Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-2.29 The Electronvolt- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.29 The Electronvolt- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -2.29 The Electronvolt- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- be able to use the electronvolt (eV) to express small energies
The Electronvolt (eV)
The electronvolt (eV) is a unit used to measure very small energies, especially in quantum physics, atomic physics, and particle physics. It is much more convenient than the joule when working with photons, electrons, and nuclear processes.
Definition of the Electronvolt
An electronvolt is the energy gained by an electron when it is accelerated through a potential difference of \( 1\ \mathrm{V} \).
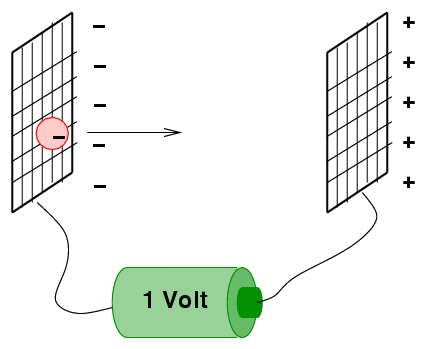
\( 1\ \mathrm{eV} = 1.6\times10^{-19}\ \mathrm{J} \)
- It is a very small amount of energy.
- Used to express photon energies, ionisation energies, atomic energy levels, and nuclear energies.
Why Use the Electronvolt?
- Expressing energies in joules gives extremely small numbers (e.g., \( 10^{-19}\ \mathrm{J} \)).
- Using eV gives neat, manageable values (e.g., \( 3\ \mathrm{eV} \), \( 10\ \mathrm{eV} \)).
- Much more intuitive for atomic-scale energies.
Examples of typical energy values:
- Visible light photons: \( 1.5\ \text{eV} \) to \( 3.5\ \text{eV} \)
- Ionisation energy of hydrogen: \( 13.6\ \text{eV} \)
- X-ray photons: \( 1000\ \text{eV} \) to \( 10^{5}\ \text{eV} \)
- Nuclear energies: MeV range
Converting Between Joules and Electronvolts
To convert from eV to J:
\( E(\mathrm{J}) = E(\mathrm{eV}) \times 1.6\times10^{-19} \)
To convert from J to eV:
\( E(\mathrm{eV}) = \dfrac{E(\mathrm{J})}{1.6\times10^{-19}} \)
Relation to Ionisation and Photon Energies
- Most atomic transitions involve a few eV.
- Photon energy equation \( E = hf \) often gives results in \( 10^{-19}\ \mathrm{J} \), ideal to convert to eV.
- Electron kinetic energies in experiments (e.g., CRT, photoelectric effect) are often measured in eV.
Example (Easy)
Convert \( 5\ \mathrm{eV} \) to joules.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( E = 5 \times 1.6\times10^{-19} = 8.0\times10^{-19}\ \mathrm{J} \)
Example (Medium)
A photon has energy \( 3.2\times10^{-19}\ \mathrm{J} \). Convert this energy to eV.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( E(\mathrm{eV}) = \dfrac{3.2\times10^{-19}}{1.6\times10^{-19}} = 2\ \mathrm{eV} \)
Example (Hard)
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of \( 2500\ \mathrm{V} \). Find its energy in both joules and electronvolts.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
In electronvolts:
\( E = 2500\ \mathrm{eV} \)
In joules:
\( E = 2500 \times 1.6\times10^{-19} = 4.0\times10^{-16}\ \mathrm{J} \)
