IB DP Biology- B1.2 Proteins- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
amino acid + amino acid →
Titin is the longest known human protein, made of a single chain containing more than \( 34{,}000 \) amino acids.
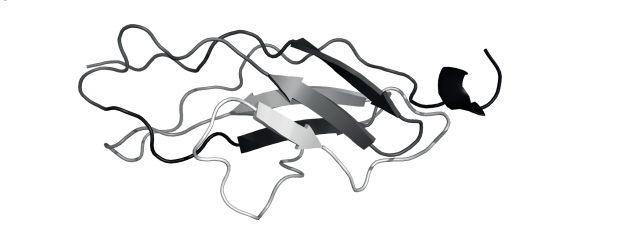
(ii) Outline the function of titin within sarcomeres.
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC B3.3: Muscle and motility — part (c-ii)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
amino acid + amino acid → a dipeptide and a molecule of water
(b)
Amino acids vary in their R-groups, which differ in chemical properties such as being polar, non-polar, acidic, basic, hydrophobic, or hydrophilic. These differences influence how amino acids interact within a polypeptide chain, determining how the protein folds into its unique three-dimensional conformation. As a result, proteins can take on an enormous variety of structures and functions.
(c)
(i) The arrows in the diagram point to beta-pleated sheets, a type of secondary structure formed through hydrogen bonding between backbone N–H and C=O groups in parallel or antiparallel regions of the polypeptide.
(ii) Titin functions as an elastic spring inside sarcomeres. It helps restore the sarcomere to its resting length after muscle contraction and also prevents excessive stretching, maintaining structural stability during muscle activity.
