IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 8.1 – Energy sources
Topic 8 Weightage : 7 %
All Questions for Topic 8.1 – Specific energy and energy density of fuel sources , Sankey diagrams , Primary energy sources , Electricity as a secondary and versatile form of energy , Renewable and non-renewable energy sources
Question
Which of the energy sources are classified as renewable and non-renewable?
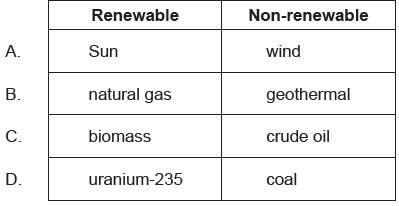
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C

Question
A wind turbine has a power output p when the wind speed is v. The efficiency of the wind turbine does not change. What is the wind speed at which the power output is \(\frac{p}{2}\)?
A. \(\frac{v}{4}\)
B. \(\frac{v}{{\sqrt 8 }}\)
C. \(\frac{v}{2}\)
D. \(\frac{v}{{\sqrt[3]{2}}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
power output is given by equation.
\(\frac{E_K}{t}=\frac{1}{2} A\rho v^3\)
Where \(A = \pi r^2\)
\(p=\frac{1}{2} A\rho v^3\) — equation (1)
Given that at power \(p\) velocity \(v\)
Now for power \(\frac{p}{2}=p’\)
Hence
\(p’ = \frac{1}{2} A\rho v’^3\)
or
\(\frac{p}{2}=\frac{1}{2} A\rho v’^3\) –eq (2)
or
From equation (1) and (2) we get
\(\frac{\frac{1}{2} A\rho v’^3}{\frac{1}{2} A\rho v^3}=\frac{1}{2}\)
or
\(v’^3 =\frac{1}{2} v^3\)
or
\(v’=\frac{v}{\sqrt[3]{2}}\)
Question
Three energy sources for power stations are
I. fossil fuel
II. pumped water storage
III. nuclear fuel.
Which energy sources are primary sources?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Primary and Secondary Sources
Primary Energy Sources | Secondary Energy Sources |
Energy sources found in the natural environment (fossil fuels, solar, wind, nuclear, hydro, etc.) | Useful transformations of the primary sources (electricity, pumped storage for hydro, etc.) |
Question
What is equivalent to \(\frac{{{\text{specific energy of a fuel}}}}{{{\text{energy density of a fuel}}}}\)?
A. density of the fuel
B. \(\frac{1}{{{\text{density of the fuel}}}}\)
C. \(\frac{{{\text{energy stored in the fuel}}}}{{{\text{density of the fuel}}}}\)
D. \(\frac{{{\text{density of the fuel}}}}{{{\text{energy stored in the fuel}}}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Specific energy, ES is the amount of energy that can be extracted from a unit mass of fuel.
Energy density, ED is the amount of energy that can be extracted from a unit volume of fuel mass.
They are related by
\(E_D=\frac{mass}{volume}E_s\)
or
\(\frac{E_s}{E_D}=\frac{Volume}{mass}=\frac{1}{\text {density of fuel}}\)
Question
The energy density of a substance can be calculated by multiplying its specific energy with which quantity?
A. mass
B. volume
C. \(\frac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{volume}}}}\)
D. \(\frac{{{\text{volume}}}}{{{\text{mass}}}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Specific energy, ES is the amount of energy that can be extracted from a unit mass of fuel.
Energy density, ED is the amount of energy that can be extracted from a unit volume of fuel mass.
They are related by
\(E_D=\frac{mass}{volume}E_s\)
or
\(\frac{E_s}{E_D}=\frac{Volume}{mass}=\frac{1}{\text {density of fuel}}\)
Question
Which of the energy sources are classified as renewable and non-renewable?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C

