IB DP Biology- A3.1 Diversity of organisms - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
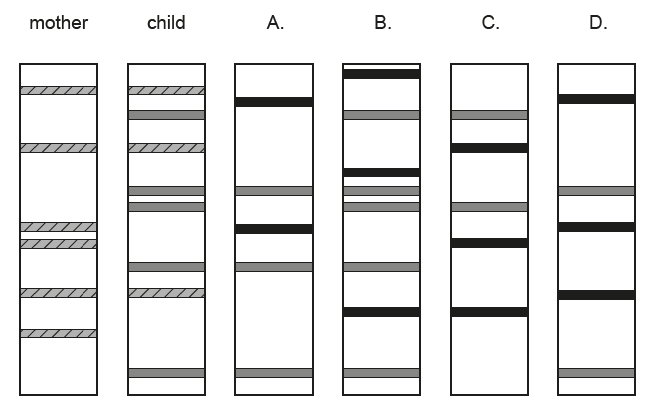
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In paternity testing, every DNA band in the child must appear either in the mother or the true father. By comparing the child’s unmatched bands with the four possible fathers, only Profile B contains all the additional bands that originate from the child but are not found in the mother. Therefore, B is the only consistent match.
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
How do autotrophs living in an aquatic ecosystem obtain carbon?
A. By diffusion of dissolved carbon dioxide and hydrogen carbonate ions
B. By feeding on heterotrophs and obtaining carbon from carbohydrates
C. By active transport of carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere
D. By ingesting organisms with carbonate shells
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. By diffusion of dissolved carbon dioxide and hydrogen carbonate ions
Explanation:
Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food, usually by photosynthesis. In aquatic ecosystems, autotrophs such as algae and cyanobacteria obtain carbon from dissolved carbon dioxide (CO₂) and hydrogen carbonate ions (HCO₃⁻) in the water.
These carbon sources come from atmospheric CO₂, which dissolves into the water and then diffuses into autotrophic cells.
Evaluating the options:
A. Correct – Aquatic autotrophs absorb dissolved CO₂ and HCO₃⁻ by diffusion. This is their primary carbon source for photosynthesis.
B. Incorrect – Feeding on heterotrophs is a heterotrophic behavior. Autotrophs synthesize their own organic molecules.
C. Incorrect – Autotrophs do not take CO₂ directly from the air; it must dissolve in water first.
D. Incorrect – Ingesting organisms with carbonate shells would require heterotrophy, not autotrophic nutrition.
Question
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
A. Eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, whereas prokaryotic cells are not.
B. Prokaryotic cells do not contain ribosomes, whereas eukaryotic cells do.
C. Eukaryotic cells contain DNA, whereas prokaryotic cells do not.
D. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, whereas eukaryotic cells do not.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. Eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, whereas prokaryotic cells are not.
Explanation: 
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller. They lack a true nucleus and do not contain membrane-bound organelles. Their DNA is located in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid.
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and compartmentalized. They possess a membrane-bound nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus.
Evaluating the options:
A. Correct – Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
B. Incorrect – Both cell types contain ribosomes. Prokaryotic ribosomes are simply smaller (70S vs. 80S).
C. Incorrect – Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain DNA. Prokaryotic DNA is just not enclosed within a nucleus.
D. Incorrect – Many prokaryotes have a cell wall, but some eukaryotes (plants, fungi, algae) also have cell walls.
