IB PHYSICS HL(Higher level) – 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.1 Electric fields
Topic 5 Weightage : 5 %
All Questions for Topic 5.1 – Charge , Electric field , Coulomb’s law , Electric current , Direct current (dc) , Potential difference
Question
Two charges 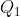 and
and 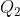 , each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum.
, each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum.
What is the electric force on 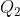 and the electric field due to
and the electric field due to 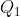 at the position of
at the position of 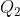 ?
?
▶️Answer/Explanation
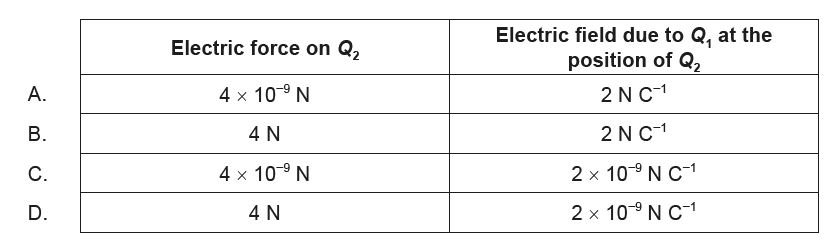
Ans: A
\(F_{Q_2}=k\frac{Q_1Q_2}{r^2}\)
\(=\frac{9\times 10^9 \times 2\times 10^{-9}\times 2\times 10^{-9}}{3^2}=4\times 10^{-9}\)
\(E_{Q_{21}}=\frac{F}{Q_1}=\frac{4\times 10^{-9}}{2\times 10^{-9}}=2\; NC^{-1}\)
Question
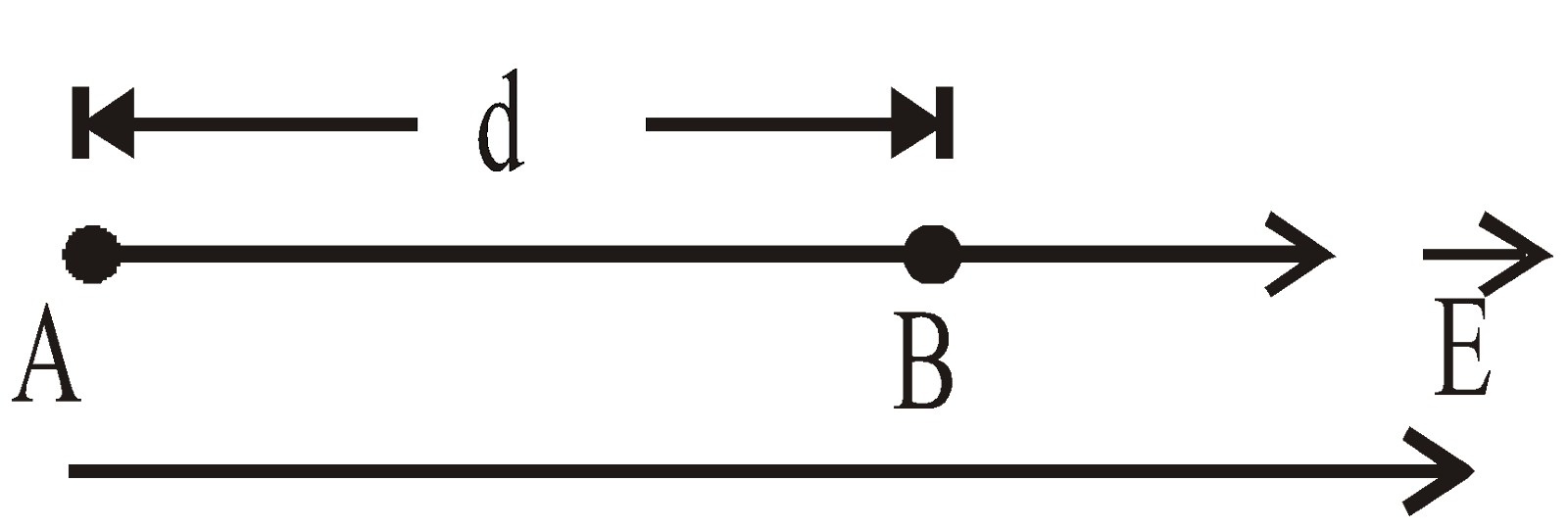
An ion of charge +Q moves vertically upwards through a small distance s in a uniform vertical electric field. The electric field has a strength E and its direction is shown in the diagram.

What is the electric potential difference between the initial and final position of the ion?
A. \(\frac{{EQ}}{s}\)
B. EQs
C. Es
D. \(\frac{E}{s}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
RELATION BETWEEN ELECTRIC FIELD AND POTENTIAL
Question
Two wires, X and Y, are made from the same metal. The wires are connected in series. The radius of X is twice that of Y. The carrier drift speed in X is vX and in Y it is vY.
What is the value of the ratio \(\frac{{{{\text{v}}_{\text{X}}}}}{{{{\text{v}}_{\text{Y}}}}}\)?
A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 2.00
D. 4.00
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
\(i=neAv_d\)
Now \(x \) and \( y \) are in series , hence \( i_x=i_y\)
or \(neA_xv_{d_x}= neA_yv_{d_y}\)
\(A_x=\pi (r_x)^2 \; ,\; A_y=\pi (r_y)^2\)
\(ne\pi (r_x)^2v_{d_x} =ne\pi (r_y)^2 v_{d_y}\)
\(\frac{v_{d_x}}{v_{d_y}}=\frac{(r_y)^2}{(r_x)^2}=\frac{(r_y)^2}{(2r_y)^2} =\frac{1}{4}=0.25\)
Question
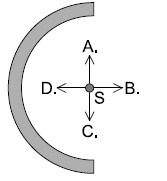
Positive charge is uniformly distributed on a semi-circular plastic rod. What is the direction of the electric field strength at point S?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
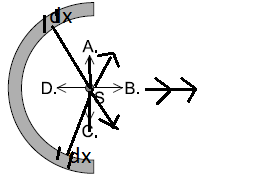
The component along y axis ( Along A and Along C) are cancelled out and along x – axis ( along B) it is added up
Question
Electrons, each with a charge e, move with speed v along a metal wire. The electric current in the wire is I.
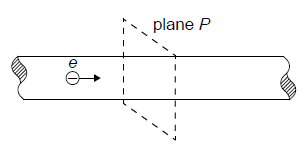
Plane P is perpendicular to the wire. How many electrons pass through plane P in each second?
A. \(\frac{e}{I}\)
B. \(\frac{{ve}}{I}\)
C. \(\frac{I}{{ve}}\)
D. \(\frac{I}{e}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
ELECTRIC CURRENT
\(q= n\times e\)
\(t= 1 \) second
\(I = \frac{n\times e}{1}\)
\(\therefore n=\frac{I}{e}\)
