Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-5.12 Nuclear Fusion- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.12 Nuclear Fusion- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.12 Nuclear Fusion- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand the mechanism of nuclear fusion and the need for very high densities of matter and very high temperatures to bring about and maintain nuclear fusion
Mechanism of Nuclear Fusion and the Need for Very High Temperature and Density
Nuclear fusion is the process in which two light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy. Although fusion releases enormous energy, it is extremely difficult to initiate and sustain because of strong electrostatic repulsion between nuclei.
The Basic Fusion Process
In a typical fusion reaction (such as in stars):
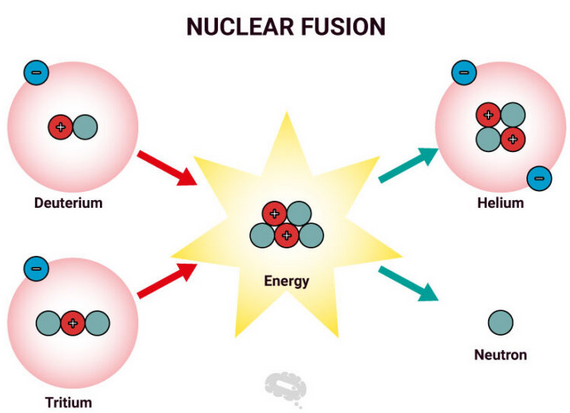
- Two light nuclei (e.g. hydrogen isotopes) approach each other.
- If they get close enough, the strong nuclear force binds them together.
- A new nucleus forms with a higher binding energy per nucleon.
- The mass defect is converted into energy using \( \Delta E = c^2 \Delta m \).
Key condition: Nuclei must come within about \( 1\times10^{-15}\ \mathrm{m} \) for the strong nuclear force to act.
Coulomb Repulsion (Electrostatic Barrier)
All nuclei are positively charged, so they repel each other due to electrostatic force.
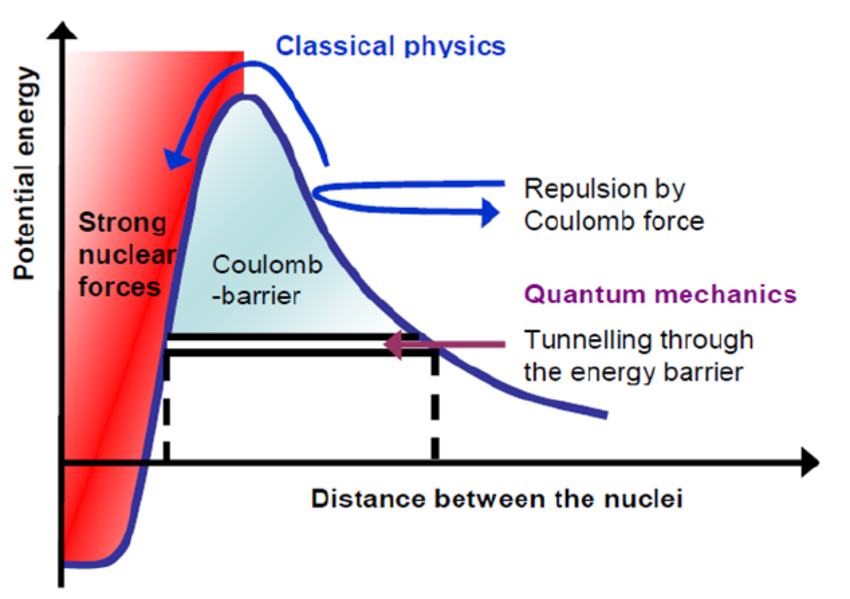
- This repulsion is called the Coulomb barrier.
- The force increases as nuclei get closer.
- Fusion cannot occur unless this barrier is overcome.
Conclusion: Very high kinetic energy is required for nuclei to get close enough to fuse.
Why Very High Temperature Is Required
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles:
\( \text{average kinetic energy} = \tfrac{3}{2} kT \)
- High temperature → nuclei move very fast.
- High speed increases chance of overcoming Coulomb repulsion.
- Fusion typically requires temperatures of the order of \( 10^7 \) to \( 10^8\ \mathrm{K} \).
Example: The core of the Sun has a temperature of about \( 1.5\times10^7\ \mathrm{K} \).
Why Very High Density Is Required
High density increases the probability of fusion reactions.
- More nuclei per unit volume.
- More frequent collisions between nuclei.
- Greater chance that collisions occur with sufficient energy.
Without high density:
- Collisions are too infrequent.
- Fusion rate is too low to sustain energy output.
Maintaining Nuclear Fusion
For fusion to be self-sustaining:
- Energy released must maintain high temperature.
- Particles must remain confined long enough to collide.
- Energy losses must be minimised.
This condition is known as plasma confinement.
Methods:
- Gravitational confinement: stars (e.g. the Sun)
- Magnetic confinement: tokamaks and fusion reactors
- Inertial confinement: high-powered lasers
Why Fusion Occurs Naturally in Stars
- Enormous gravitational pressure creates extremely high density.
- Gravitational energy raises temperature to fusion levels.
- Fusion energy balances gravitational collapse.
This balance keeps stars stable over billions of years.
Example (Easy)
Why do nuclei need very high kinetic energy for fusion?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Nuclei are positively charged.
- They repel each other due to electrostatic force.
- High kinetic energy allows them to overcome this repulsion.
Example (Medium)
Explain why high temperature alone is not sufficient for sustained fusion.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- High temperature gives nuclei high kinetic energy.
- But without high density, collisions are too rare.
- Fusion rate would be too low to sustain energy output.
Example (Hard)
Explain why nuclear fusion is difficult to achieve on Earth but occurs naturally in stars.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Stars have immense gravitational pressure.
- This creates very high temperature and density.
- Earth lacks gravitational confinement of sufficient strength.
- Artificial confinement methods are technologically challenging.
