IB DP Biology- A1.2 Nucleic acids- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
The diagram below represents a nucleic acid molecule, with several of its bases labeled.
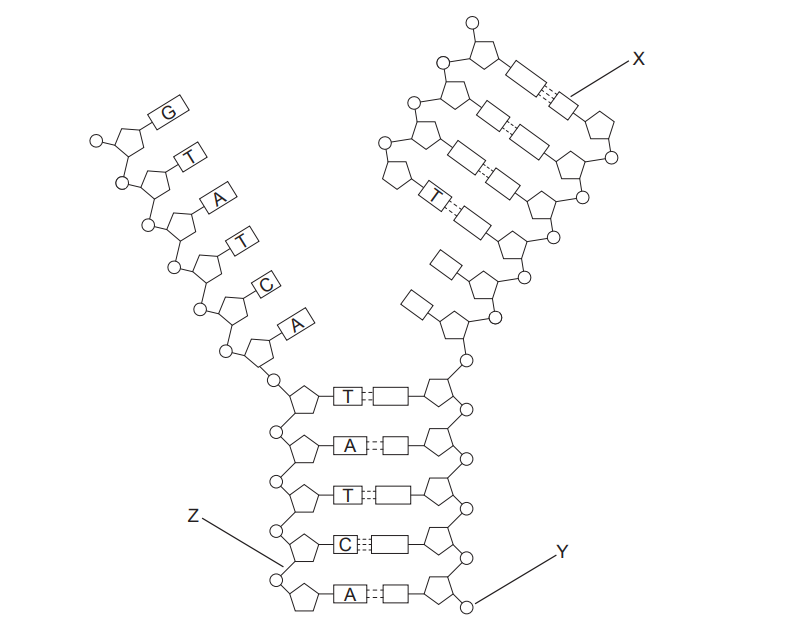
(a) Identify which type of nucleic acid is shown.
(b) State, with a reason, whether the process illustrated is transcription or DNA replication.
(c) Deduce the identity of the base labelled \(X\) in the diagram.
(d) Identify the terminal labelled \(Y\) on the diagram.
(e) (i) Name the type of bond labelled \(Z\).
(ii) Two different enzymes assist in forming this type of bond during the process. Explain how each enzyme contributes.
Most-appropriate topic codes:
• TOPIC D1.1: DNA replication — parts (b), (d), (e-ii)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
The nucleic acid shown is DNA. It is double-stranded and contains the base thymine (\(T\)), which is only present in DNA.
(b)
The diagram represents DNA replication. This is because both strands are being copied and thymine (\(T\)) is incorporated. If the diagram showed transcription, uracil (\(U\)) would replace thymine when pairing with adenine (\(A\)).
(c)
Base \(X\) is paired with guanine (\(G\)). According to base pairing rules, guanine pairs with cytosine (\(C\)).
(d)
The terminal labelled \(Y\) represents the \(5’\) end of the DNA strand, where a phosphate group is attached to the \(5’\) carbon of deoxyribose.
(e)(i)
Bond \(Z\) is a phosphodiester bond, a covalent linkage connecting the phosphate of one nucleotide to the \(3’\) carbon of the next sugar.
(e)(ii)
Two enzymes catalyse the formation of phosphodiester bonds during replication:
- DNA polymerase: Adds nucleotides to the growing strand by forming phosphodiester bonds at the \(3’\) end, synthesizing the new DNA strand.
- DNA ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand by sealing gaps and completing the phosphodiester backbone.
