IB DP Biology- B2.1 Membranes and membrane transport- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
The diagram shows the original cell membrane model proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972.

(a) Identify with the letter H the hydrophilic region of a phospholipid molecule.
(b) Describe how this membrane model differs from the Davson–Danielli model.
(c) Explain the function of molecules such as M in the operation of sodium–potassium pumps.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
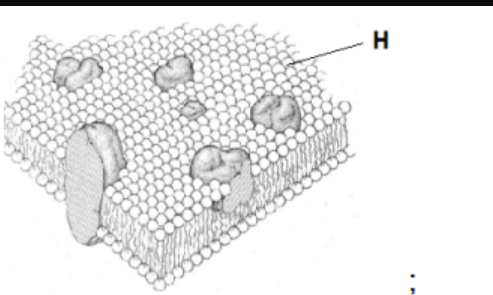
The label H indicates the hydrophilic head of the phospholipid. This polar region interacts with water inside and outside the cell, while the hydrophobic fatty-acid tails orient inward, forming the bilayer structure described by the fluid mosaic model.
(b)
The Singer–Nicolson (fluid mosaic) model and the Davson–Danielli model differ in several important ways:
- Fluid Mosaic Model:
- Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer.
- Membrane components can move, giving the membrane a fluid nature.
- Includes integral proteins spanning the bilayer—not only at the surface.
- Davson–Danielli Model:
- Proposed a protein–lipid–protein sandwich arrangement.
- Proteins were thought to coat both sides of the bilayer.
- Did not account for transmembrane proteins or membrane fluidity.
Key difference: The fluid mosaic model includes mobile, embedded proteins, while the Davson–Danielli model proposed static surface proteins.
(c)
Molecules like M function as part of the sodium–potassium pump, an active transport protein. Using energy from ATP, the pump moves 3 Na⁺ ions out of the cell and 2 K⁺ ions in.
This process allows the cell to:
- Maintain its electrical gradient (essential for nerve and muscle function)
- Regulate osmotic balance and cell volume
- Preserve correct ion concentrations on either side of the membrane
