IB DP Biology- B1.1 Carbohydrates and lipids- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC B2.1: Membranes and membrane transport — parts (b), (d), (e)
• TOPIC B1.1: Carbohydrates and lipids — part (c)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
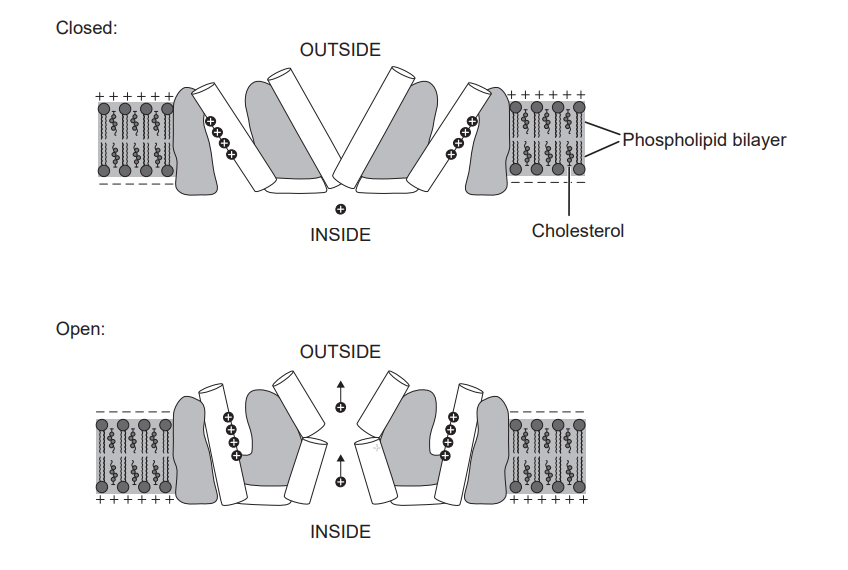
(a)
When a neuron depolarizes due to the entry of \(\text{Na}^+\), the change in membrane voltage triggers the voltage-gated potassium channels to open. As these channels open, \(\text{K}^+\) ions move out of the axon by diffusion. This outward flow of positive charge helps the membrane to return to a negative potential, causing repolarization and eventually contributing to the restoration of the resting potential.
(b)
An example is a ligand-gated ion channel (also known as a neurotransmitter-gated channel).
(c)
Phospholipids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. Their phosphate head groups are attracted to water (hydrophilic), while their fatty acid tails repel water (hydrophobic). This dual nature allows them to spontaneously form bilayers.
(d)
Cholesterol helps to stabilize membrane fluidity. At higher temperatures, it reduces excessive fluidity, and at lower temperatures, it prevents the membrane from becoming too rigid.
(e)
Fatty acids with unsaturated tails increase membrane fluidity because their bends (kinks) prevent tight packing. Fatty acids that are mostly saturated decrease fluidity because they pack together more tightly.
