Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-1.17 Work- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -1.17 Work- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -1.17 Work- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 1.17 be able to use the equation for work $\Delta W = F\Delta s$, including calculations when the force is not along the line of motion
Work Done \( \Delta W = F \Delta s \) (Including Forces Not Along the Line of Motion)
Definition of Work
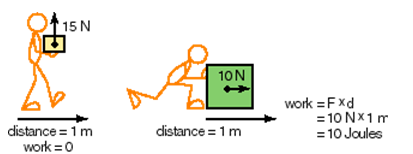
Work is done when a force causes a displacement in the direction of the force.
\( \Delta W = F \Delta s \)
- \( F \) = force applied (N)
- \( \Delta s \) = displacement in the direction of the force (m)
- Unit of work: joule (J)
When the Force Is Not Along the Line of Motion
If the force is applied at an angle \( \theta \) to the direction of motion, only the component of the force parallel to the displacement does work.
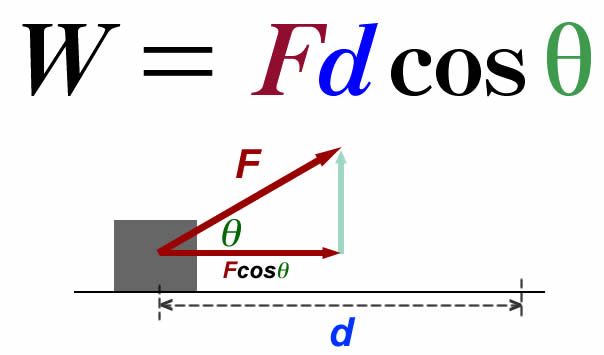
\( \Delta W = F \Delta s \cos\theta \)
- \( F\cos\theta \) is the component of force in the direction of motion.
- If \( \theta = 0^\circ \): full force does work.
- If \( \theta = 90^\circ \): no work is done (e.g., carrying a bag horizontally while gravity acts downward).
- If \( \theta > 90^\circ \): the force opposes the motion → work done is negative.
Key Points
![]()
- Negative work: force opposite to motion (e.g., friction).
- Zero work: force perpendicular to motion (e.g., centripetal force in circular motion).
- Work depends on displacement in direction of force, not path travelled.
- Work done transfers energy.
Example (Easy)
A constant force of \( 12\, \mathrm{N} \) moves an object \( 4\, \mathrm{m} \) in the direction of the force. Find the work done.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( \Delta W = F \Delta s = 12 \times 4 = 48\, \mathrm{J} \)
Example (Medium)
A \( 50\, \mathrm{N} \) force is applied at \( 60^\circ \) to the direction of motion. The object moves \( 3.0\, \mathrm{m} \). Calculate the work done.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use the parallel component \( F \cos\theta \).
\( \Delta W = F \Delta s \cos\theta = 50 \times 3.0 \times \cos60^\circ \)
\( = 50 \times 3.0 \times 0.5 = 75\, \mathrm{J} \)
Example (Hard)
A box is pulled using a rope making an angle of \( 35^\circ \) with the horizontal. The tension in the rope is \( 120\, \mathrm{N} \) and the box moves \( 8\, \mathrm{m} \) horizontally. Find:
- (a) Work done by the pulling force
- (b) Work done against friction if friction = \( 40\, \mathrm{N} \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) Work done by pulling force:
\( \Delta W = F \Delta s \cos\theta = 120 \times 8 \times \cos35^\circ \)
\( = 120 \times 8 \times 0.819 = 787\, \mathrm{J} \) (approx.)
(b) Work done against friction:
\( \Delta W_{\text{friction}} = F_{\text{fr}} \Delta s = 40 \times 8 = 320\, \mathrm{J} \)
This work is negative because friction opposes motion.
