Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics-5.37 Black Body Radiation- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.37 Black Body Radiation- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Physics -5.37 Black Body Radiation- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand what is meant by a black body radiator and be able to interpret radiation curves for such a radiator
Black Body Radiator and Interpretation of Radiation Curves
A black body radiator is an idealised object used to model the emission of thermal radiation.
What Is a Black Body Radiator? 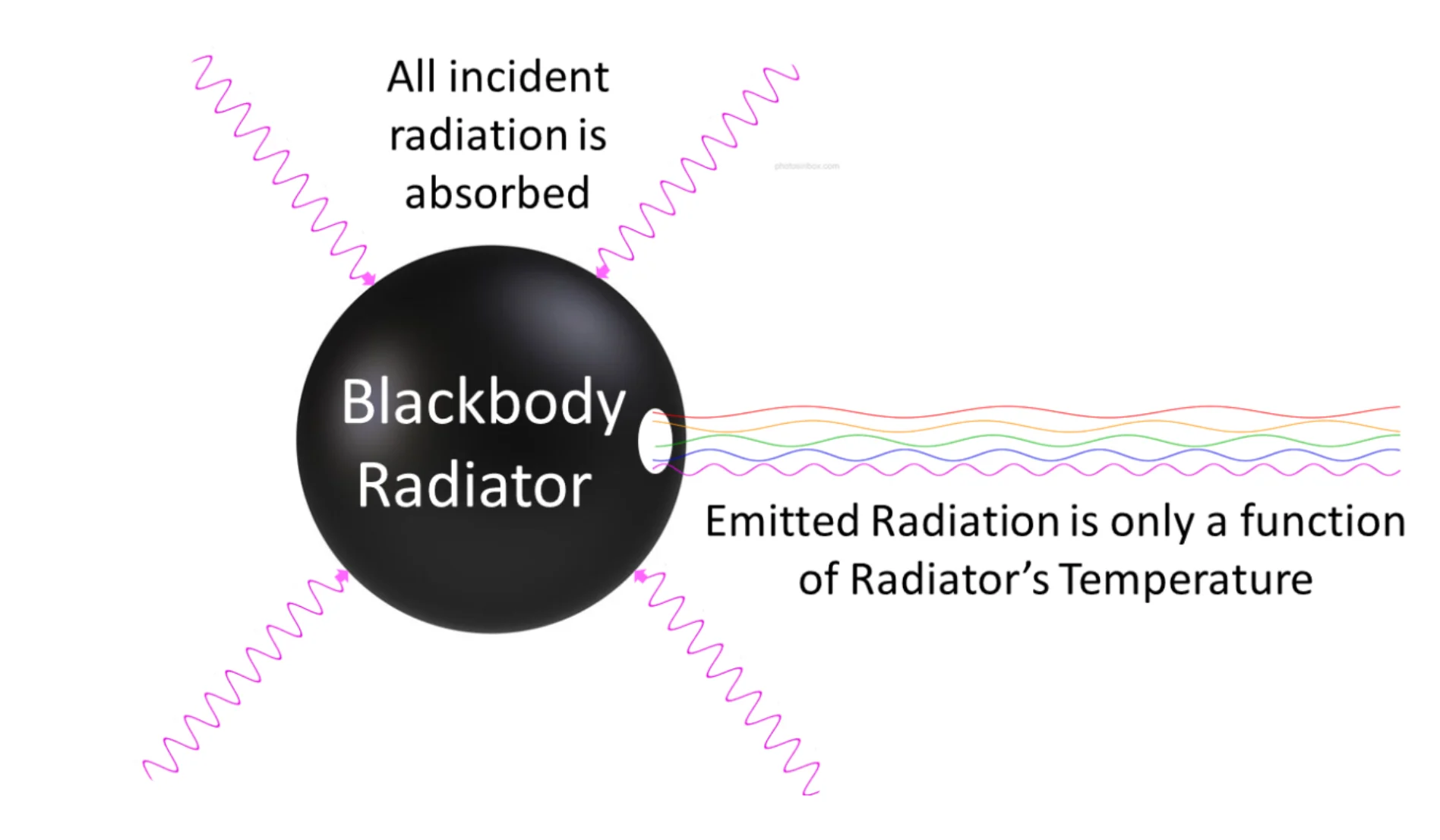
A black body is a body that:
- Absorbs all electromagnetic radiation incident on it.
- Reflects no radiation.
- Emits the maximum possible radiation at any given temperature.
Important:
- A black body is a perfect absorber and perfect emitter.
- Real objects approximate black body behaviour.
Emission of Radiation by a Black Body
The radiation emitted by a black body depends only on:
- Its temperature.
- Not on its shape or material.
This radiation is emitted over a continuous range of wavelengths.
Radiation Curves for a Black Body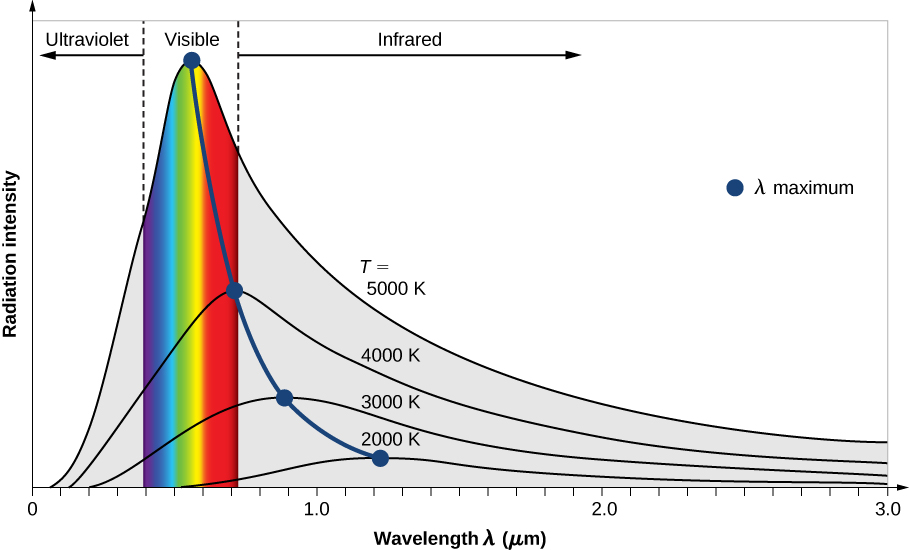
A radiation curve is a graph of:
- Intensity (or power per unit area per wavelength)
- Against wavelength
Each curve corresponds to a different temperature.
Key Features of Black Body Radiation Curves
- Each curve has a single peak.
- The peak occurs at a wavelength called the peak wavelength.
- As temperature increases, the peak moves to shorter wavelengths.
- The total area under the curve increases with temperature.
Key ideas:
- Hotter objects emit more radiation.
- Hotter objects emit radiation of shorter wavelengths.
Effect of Increasing Temperature
When temperature increases:
- The peak intensity increases.
- The peak wavelength decreases.
- The total energy emitted increases rapidly.
This explains why:
- Cool objects glow red.
- Hot objects glow white or blue.
Interpreting Radiation Curves
- The curve with the highest peak corresponds to the highest temperature.
- A shift of the curve left means an increase in temperature.
- The area under the curve represents total power emitted.
Important distinction:
- Peak height ≠ total energy.
- Total energy depends on the entire area under the curve.
Real Black Body Examples
- A cavity with a small hole acts as a near-perfect black body.
- The Sun behaves approximately as a black body.
- Stars can be analysed using black body radiation curves.
Example (Easy)
What is meant by a black body?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
A black body is an object that absorbs all incident radiation and emits the maximum possible radiation for its temperature.
Example (Medium)
What happens to the radiation curve when the temperature of a black body increases?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The peak intensity increases.
- The peak wavelength shifts to shorter wavelengths.
- The total area under the curve increases.
Example (Hard)
Two black body curves are shown. One has a higher peak and is shifted to the left. Which object is hotter and why?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The curve shifted to the left corresponds to a shorter peak wavelength.
- Shorter peak wavelength indicates higher temperature.
- The higher peak shows greater intensity.
