Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.7 The Effects of Drugs on Nervous Transmission- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.7 The Effects of Drugs on Nervous Transmission- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -8.7 The Effects of Drugs on Nervous Transmission- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 8.7 understand how the effects of drugs can be caused by their influence on nerve impulse transmission, illustrated by nicotine, lidocaine and cobra venom alpha toxin, the use of L-DOPA in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and the action of MDMA (ecstasy)
Effects of Drugs on Nerve Impulse Transmission
🌱 Introduction
Drugs can alter nerve impulses by affecting:
- Neurotransmitter release
- Neurotransmitter receptors
- Ion channel activity
This changes how signals are sent in the nervous system.
1. Nicotine
- Found in tobacco.
- Mimics acetylcholine (ACh) → binds to nicotinic receptors on post-synaptic membrane.
- Effect: stimulates neurones, increases alertness and heart rate.
- Can cause addiction because it continually stimulates reward pathways.
2. Lidocaine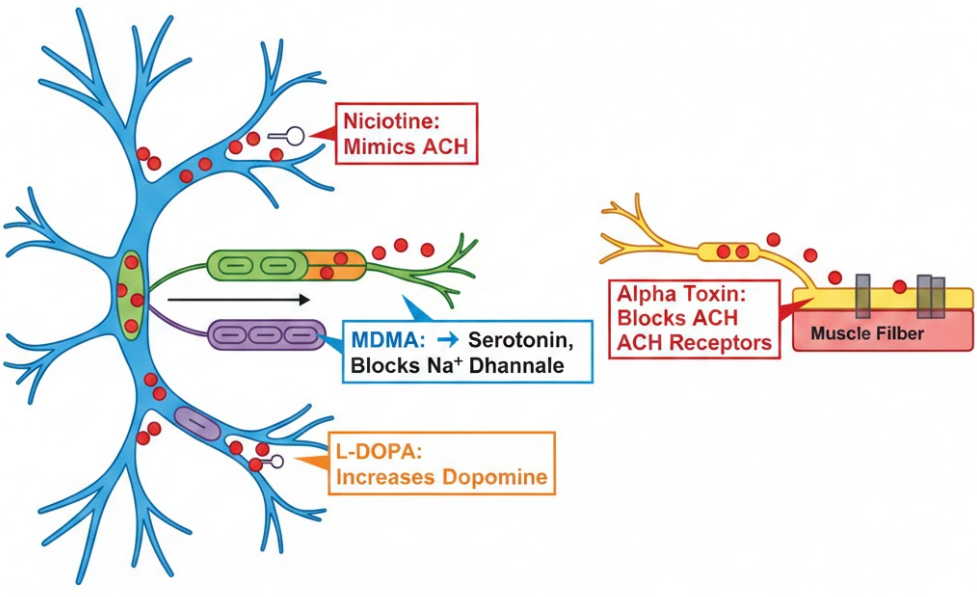
- Local anaesthetic.
- Blocks voltage-gated Na⁺ channels in neurones.
- Effect: prevents depolarisation → stops impulse transmission.
- Outcome: temporary loss of sensation (numbness) in specific area.
3. Cobra Venom Alpha Toxin
- Neurotoxin.
- Binds to nicotinic ACh receptors at neuromuscular junction.
- Effect: prevents ACh from binding → muscles cannot contract.
- Outcome: paralysis, potentially fatal if respiratory muscles affected.
4. L-DOPA (Parkinson’s Disease Treatment)
- Parkinson’s disease: loss of dopaminergic neurones → reduced dopamine.
- L-DOPA = precursor of dopamine; crosses the blood-brain barrier.
- Effect: restores dopamine levels, improves movement and coordination.
5. MDMA (Ecstasy)
- Psychoactive drug.
- Increases serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline release.
- Effect: heightened mood, alertness, and euphoria.
- Excess use → depletes neurotransmitters, may cause anxiety, depression, or overheating.
📊 Summary Table
| Drug / Substance | Target | Effect on Nerve Transmission | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nicotine | Nicotinic ACh receptors | Stimulates post-synaptic neurone | Alertness, addiction |
| Lidocaine | Na⁺ channels | Blocks depolarisation | Numbness, pain relief |
| Cobra α-toxin | Nicotinic ACh receptors | Prevents ACh binding | Muscle paralysis |
| L-DOPA | Dopaminergic neurones | Increases dopamine | Improves Parkinson’s symptoms |
| MDMA | Serotonin/dopamine release | Increases neurotransmitters | Euphoria, mood changes |
📦 Quick Recap
Drugs can mimic, block, or enhance neurotransmitters.
Nicotine → stimulates ACh receptors.
Lidocaine → blocks Na⁺ channels → stops impulses.
Cobra venom α-toxin → blocks ACh receptors → paralysis.
L-DOPA → increases dopamine → treats Parkinson’s.
MDMA → boosts serotonin/dopamine → euphoria, potential neurotoxicity.
Drugs can mimic, block, or enhance neurotransmitters.
Nicotine → stimulates ACh receptors.
Lidocaine → blocks Na⁺ channels → stops impulses.
Cobra venom α-toxin → blocks ACh receptors → paralysis.
L-DOPA → increases dopamine → treats Parkinson’s.
MDMA → boosts serotonin/dopamine → euphoria, potential neurotoxicity.
