IB DP Biology- A1.1 Water - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which symbol indicates the polarity of the oxygen atom in the water molecule?
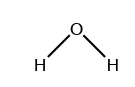
(B) δ⁻
(C) +
(D) −
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
Where do hydrogen bonds form?
A. Between the slight negative charge of hydrogen and slight positive charge of oxygen within a water molecule
B. Between the slight positive charge of hydrogen and slight negative charge of oxygen within a water molecule
C. Between the slight positive charge of hydrogen and slight negative charge of oxygen in different water molecules
D. Between the slight negative charge of hydrogen and slight positive charge of oxygen in different water molecules
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. Between the slight positive charge of hydrogen and slight negative charge of oxygen in different water molecules
Explanation:
Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions that happen when a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule is pulled toward a slightly negative atom (like oxygen) in a nearby molecule. In water, these bonds form between different water molecules — not within a single one — and they help explain why water sticks together so well.
Evaluating the options:
A. Incorrect – This says hydrogen is slightly negative and oxygen is slightly positive, which is the opposite of true. Also, hydrogen bonds don’t happen inside a single molecule.
B. Incorrect – The charges are right (hydrogen is slightly positive, oxygen is slightly negative), but this describes a bond within one water molecule. Hydrogen bonds happen between different molecules.
C. Correct – This is exactly right. Hydrogen bonds form between the slightly positive hydrogen of one water molecule and the slightly negative oxygen of another water molecule.
D. Incorrect – This reverses the charges. Hydrogen is not slightly negative, and oxygen is not slightly positive. That’s not how water molecules interact.
