Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-4.7 Radians & Angular Displacement- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -4.7 Radians & Angular Displacement- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -4.7 Radians & Angular Displacement- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- be able to express angular displacement in radians and in degrees, and convert between these units
Angular Displacement in Radians and Degrees
Angular displacement describes how far an object has rotated about a fixed point or axis. It can be measured in either degrees or radians, but radians are the SI unit used in physics equations.
Angular Displacement in Degrees
![]()
- A full circle is divided into 360 degrees.
- Degrees are commonly used in geometry and everyday situations.
- Symbol used: \( ^\circ \).
Full rotation \( = 360^\circ \)
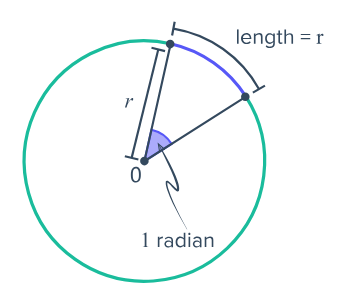
Angular Displacement in Radians
The radian is defined using the geometry of a circle.
 F
F
Definition:
One radian is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius.
Key results:
- Arc length of a full circle = \( 2\pi r \)
- Therefore, a full circle corresponds to \( 2\pi \) radians
Full rotation \( = 2\pi\ \text{radians} \)
Relationship Between Degrees and Radians
Since:
\( 360^\circ = 2\pi\ \text{radians} \)
We obtain the conversion factors:
\( 180^\circ = \pi\ \text{radians} \)
Conversion Formulae
![]()
Degrees to radians:
\( \theta(\text{radians}) = \theta(^\circ)\times\dfrac{\pi}{180} \)
Radians to degrees:
\( \theta(^\circ) = \theta(\text{radians})\times\dfrac{180}{\pi} \)
Why Radians Are Used in Physics
- Radians are dimensionless.
- Many physics equations (e.g. arc length, angular velocity, SHM) only work correctly in radians.
- Using degrees in these equations gives incorrect results.
Common Angular Values
| Degrees | Radians |
|---|---|
| \( 30^\circ \) | \( \dfrac{\pi}{6} \) |
| \( 45^\circ \) | \( \dfrac{\pi}{4} \) |
| \( 60^\circ \) | \( \dfrac{\pi}{3} \) |
| \( 90^\circ \) | \( \dfrac{\pi}{2} \) |
| \( 180^\circ \) | \( \pi \) |
| \( 360^\circ \) | \( 2\pi \) |
Example (Easy)
Convert \( 60^\circ \) to radians.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( \theta = 60 \times \dfrac{\pi}{180} = \dfrac{\pi}{3}\ \text{radians} \)
Example (Medium)
Convert \( \dfrac{5\pi}{6} \) radians to degrees.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( \theta = \dfrac{5\pi}{6} \times \dfrac{180}{\pi} = 150^\circ \)
Example (Hard)
A wheel rotates through \( 2.5 \) revolutions. Express this angular displacement in radians.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
One revolution = \( 2\pi \) radians
\( \theta = 2.5 \times 2\pi = 5\pi\ \text{radians} \)
