Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-2.13 Refraction & Refractive Index- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.13 Refraction & Refractive Index- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.13 Refraction & Refractive Index- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- know and understand that at the interface between medium 1 and medium 2 \(n_1\sin\theta_1=n_2\sin\theta_2\) where refractive index is \(n=\dfrac{c}{v}\)
Snell’s Law at a Boundary and Refractive Index \( n = \dfrac{c}{v} \)
When a wave passes from one transparent medium into another (e.g., air → glass), it changes speed, causing refraction. Snell’s law describes the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction.
Snell’s Law
At the interface between medium 1 and medium 2:
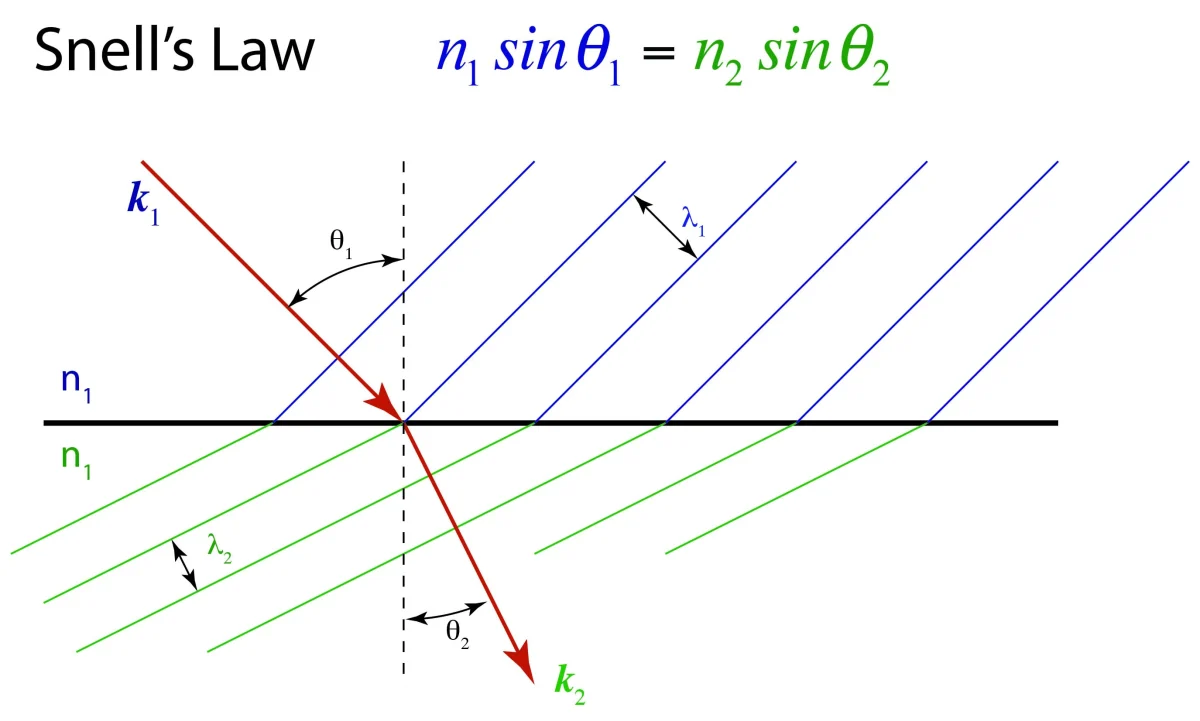
$ n_1 \sin\theta_1 = n_2 \sin\theta_2 $
- \( n_1 \) = refractive index of medium 1
- \( n_2 \) = refractive index of medium 2
- \( \theta_1 \) = angle of incidence
- \( \theta_2 \) = angle of refraction
Meaning:
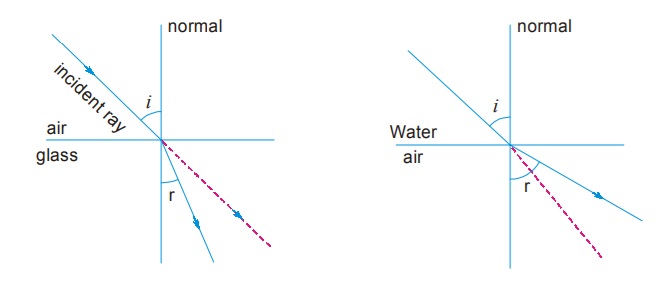
- If light slows down → it bends towards the normal.
- If light speeds up → it bends away from the normal.
- Refraction only occurs when wave speed changes.
Refractive Index
The refractive index of a medium is defined as:
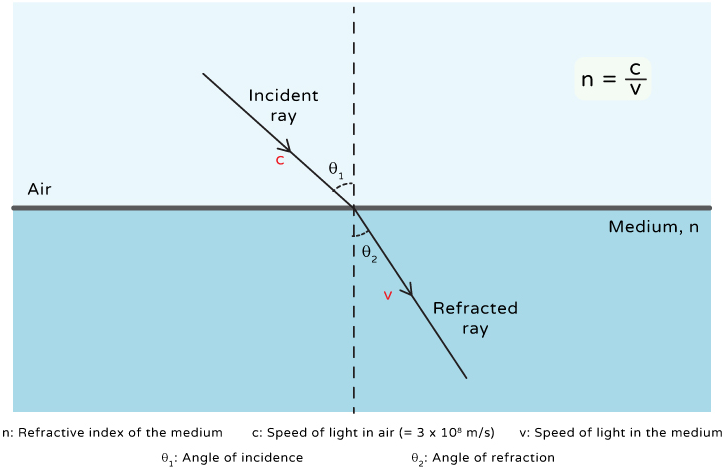
$ n = \frac{c}{v} $
- \( n \) = refractive index (no units)
- \( c \) = speed of light in vacuum (\(3.00\times 10^8 \,\mathrm{m\,s^{-1}}\))
- \( v \) = speed of light in the medium
Important: The refractive index is always ≥ 1 because light slows down in any medium.
Using Refractive Index in Snell’s Law
At a boundary:
$ \frac{c}{v_1}\sin\theta_1 = \frac{c}{v_2}\sin\theta_2 $
Simplifies to:
$ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\sin\theta_2} = \frac{v_1}{v_2} $
Light bends towards slower medium (higher refractive index).
Physical Interpretation
- Refraction occurs because wavelength changes when wave speed changes.
- Frequency stays the same when crossing a boundary.
- Refractive index describes optical density of medium.
- Higher \( n \) means wave travels slower.
Example (Easy)
A light ray enters glass from air. Given \( n_{\text{air}} = 1.00 \) and \( n_{\text{glass}} = 1.50 \), find the angle of refraction if the incident angle is \( 30^\circ \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
$ n_1 \sin\theta_1 = n_2 \sin\theta_2 $
$ 1.00 \sin 30^\circ = 1.50 \sin\theta_2 $
$ 0.5 = 1.50 \sin\theta_2 $
$ \sin\theta_2 = \frac{0.5}{1.50} = 0.333 $
$ \theta_2 \approx 19.5^\circ $
The light bends towards the normal.
Example (Medium)
The speed of light in a liquid is \( 2.00\times10^8 \,\mathrm{m\,s^{-1}} \). Find the refractive index.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
$ n = \frac{c}{v} = \frac{3.00\times10^8}{2.00\times10^8} = 1.5 $
Refractive index = 1.5
Example (Hard)
Light passes from medium A into medium B. A student measures: $ \theta_1 = 40^\circ,\quad \theta_2 = 25^\circ $ Find the ratio of refractive indices \( \frac{n_2}{n_1} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
$ n_1\sin\theta_1 = n_2\sin\theta_2 $ $ \frac{n_2}{n_1} = \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\sin\theta_2} $ $ = \frac{\sin 40^\circ}{\sin 25^\circ} = \frac{0.643}{0.423} \approx 1.52 $
Medium B has 1.52 times higher refractive index.
