IB DP Biology- A2.2 Cell structure - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The table shows features of three types of cells (X, Y, and Z).
| Feature | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell wall | absent | present | present |
| Centrioles | present | absent | absent |
| Large vacuole | absent | present | present |
| Plastids | absent | present | absent |
To which kingdom do each of the cells belong?
| X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|
| Animal | Fungi | Plant |
| Fungi | Animal | Protist |
| Animal | Plant | Fungi |
| Protist | Animal | Plant |
(A) Animal – Fungi – Plant
(B) Fungi – Animal – Protist
(C) Animal – Plant – Fungi
(D) Protist – Animal – Plant
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Cell Y has a cell wall, large vacuole, and plastids, identifying it as a plant cell.
Cell Z has a cell wall and large vacuole but no plastids, typical of a fungal cell.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
The image shows a single Paramecium with food vacuoles that contain ingested cells of the unicellular green alga Chlorella.
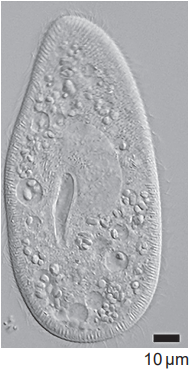
What can be deduced about Paramecium?
A. It is an autotroph.
B. It cannot perform all of the functions of life.
C. It carries out heterotrophic nutrition.
D. It is a prokaryote.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. It carries out heterotrophic nutrition.
Explanation: 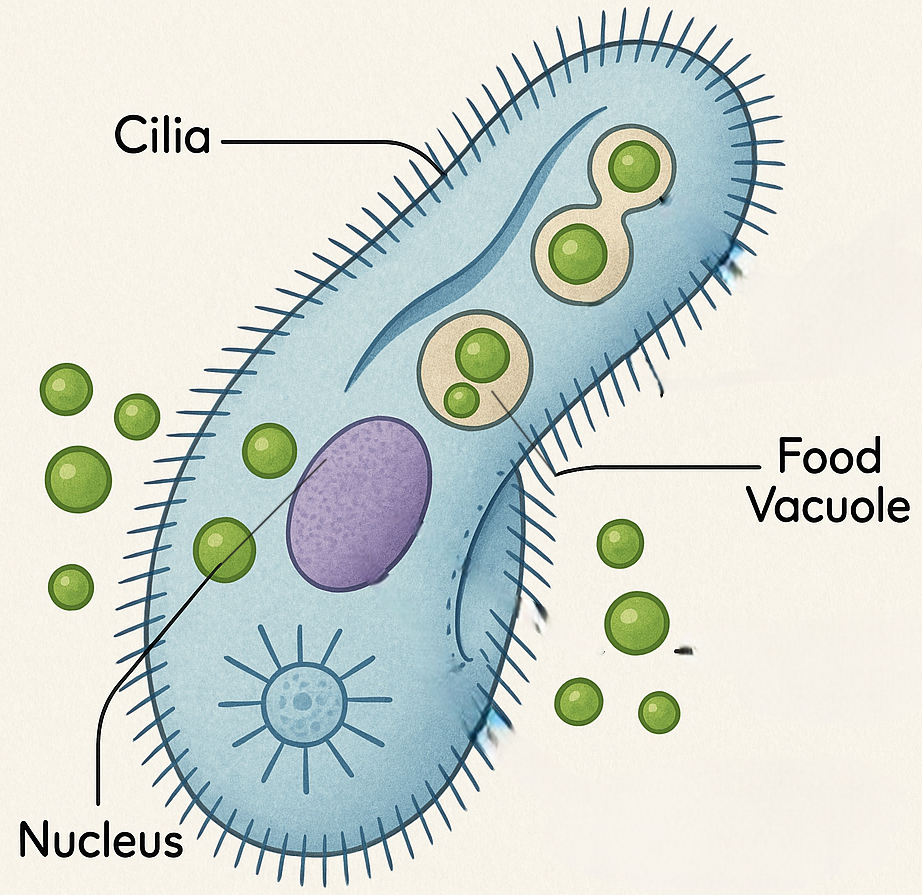
Heterotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain energy by consuming other organisms or organic matter. Unlike autotrophs (such as plants and algae) that use sunlight to produce food via photosynthesis, heterotrophs ingest or absorb preformed organic materials.
Paramecia are single-celled eukaryotic organisms that feed on smaller organisms like algae or bacteria. They use cilia to sweep food into their oral groove, where food vacuoles form and digestion occurs through enzymatic breakdown of ingested material.
Evaluating the options:
A. Incorrect – Paramecium is not an autotroph. Autotrophs synthesize their own food via photosynthesis. Paramecia ingest Chlorella and other small organisms instead.
B. Incorrect – Paramecia can perform all the functions of life (metabolism, growth, reproduction, response, homeostasis, and nutrition), even though they are unicellular.
C. Correct – Paramecia perform heterotrophic nutrition by ingesting and digesting other organisms in food vacuoles to obtain nutrients and energy.
D. Incorrect – Paramecium is a eukaryote with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, unlike prokaryotes such as bacteria.
Question
The micrograph of a section through a plant stem shows at least ten different types of cells.

What explains the differences between these cells?
A. Only one gene is expressed in each cell type.
B. Different genes are expressed in each cell type.
C. Only useful genes remain in the DNA of each cell type.
D. Changes in the DNA sequence take place when these cells develop.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B. Different genes are expressed in each cell type.
Explanation: In multicellular organisms (including plants), nearly all cells contain the same DNA. The differences among cell types arise from differential gene expression—distinct sets of genes are turned on or off in each cell type. This selective expression produces different proteins, which in turn confer the unique structures and functions of xylem, phloem, parenchyma, sclerenchyma, etc., even within the same organ.
Evaluating the options:
A. Incorrect — Cells express many genes, not just one. The pattern (profile) of expressed genes differs by cell type.
B. Correct — Different cell types arise because different genes are expressed, despite identical genomes.
C. Incorrect — Cells do not delete “unused” genes; they retain the full genome and regulate genes primarily via expression control.
D. Incorrect — The DNA sequence generally does not change during normal differentiation; what changes is which genes are active.
