IB DP Biology- A4.1 Evolution and speciation- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The images below show an Ichthyosaurus and a dolphin. The Ichthyosaurus was an extinct aquatic reptile known from fossils, whereas dolphins are modern mammals.
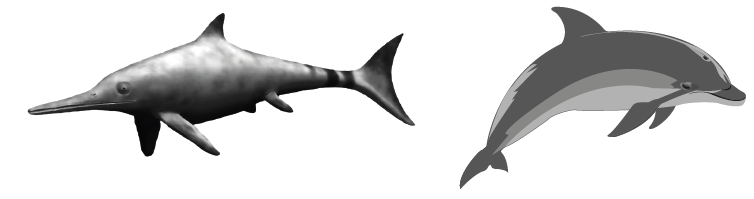
How can the evolution of these two species best be described?
A. Their streamlined bodies show divergent evolution.
B. Their streamlined bodies are analogous structures.
C. Their pentadactyl limbs are an example of convergent evolution.
D. Their pentadactyl limbs are analogous structures.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The Ichthyosaurus (a reptile) and the dolphin (a mammal) evolved independently but developed similar streamlined body shapes for efficient swimming. These similarities arose due to similar environmental pressures, not because of shared ancestry. Hence, their streamlined forms are analogous structures — a result of convergent evolution.
✅ Answer: (B) Their streamlined bodies are analogous structures.
✅ Answer: (B) Their streamlined bodies are analogous structures.
Question
What can lead to reproductive isolation after just one generation?
A. Polyploidy
B. Increased mutation rate
C. Changed allele frequencies
D. Independent assortment of chromosomes
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Polyploidy is when an organism has extra sets of chromosomes (e.g., 3n, 4n instead of 2n).
- It can happen suddenly in one generation, especially in plants.
- Polyploid organisms cannot breed with the original population due to mismatched chromosome numbers.
- This causes instant reproductive isolation, leading to new species formation.
