Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-1.12 Newton’s Third Law of Motion- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -1.12 Newton’s Third Law of Motion- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -1.12 Newton’s Third Law of Motion- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 1.12 know and understand Newton’s third law of motion and know the properties of pairs of forces in an interaction between two bodies
Newton’s Third Law of Motion and Properties of Interaction Pairs
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Newton’s third law states that:
“For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
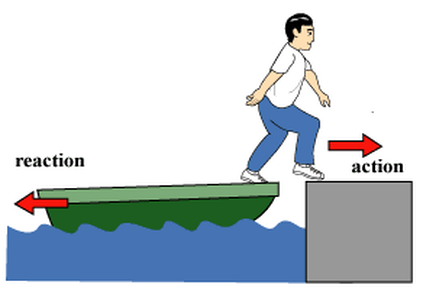
This law describes the forces that two bodies exert on each other during an interaction.
Key Statement in Physics Form:
If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B exerts an equal and opposite force on body A.
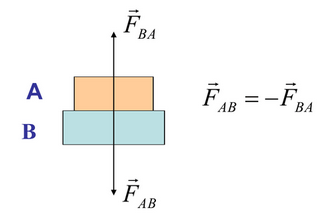
Symbolically:
\( \vec{F}_{AB} = -\vec{F}_{BA} \)
- \( \vec{F}_{AB} \) = force exerted by A on B
- \( \vec{F}_{BA} \) = force exerted by B on A
Properties of Newton’s Third Law Force Pairs
- The forces are equal in magnitude.
- The forces are opposite in direction.
- The forces act on two different bodies (never on the same body).
- The forces are of the same type (e.g., both gravitational, both normal, both magnetic).
- Both forces occur simultaneously, not one after the other.
Examples of Action–Reaction Pairs
![]()
- A book on a table:
- Book pushes the table down.
- Table pushes the book up (equal and opposite).
- A rocket launching:
- Rocket pushes gas downwards.
- Gas pushes rocket upwards.
- Walking:
- Foot pushes ground backwards.
- Ground pushes foot forward.
Common Misconceptions
- Action–reaction forces do NOT cancel out because they act on different bodies.
- They are not cause–effect; they occur simultaneously.
- Normal reaction is NOT the third-law pair of weight.
- Weight is Earth pulling object downward.
- Reaction pair: object pulls Earth upward.
Example (Easy)
A ball pushes down on the ground with a force of 50 N. What is the force exerted by the ground on the ball?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
By Newton’s third law, the ground pushes upward on the ball with a force of 50 N (equal in magnitude, opposite in direction).
Example (Medium)
A car’s wheels push backwards on the road with a force of \( 2500\, \mathrm{N} \). Identify the reaction force.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The road pushes the wheels forward with a force of \( 2500\, \mathrm{N} \).
These two forces form a Newton’s third law pair.
Example (Hard)
A person of mass 70 kg stands on the floor. The Earth pulls the person downward with a force of \( 686\, \mathrm{N} \). Identify the third-law pair and explain why the normal reaction from the floor is not the third-law pair of weight.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Weight pair:
Earth pulls person downward with \( 686\, \mathrm{N} \). Person pulls Earth upward with \( 686\, \mathrm{N} \).
Why normal reaction is NOT the third-law pair:
- Normal reaction acts on the person (from the floor).
- Weight acts on the person (from Earth).
- Therefore, they act on the same body → not a third-law pair.
- Third-law forces must act on different bodies.
