein.
Key concept: “cut with same enzyme → join with ligase → host expresses”.
Recombinant DNA: DNA from two different sources.
Restriction enzymes: cut DNA at specific sites.
DNA ligase: joins DNA fragments to make stable rDNA.
Vector: carries foreign gene into host.
Host: expresses the foreign gene to produce desired protein.
Key concept: “cut with same enzyme → join with ligase → host expresses”.
