Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.5 Myelination & Saltatory Conduction- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.5 Myelination & Saltatory Conduction- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.5 Myelination & Saltatory Conduction- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.5 understand the role of myelination in saltatory conduction
Role of Myelination in Saltatory Conduction
🌱 Introduction
Myelin is a fatty sheath produced by Schwann cells around axons in the PNS (or oligodendrocytes in CNS).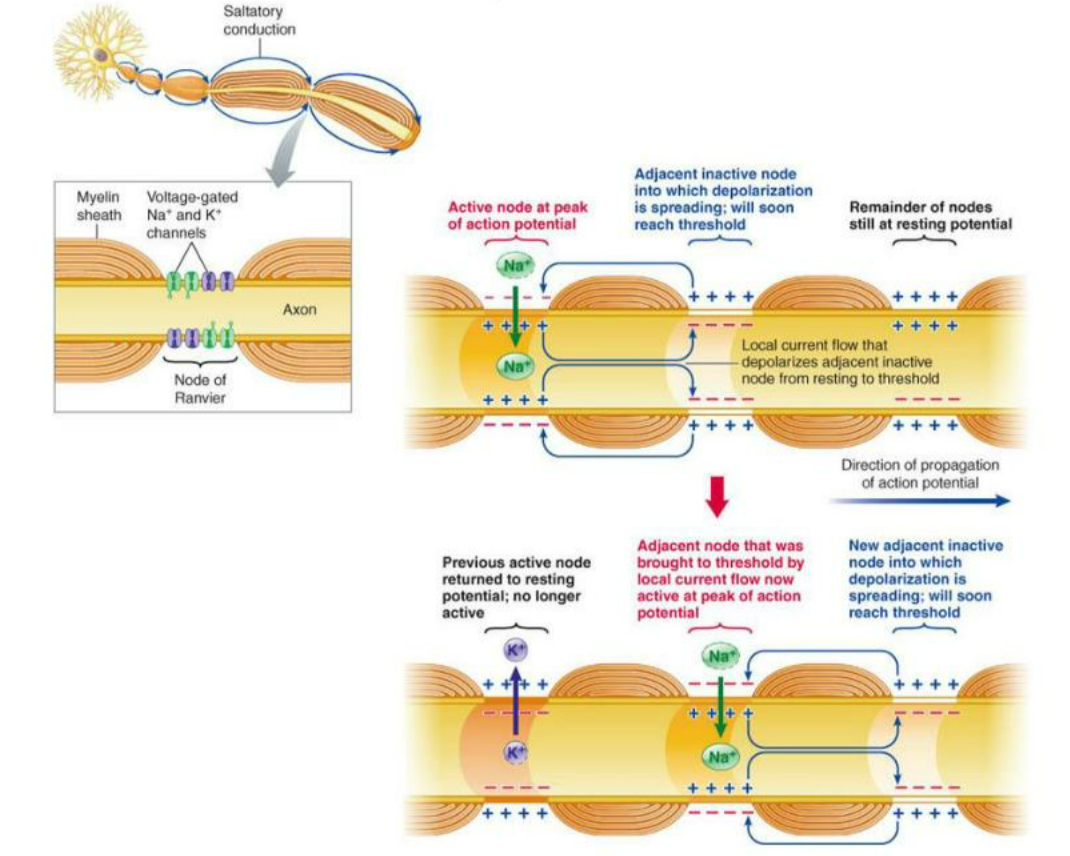 It insulates the axon and allows impulses to travel faster and more efficiently.
It insulates the axon and allows impulses to travel faster and more efficiently.
🔍 Key Features
1. Structure
- Axon is wrapped in layers of myelin.
- Nodes of Ranvier: small gaps between myelin segments.
- Axon membrane exposed only at nodes.
2. How Saltatory Conduction Works
- Action potential occurs only at the nodes.
- Depolarisation jumps from one node to the next instead of moving continuously.
- Reduces the number of times ions cross the membrane → faster impulse.
3. Advantages of Myelination
- Speeds up conduction: impulses travel much faster than in unmyelinated axons.
- Energy efficient: fewer ions moved → less ATP used by sodium-potassium pumps.
- Prevents signal loss: insulation keeps the impulse strong over long distances.
📌 Summary Table
| Feature | Myelinated Axon | Unmyelinated Axon |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction type | Saltatory | Continuous |
| Speed | Fast (100 m/s approx.) | Slow (1–10 m/s) |
| Energy use | Low | High |
| Signal strength | Maintained | Can weaken over distance |
📦 Quick Recap
Myelin = fatty insulation around axon.
Nodes of Ranvier = gaps where depolarisation occurs.
Saltatory conduction = impulse jumps node to node → faster + energy-efficient.
Myelination allows rapid, strong, and efficient nerve signalling.
Myelin = fatty insulation around axon.
Nodes of Ranvier = gaps where depolarisation occurs.
Saltatory conduction = impulse jumps node to node → faster + energy-efficient.
Myelination allows rapid, strong, and efficient nerve signalling.
