IB DP Biology- B3.1 Gas exchange- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The graph below illustrates how lung volume changes during both normal breathing and forced ventilation (deep inhalation and exhalation).
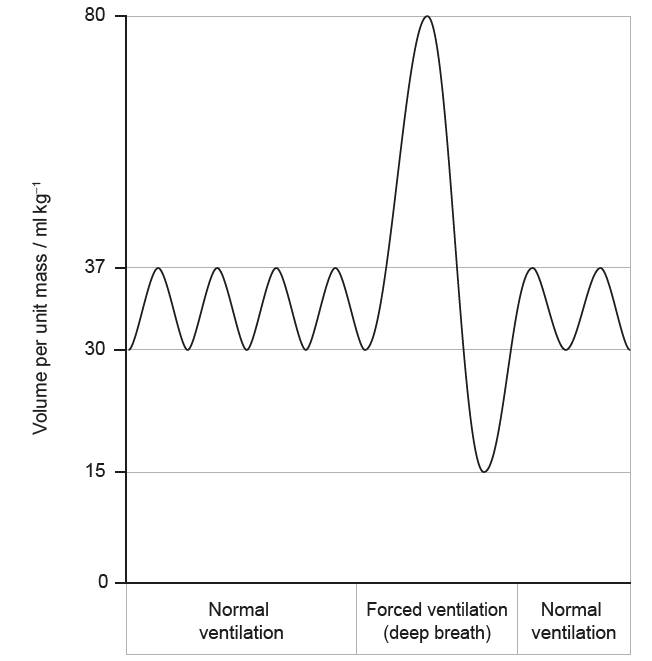
Based on the data shown, what is the vital capacity of the lungs?
A. 7 ml kg−1
B. 37 ml kg−1
C. 65 ml kg−1
D. 80 ml kg−1
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The vital capacity is the difference between the maximum inhalation volume and the minimum exhalation volume.
From the graph, the peak is approximately 80 ml kg−1 and the lowest point is around 15 ml kg−1.
Therefore, the vital capacity = 80 − 15 = 65 ml kg−1.
✅ Answer: (C) 65 ml kg−1
From the graph, the peak is approximately 80 ml kg−1 and the lowest point is around 15 ml kg−1.
Therefore, the vital capacity = 80 − 15 = 65 ml kg−1.
✅ Answer: (C) 65 ml kg−1
Question
Which is an adaptation that increases the rate of gas exchange in the lungs?
A. Small surface area
B. Dry surface
C. High vascularization
D. Muscular alveoli
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: (C) High vascularization
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across thin respiratory surfaces. A dense network of capillaries maintains steep concentration gradients, allowing rapid and efficient diffusion.
Option evaluation:
• A. Small surface area — Incorrect. Efficient gas exchange requires a large surface area, not a reduced one.
• B. Dry surface — Incorrect. Gases must dissolve in moisture to diffuse; a dry surface would slow diffusion.
• C. High vascularization — Correct. A rich capillary supply ensures continuous transport of gases, speeding up diffusion.
• D. Muscular alveoli — Incorrect. Alveoli are elastic, not muscular; muscle tissue does not aid in gas exchange.
✅ Answer: (C)
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across thin respiratory surfaces. A dense network of capillaries maintains steep concentration gradients, allowing rapid and efficient diffusion.
Option evaluation:
• A. Small surface area — Incorrect. Efficient gas exchange requires a large surface area, not a reduced one.
• B. Dry surface — Incorrect. Gases must dissolve in moisture to diffuse; a dry surface would slow diffusion.
• C. High vascularization — Correct. A rich capillary supply ensures continuous transport of gases, speeding up diffusion.
• D. Muscular alveoli — Incorrect. Alveoli are elastic, not muscular; muscle tissue does not aid in gas exchange.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
For what reason do large organisms need specialized gas exchange structures?
A. They have a large surface area to volume ratio.
B. There is a short distance to the centre of their body.
C. They have a relatively small surface in contact with the outside.
D. Their skin is impermeable to respiratory gases.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: (C) They have a relatively small surface in contact with the outside
 Large organisms cannot rely on simple diffusion through the body surface because their surface area is too small relative to their large volume. Diffusion distances to internal tissues are long, so specialized gas exchange organs (like lungs or gills) are needed to greatly increase surface area and maintain rapid gas exchange.
Large organisms cannot rely on simple diffusion through the body surface because their surface area is too small relative to their large volume. Diffusion distances to internal tissues are long, so specialized gas exchange organs (like lungs or gills) are needed to greatly increase surface area and maintain rapid gas exchange.
Evaluation of options:
• A. Incorrect — Large organisms actually have a **small** surface area to volume ratio, not a large one.
• B. Incorrect — The distance to the centre of the body is long, making diffusion too slow.
• C. Correct — Their limited external surface area compared to volume requires specialized organs for efficient gas exchange.
• D. Incorrect — Some species have impermeable skin, but the primary issue is surface area-to-volume ratio, not skin permeability.
✅ Answer: (C)
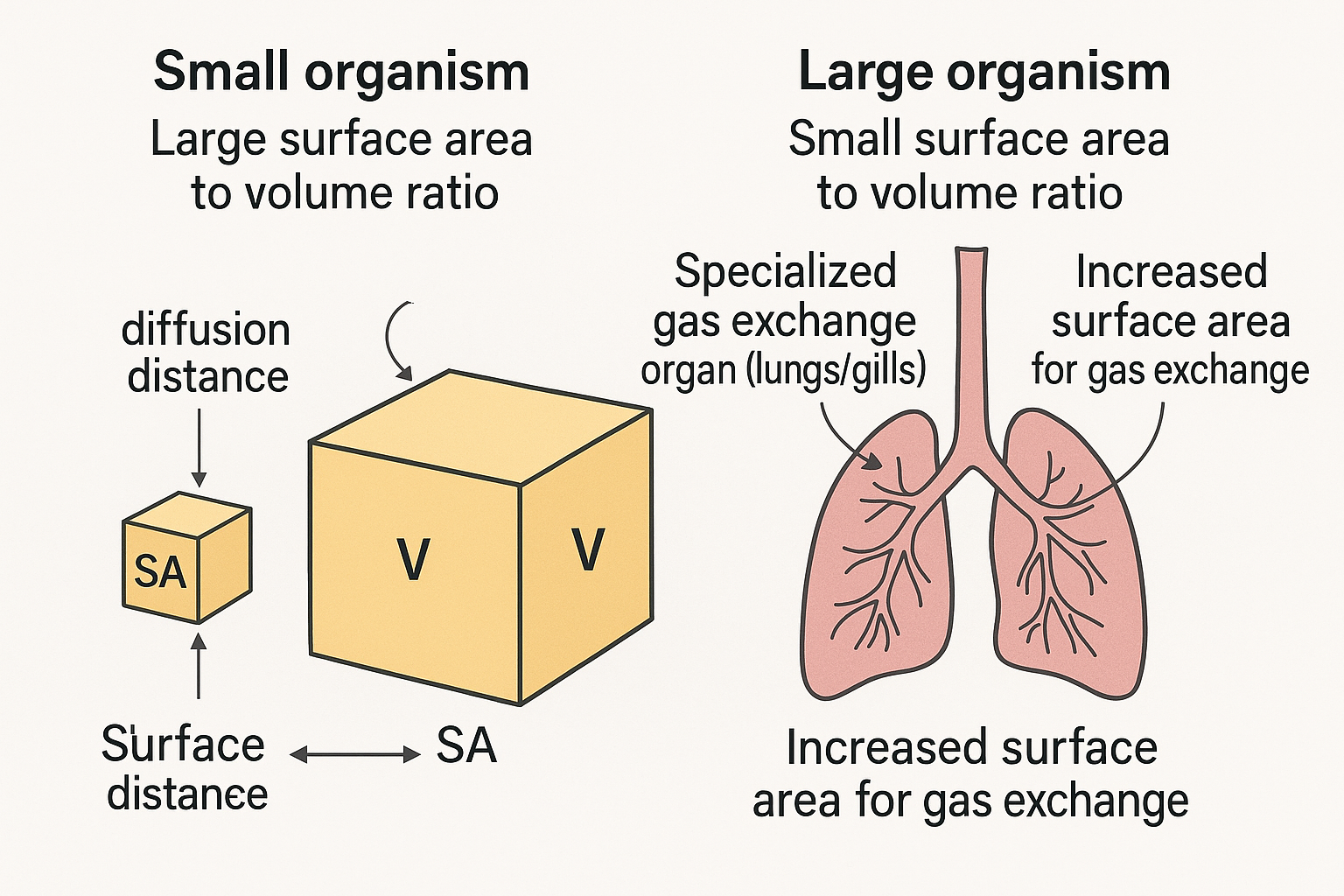 Large organisms cannot rely on simple diffusion through the body surface because their surface area is too small relative to their large volume. Diffusion distances to internal tissues are long, so specialized gas exchange organs (like lungs or gills) are needed to greatly increase surface area and maintain rapid gas exchange.
Large organisms cannot rely on simple diffusion through the body surface because their surface area is too small relative to their large volume. Diffusion distances to internal tissues are long, so specialized gas exchange organs (like lungs or gills) are needed to greatly increase surface area and maintain rapid gas exchange.Evaluation of options:
• A. Incorrect — Large organisms actually have a **small** surface area to volume ratio, not a large one.
• B. Incorrect — The distance to the centre of the body is long, making diffusion too slow.
• C. Correct — Their limited external surface area compared to volume requires specialized organs for efficient gas exchange.
• D. Incorrect — Some species have impermeable skin, but the primary issue is surface area-to-volume ratio, not skin permeability.
✅ Answer: (C)
