Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.6 Synapses & Neurotransmitters- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.6 Synapses & Neurotransmitters- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.6 Synapses & Neurotransmitters- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.6 (i) know the structure and function of synapses in nerve impulse transmission, including the role of neurotransmitters and acetylcholine
(ii) understand how the pupil dilates and contracts
Synapses and Nerve Impulse Transmission
🌱 (i) Structure and Function of Synapses
What is a Synapse?
- A junction between two neurones (pre-synaptic → post-synaptic) or a neurone and effector.
- Allows one-way transmission of impulses.
Structure of a Chemical Synapse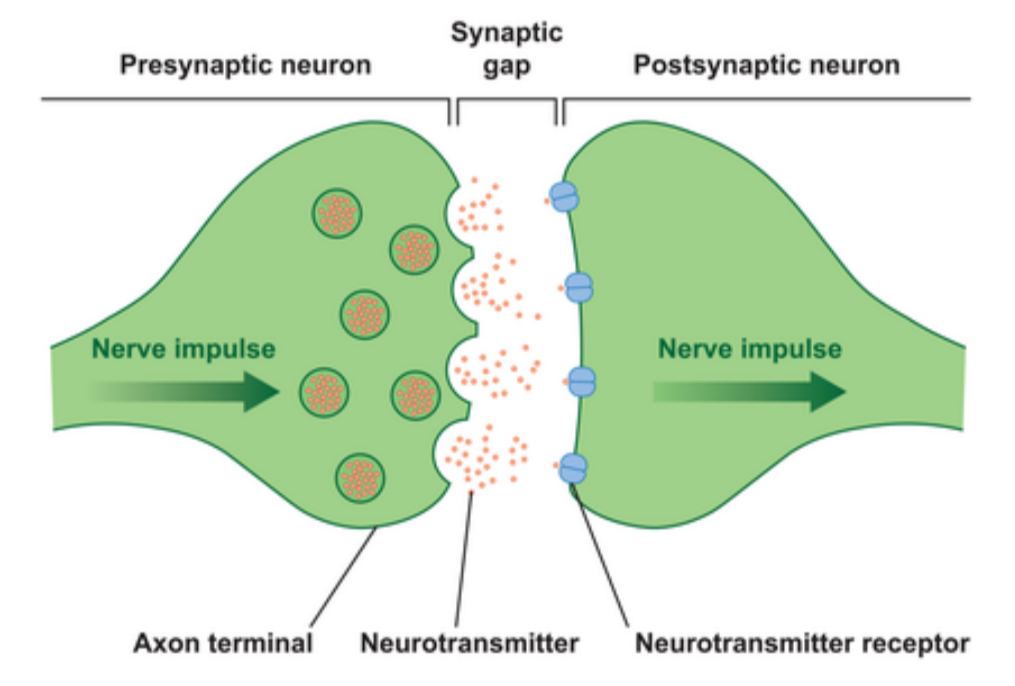
- Pre-synaptic neurone terminal: contains synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters (e.g., acetylcholine).
- Synaptic cleft: tiny gap between pre- and post-synaptic membranes.
- Post-synaptic membrane: has receptor proteins for neurotransmitters.
How Transmission Happens
- Action potential reaches pre-synaptic terminal.
- Voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels open → Ca²⁺ enters.
- Vesicles release acetylcholine (ACh) into the synaptic cleft.
- ACh binds to receptors on the post-synaptic membrane.
- Sodium channels open → depolarisation occurs in post-synaptic neurone.
- Impulse continues if threshold is reached.
- ACh is broken down by acetylcholinesterase → stops signal.
Key Points
- Synapses ensure unidirectional flow.
- Allow amplification or inhibition of signals.
- Acetylcholine is a common neurotransmitter at neuromuscular junctions.
👁️ (ii) Pupil Reflex: Dilation and Contraction
What is the Pupil Reflex?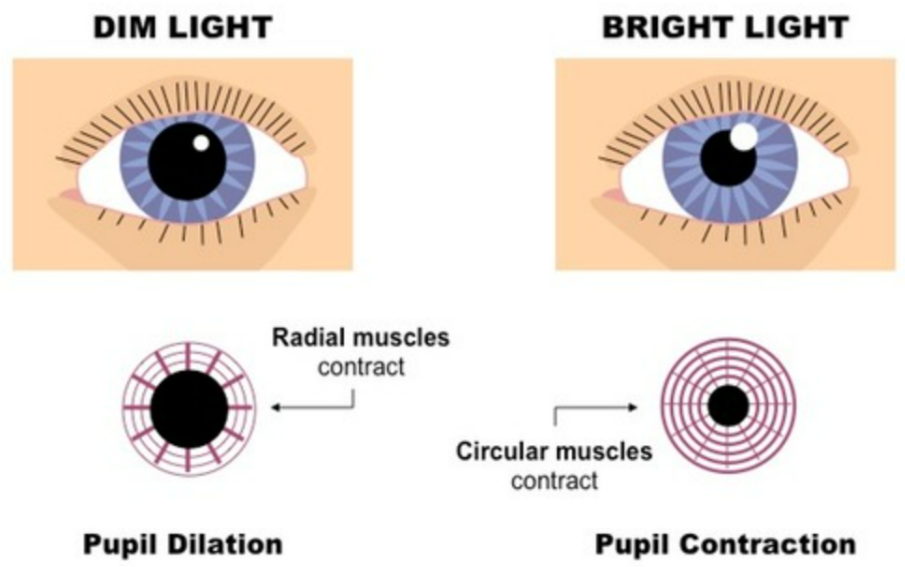
- Iris controls pupil size in response to light intensity.
- Regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
Contraction (Pupillary Light Reflex)
- Bright light → circular muscles of iris contract → pupil gets smaller (constriction).
- Parasympathetic nervous system controls this.
Dilation
- Dim light → radial muscles of iris contract → pupil gets larger (dilation).
- Sympathetic nervous system controls this.
🔹 Summary Table
| Feature | Constriction | Dilation |
|---|---|---|
| Light level | Bright | Dim |
| Iris muscles | Circular | Radial |
| Nervous control | Parasympathetic | Sympathetic |
| Pupil size | Small | Large |
📦 Quick Recap
Synapses:
Junction between neurones or neurone & effector.
ACh released → binds to receptors → impulse continues.
Broken down by acetylcholinesterase.
Pupil Reflex:
Bright light → circular muscles contract → pupil constricts.
Dim light → radial muscles contract → pupil dilates.
Controlled by autonomic nervous system (parasympathetic vs sympathetic).
Synapses:
Junction between neurones or neurone & effector.
ACh released → binds to receptors → impulse continues.
Broken down by acetylcholinesterase.
Pupil Reflex:
Bright light → circular muscles contract → pupil constricts.
Dim light → radial muscles contract → pupil dilates.
Controlled by autonomic nervous system (parasympathetic vs sympathetic).
