IB DP Biology- B2.2 Organelles and compartmentalization- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder associated with defects in the CFTR protein. CFTR is a gated ion channel that requires binding of ATP to open and permit chloride ions (Cl−) to move across the membrane.
(a) In the cell model provided, draw arrows to show the pathway for production of a normal CFTR protein, from gene expression through to its final position in the cell membrane.
(b) Identify the most likely cellular location of the ribosomes that synthesize CFTR protein.
(c) State the most likely cellular location of a mutant CFTR protein that has an amino acid substitution in the ATP-binding site.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
(a)
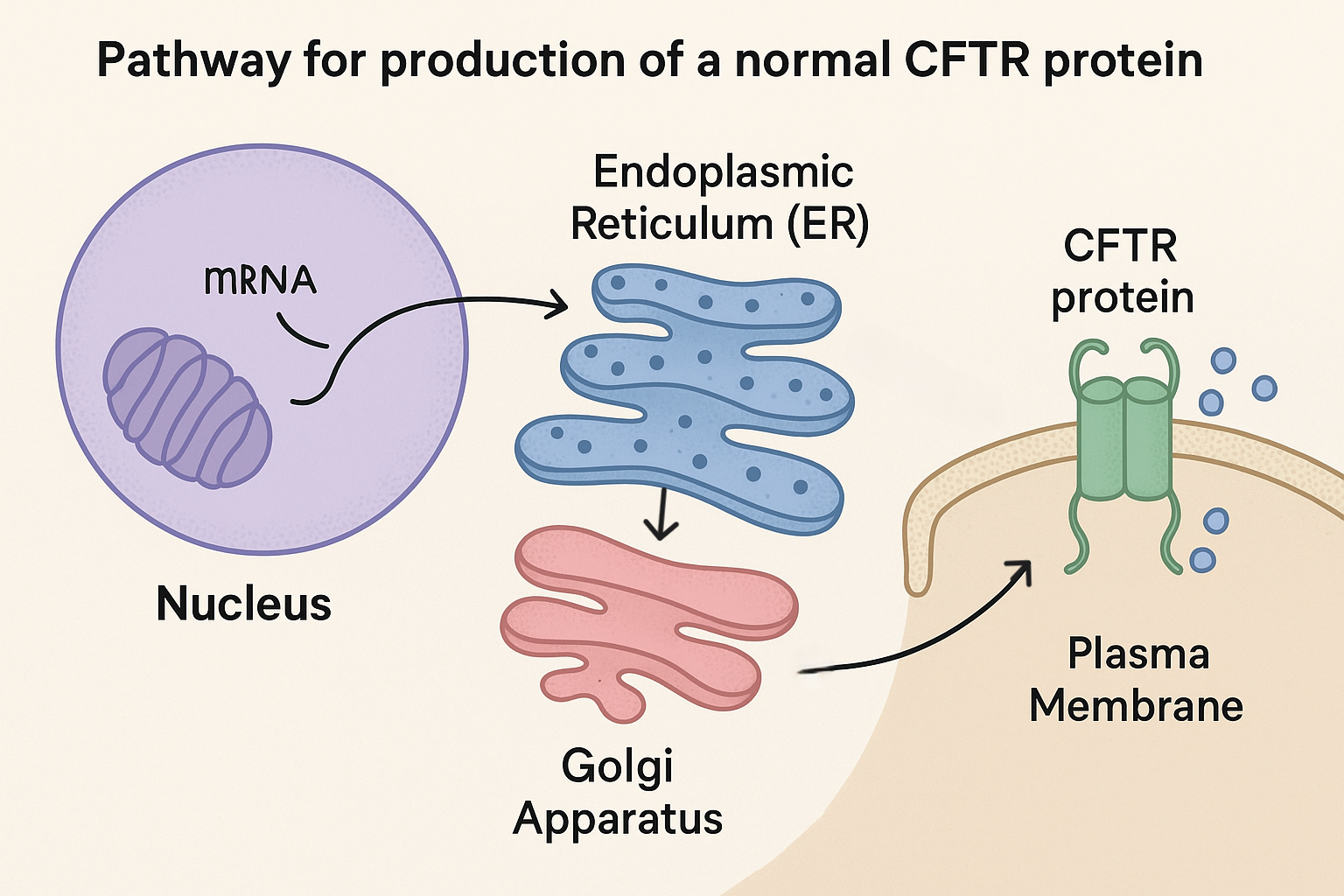
A typical pathway for a correctly folded CFTR protein is:
• CFTR gene is transcribed in the nucleus to form mRNA.
• mRNA exits the nucleus via a nuclear pore.
• mRNA is translated by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), inserting CFTR into the RER membrane.
• CFTR protein is transported in vesicles from the RER to the Golgi apparatus, where it is further modified and packaged.
• Vesicles then carry CFTR from the Golgi to the plasma membrane, where the protein is inserted and functions as a gated Cl− channel.
• CFTR gene is transcribed in the nucleus to form mRNA.
• mRNA exits the nucleus via a nuclear pore.
• mRNA is translated by ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), inserting CFTR into the RER membrane.
• CFTR protein is transported in vesicles from the RER to the Golgi apparatus, where it is further modified and packaged.
• Vesicles then carry CFTR from the Golgi to the plasma membrane, where the protein is inserted and functions as a gated Cl− channel.
(b)
The ribosomes that synthesize CFTR are located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
CFTR is a membrane protein, so it is produced by ribosomes bound to the RER, rather than by free ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
(c)
The most likely location of a mutant CFTR protein with an altered ATP-binding site is the endoplasmic reticulum.
The amino acid substitution in the ATP-binding region often causes CFTR to misfold. Misfolded proteins are usually recognized and retained in the ER for quality control and targeted for degradation, so they typically do not reach the Golgi or the plasma membrane.
