Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-4.29 Induced E.M.F between Linked Coils- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -4.29 Induced E.M.F between Linked Coils- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -4.29 Induced E.M.F between Linked Coils- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand the factors affecting the e.m.f. induced in a coil when there is a change of current in another coil linked with this coil
Mutual Induction: Factors Affecting the Induced e.m.f.
When the current in one coil changes, the magnetic field it produces changes. If a second coil is linked by this changing magnetic field, an e.m.f. is induced in the second coil. This phenomenon is called mutual induction.
Faraday’s Law Applied to Mutual Induction
The magnitude of the induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage:
\( \varepsilon = \dfrac{\Delta (N\phi)}{\Delta t} \)
For mutual induction, the magnetic flux \( \phi \) in the secondary coil is produced by the current in the primary coil.
Role of Changing Current
- A steady current in the primary coil produces a constant magnetic field.
- A changing current produces a changing magnetic field.
- This changing field causes a change in flux linkage in the secondary coil.
- An induced e.m.f. appears only while the current is changing.
Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Induced e.m.f.
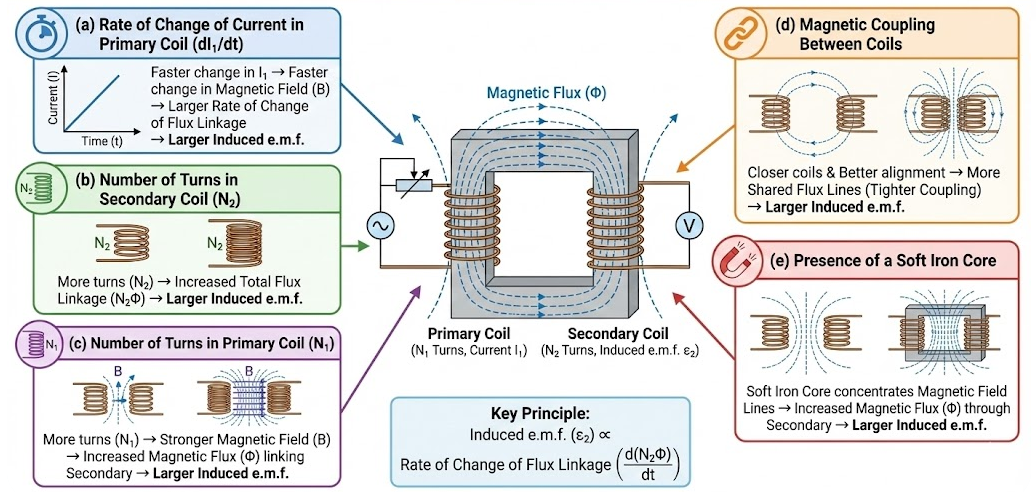
(a) Rate of Change of Current in the Primary Coil
- A faster change in current produces a faster change in magnetic field.
- This increases the rate of change of flux linkage.
- Hence, the induced e.m.f. is larger.
(b) Number of Turns in the Secondary Coil
- Flux linkage is given by \( N\phi \).
- Increasing the number of turns increases total flux linkage.
- This increases the induced e.m.f.
(c) Number of Turns in the Primary Coil
- More turns in the primary coil produce a stronger magnetic field.
- This increases the magnetic flux linking the secondary coil.
- The induced e.m.f. therefore increases.
(d) Magnetic Coupling Between the Coils
- Closer coils share more magnetic field lines.
- Better alignment increases the shared flux.
- Tighter coupling produces a larger induced e.m.f.
(e) Presence of a Soft Iron Core
- A soft iron core concentrates magnetic field lines.
- This increases magnetic flux through the secondary coil.
- The induced e.m.f. is increased.
Direction of the Induced e.m.f.
- The direction depends on whether the flux linkage is increasing or decreasing.
- Lenz’s law states that the induced e.m.f. opposes the change causing it.
Example (Easy)
The current in a primary coil is changed more rapidly. State and explain the effect on the induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The rate of change of magnetic field increases.
- The rate of change of flux linkage increases.
- The induced e.m.f. is larger.
Example (Medium)
Explain why inserting a soft iron core increases the induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Iron increases magnetic permeability.
- More magnetic field lines link the secondary coil.
- Flux linkage increases.
- The induced e.m.f. increases.
Example (Hard)
Two coils are placed close together. The current in the primary coil is steady. Explain why no e.m.f. is induced in the secondary coil.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The magnetic field is constant.
- Flux linkage does not change.
- Rate of change of flux linkage is zero.
- No induced e.m.f. is produced.
