Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-5.24 Resonance- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.24 Resonance- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.24 Resonance- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand what is meant by resonance
Resonance in Oscillating Systems
Resonance occurs when an oscillating system is driven by an external force at a frequency equal to its natural frequency, causing the system to oscillate with maximum amplitude.
Forced Oscillations
Resonance occurs in systems undergoing forced oscillations, where:
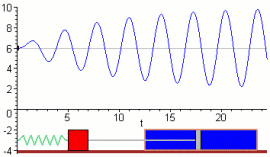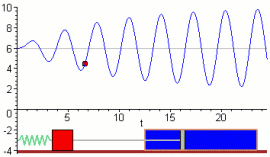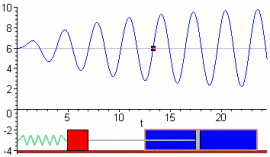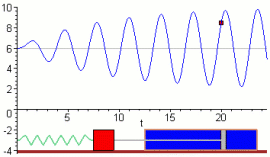
- An external periodic force acts on the system.
- The driving force supplies energy continuously.
- The system oscillates at the frequency of the driving force.
Meaning of Resonance
Resonance occurs when:
![]()
Driving frequency = natural frequency
- Energy transfer from the driving force to the system is maximum.
- The amplitude of oscillation becomes maximum.
- The system vibrates strongly.
Resonance Curve
The effect of resonance is shown using an amplitude–frequency graph.
![]()
- Amplitude is plotted on the vertical axis.
- Driving frequency is plotted on the horizontal axis.
- A sharp peak occurs at the resonant frequency.
Key idea: The peak corresponds to resonance.
Effect of Damping
Damping is the loss of energy from the system due to friction or air resistance.
![]()
- Increased damping reduces the maximum amplitude.
- The resonance peak becomes broader and lower.
- Resonant frequency shifts slightly to a lower value.
Light damping: sharp resonance peak Heavy damping: reduced resonance effect
Examples of Resonance
- A child on a swing being pushed at the right frequency.
- Musical instruments producing loud sounds.
- Radio tuning circuits.
- Bridges oscillating due to wind or traffic.
Advantages and Dangers of Resonance
Useful applications:
- Musical instruments amplify sound.
- Radios select specific frequencies.
- Ultrasound and medical imaging.
Potential dangers:
- Structural damage to bridges and buildings.
- Machines vibrating excessively.
- Failure of mechanical components.
Example (Easy)
What is meant by resonance?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Resonance is when a system oscillates with maximum amplitude because the driving frequency equals its natural frequency.
Example (Medium)
Why does a swing move higher when pushed at the correct time?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The pushes match the natural frequency.
- Energy transfer is maximised.
- The amplitude increases due to resonance.
Example (Hard)
Explain why damping is added to structures such as bridges.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Damping reduces oscillation amplitude.
- It prevents large vibrations at resonance.
- This reduces the risk of structural failure.
