Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-5.14 Alpha, Beta & Gamma Radiation- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.14 Alpha, Beta & Gamma Radiation- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.14 Alpha, Beta & Gamma Radiation- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand the relationships between the nature, penetration, ionising ability and range in different materials of nuclear radiations (alpha, beta and gamma)
Nature, Penetration, Ionising Ability and Range of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Radiation
Nuclear radiation occurs when unstable nuclei emit particles or electromagnetic radiation in order to become more stable. The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ).
Nature of Nuclear Radiations
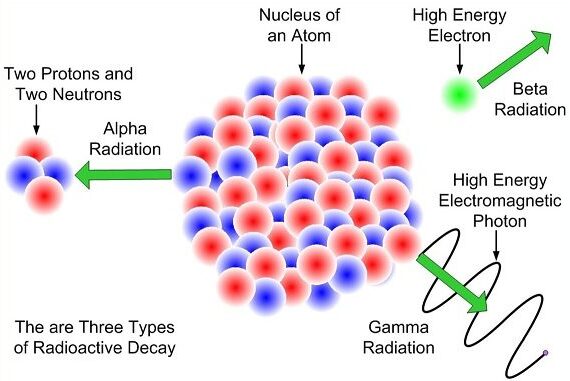
- Alpha radiation (α): helium nucleus consisting of 2 protons and 2 neutrons
- Beta radiation (β): fast-moving electron (or positron)
- Gamma radiation (γ): high-energy electromagnetic wave
Key comparison:
- Alpha and beta are particles.
- Gamma is electromagnetic radiation.
Ionising Ability
Ionising ability refers to how effectively radiation removes electrons from atoms.
![]()
- Alpha: very high ionising ability
- Beta: moderate ionising ability
- Gamma: low ionising ability
Reason:
- Alpha particles have large mass and charge.
- Beta particles have smaller mass and charge.
- Gamma rays have no mass or charge.
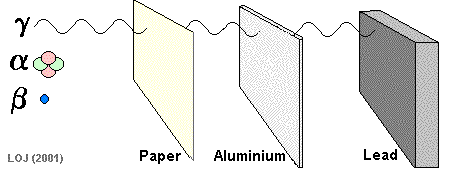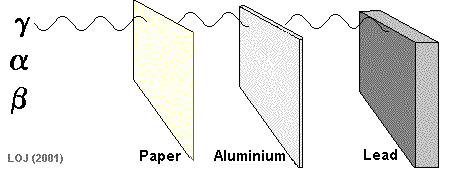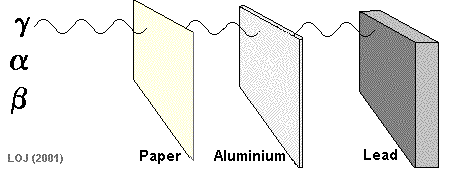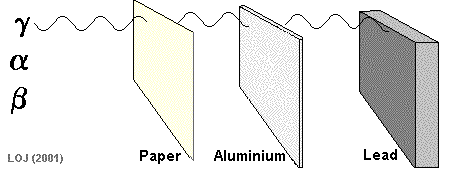
Penetration Power
Penetration refers to how easily radiation passes through matter.
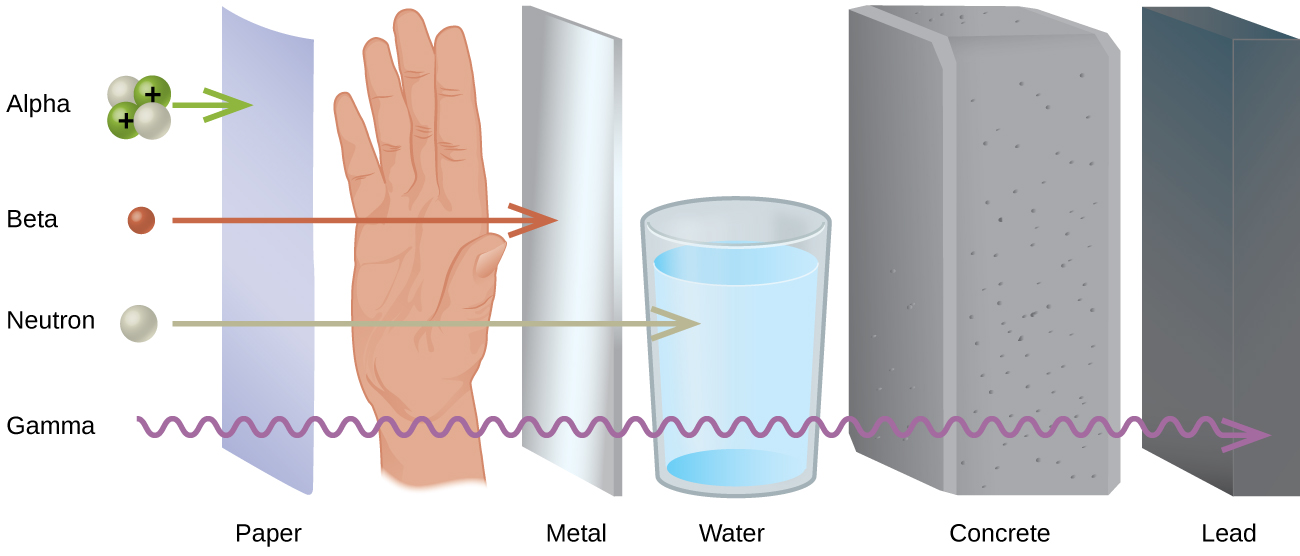
- Alpha: stopped by paper or skin
- Beta: stopped by a few millimetres of aluminium
- Gamma: requires thick lead or concrete
Key relationship:
- High ionising ability → low penetration
- Low ionising ability → high penetration
Range in Different Materials
The range is the distance radiation travels before losing all its energy.
- Alpha: a few cm in air
- Beta: a few metres in air
- Gamma: very long range, gradually absorbed
In solids:
- Alpha travels only micrometres.
- Beta travels a few millimetres.
- Gamma penetration depends on thickness and density.
Summary of Relationships
- Alpha: highest ionisation, shortest range, weakest penetration.
- Beta: medium ionisation, medium range, moderate penetration.
- Gamma: lowest ionisation, longest range, strongest penetration.
Important: Although alpha radiation is weakly penetrating, it is extremely dangerous if ingested.
Example (Easy)
Which type of radiation has the greatest ionising ability?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Alpha radiation has the greatest ionising ability due to its large mass and charge.
Example (Medium)
Why is gamma radiation more penetrating than alpha radiation?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Gamma rays have no mass or charge.
- They interact less frequently with matter.
- Therefore, they travel further through materials.
Example (Hard)
Explain why alpha radiation is the most dangerous inside the body but the least dangerous outside.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Alpha particles cause intense ionisation.
- Inside the body, they damage cells severely.
- Outside the body, they cannot penetrate skin.
