Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-2.14 Critical Angle- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.14 Critical Angle- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.14 Critical Angle- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- be able to calculate critical angle using \(\sin C=\dfrac{1}{n}\)
Critical Angle and Total Internal Reflection \( \sin C = \frac{1}{n} \)
When light travels from a denser medium (higher refractive index) to a less dense medium (lower refractive index), the angle of refraction increases. Beyond a certain incident angle, refraction no longer occurs — the light is totally reflected. This incident angle is the critical angle.
What is the Critical Angle?
The critical angle \( C \) is the angle of incidence in a denser medium for which the angle of refraction is \( 90^\circ \).
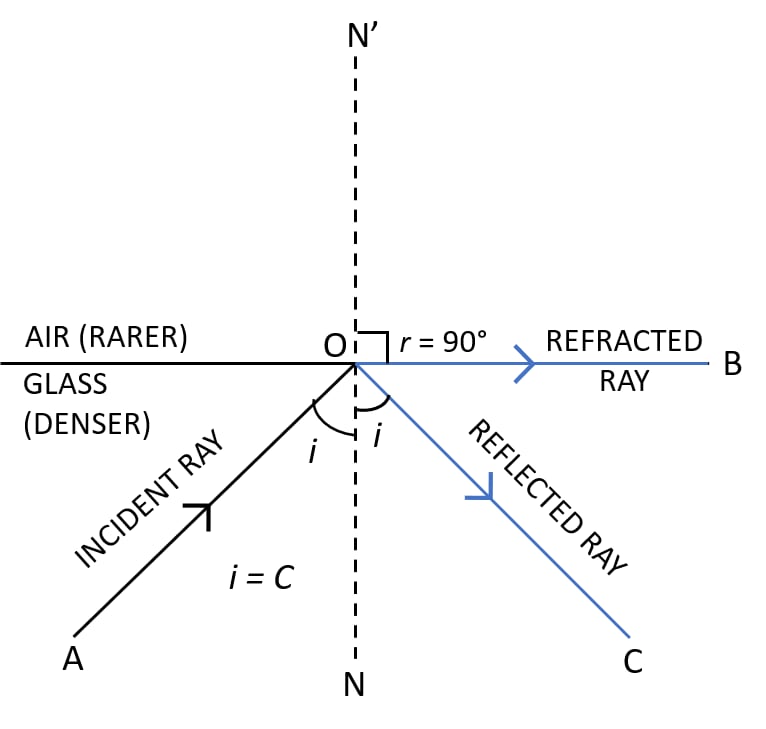
Occurs only when:
- \( n_1 > n_2 \) (light going from denser to rarer medium)
- Refracted ray travels along the boundary
Formula for the Critical Angle
From Snell’s law:
$ n_1 \sin C = n_2 \sin 90^\circ $
Since \( \sin 90^\circ = 1 \), and if the less dense medium is air \( (n_2 = 1) \):
$ \sin C = \frac{1}{n} $
- \( C \) = critical angle
- \( n \) = refractive index of the denser medium
Total Internal Reflection (TIR)
Total internal reflection occurs when:
- Light travels from higher \( n \) → lower \( n \)
- Angle of incidence > critical angle
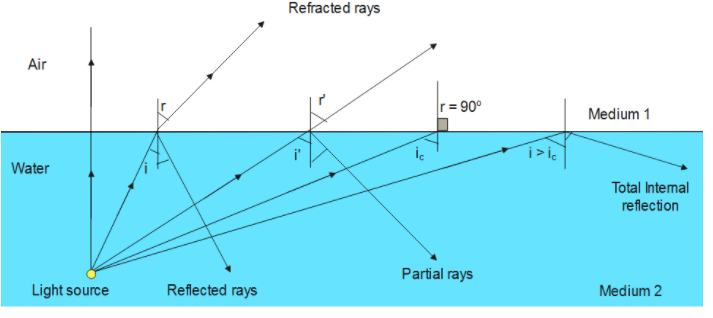
Effects:
- No refracted ray
- All light is reflected back into the denser medium
- Reflection obeys the normal law of reflection
Applications:
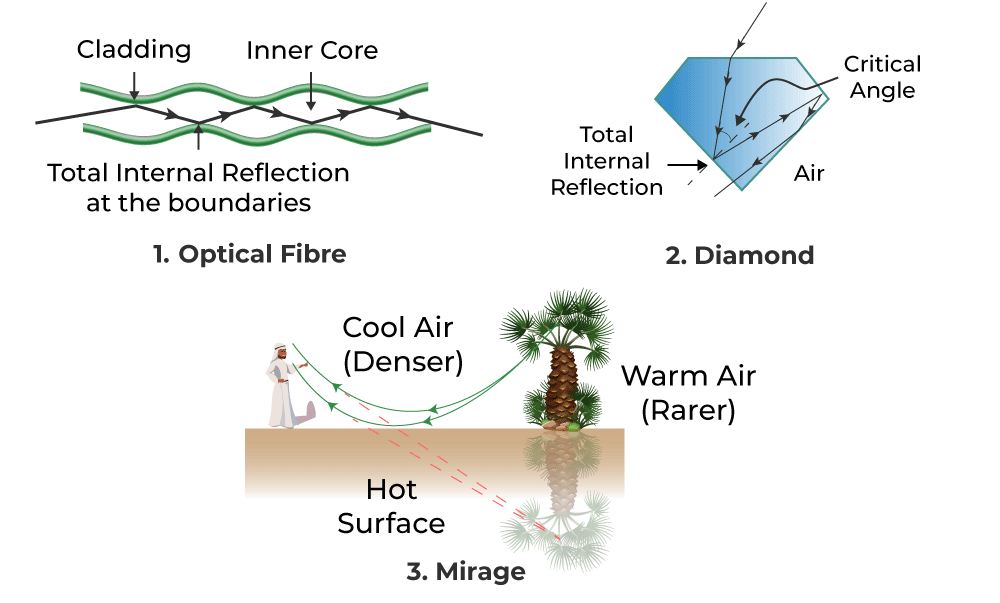
- Optical fibres
- Endoscopes
- Prism binoculars
- Diamond sparkle (high refractive index → small critical angle)
Using \( \sin C = \frac{1}{n} \)
Given the refractive index of a medium, the critical angle can be calculated by:
$ C = \sin^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{n}\right) $
Notes:
- Applies only when light is leaving the denser medium.
- If \( n \leq 1 \), no critical angle exists.
- Higher refractive index → smaller critical angle.
Example (Easy)
Diamond has refractive index \( n = 2.42 \). Find the critical angle at the diamond–air boundary.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
$ \sin C = \frac{1}{n} = \frac{1}{2.42} = 0.413 $
$ C = \sin^{-1}(0.413) \approx 24.4^\circ $
Critical angle ≈ \( 24^\circ \)
Example (Medium)
A transparent plastic has refractive index \( n = 1.50 \). Calculate the critical angle.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
$ \sin C = \frac{1}{1.50} = 0.667 $ $ C = \sin^{-1}(0.667) \approx 41.8^\circ $
Critical angle ≈ \( 42^\circ \)
Example (Hard)
A ray travels from glass (refractive index 1.60) into water (refractive index 1.33). Find the critical angle at this boundary.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The formula \( \sin C = \frac{1}{n} \) applies only when the less dense medium is air. Here we must use Snell’s law because both media have refractive indices > 1.
Step 1: For critical angle, refracted angle = 90°
$ n_1 \sin C = n_2 \sin 90^\circ $
$ 1.60 \sin C = 1.33 $
Step 2: Solve
$ \sin C = \frac{1.33}{1.60} = 0.831 $ $ C = \sin^{-1}(0.831) \approx 56.3^\circ $
Critical angle ≈ \( 56^\circ \)
