IB DP Biology- B1.1 Carbohydrates and lipids IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which of these molecules is amphipathic?
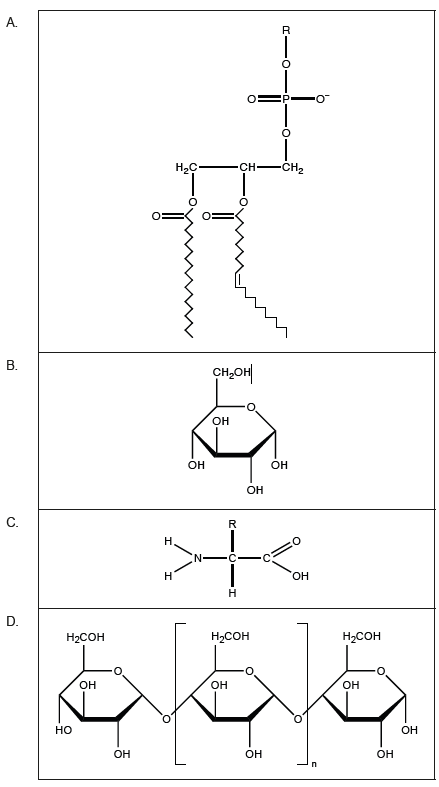
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The molecule in option (A) has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions: a polar phosphate head group and nonpolar fatty acid tails. This dual nature makes it amphipathic, like a phospholipid found in cell membranes.
✅ Answer: (A)
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which molecule can have cis and trans isomers?
A. 

B. 

C. 

D. 

▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
Cis-trans isomerism occurs when:
- There’s a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
- Each carbon in the double bond has two different groups attached.
Now, let’s check each option:
Option A:
- It’s a phospholipid, with long fatty acid chains.
- But no visible C=C double bond.
- No cis-trans isomerism possible.
Option B:
- This is a triglyceride (3 fatty acids + glycerol).
- All single bonds (C-C) in fatty acid chains.
- No cis-trans isomerism.
Option C:
- We see a C=C double bond near the middle of the chain.
- And each carbon in the double bond has two different groups.
- Yes, this molecule can show cis (same side) and trans (opposite side) isomerism.
Option D:
- Fully saturated fatty acid – all single bonds.
- No double bond, no isomerism.
