IB DP Biology- A4.1 Evolution and speciation - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The images below show an Ichthyosaurus and a dolphin. The Ichthyosaurus was an extinct aquatic reptile known from fossils, whereas dolphins are modern mammals.
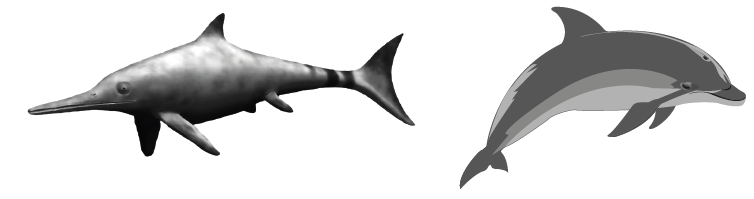
How can the evolution of these two species best be described?
A. Their streamlined bodies show divergent evolution.
B. Their streamlined bodies are analogous structures.
C. Their pentadactyl limbs are an example of convergent evolution.
D. Their pentadactyl limbs are analogous structures.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B) Their streamlined bodies are analogous structures.
Question
In a natural classification, what do all members of a genus have in common?
A. They all have the same binomial name.
B. They all belong to the same species.
C. They can freely interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
D. They have all evolved from the same common ancestor.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: D. They have all evolved from the same common ancestor
Explanation:
In natural classification, organisms are grouped according to their evolutionary relationships. A genus includes multiple species that are closely related because they share a common ancestor. Each species within a genus has a unique binomial name, but the genus name is common to all species in that group.
Evaluation of Each Option:
A. Incorrect — Members of a genus share the same genus name, but their species names differ, so their binomial names are not identical.
B. Incorrect — A genus contains multiple species, not just one.
C. Incorrect — Species from the same genus generally cannot interbreed successfully to produce fertile offspring.
D. Correct — All members of a genus share a common evolutionary origin, having evolved from the same ancestor.
Question
A short sequence of amino acids (represented by letters) in cytochrome \(c\) is shown for six (\(6\)) vertebrates. Letters in bold indicate identical amino acids for all species.

Which statement refers to this section of cytochrome \(c\)?
A. The DNA base sequences for human and rhesus monkey are different.
B. The most DNA base changes are between humans and snapping turtles.
C. The largest number of amino acid differences is two (\(2\)).
D. The amino acid at position \(32\) is the most variable.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: D. The amino acid at position \(32\) is the most variable.
Explanation:
The figure highlights identical residues in bold across the \(6\) species. Positions that differ among species are variable. From the alignment, position \(32\) shows the greatest variability across species, so it is the most variable site.
Evaluation of Options:
A. Incorrect — The alignment shows amino acids, not DNA; identical amino acids can arise from different codons, so DNA differences cannot be inferred directly.
B. Incorrect — DNA base changes cannot be counted from protein sequence alone; the prompt provides only amino acid data.
C. Incorrect — The alignment shows more than \(2\) amino acid differences across species/positions; the largest number is not constrained to \(2\).
D. Correct — Position \(32\) varies the most among the species shown, making it the most variable residue.
